Abstract
Rationale and objective
Impulsive behavior has been suggested to occur due to a dysfunction of serotonergic 5-HT neurotransmission. After evaluation by a self-reporting measure, a polymorphism in the promoter of the 5-HT2A receptor gene has been proposed to underlie the impulsive behavior; however, this hypothesis is not convincing. In this study, we examined whether this 5-HT2A receptor gene polymorphism is involved in impulsive aggression by evaluating a behavioral task (go/no-go task) in normal volunteers.
Materials and methods
The polymorphism of the 5-HT2A receptor gene promoter was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction using lymphocytes from 71 volunteers. Impulsivity was defined as the number of commission errors (responding when one should not) made during a go/no-go task (a larger number of commission errors indicates greater difficulty in inhibiting the behavior).
Results
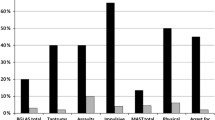
The subjects in the group with the A-1438A allele of the 5-HT2A receptor gene (A-1438A group) made more commission errors under the punishment–reward condition in a go/no-go task than those in the G-1438G group.
Conclusions
These results suggest the possible involvement of the A-1438A polymorphism of the 5-HT2A receptor gene in impulsive behavior; this was evaluated using a behavioral task measure that can directly reveal the traits of human impulsive behavior.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barratt ES (1994) Impulsiveness and aggression. In: Monahan J, Steadman HJ (eds) Violence and mental disorders, developments in risk assessment. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Berggard C, Damberg M, Longato-Stadler E, Hallman J, Oreland L, kan Garpenstrand H (2003) The serotonin 2A -1438 G/A receptor polymorphism in a group of Swedish male criminals. Neurosci Lett 347:196–198
Cherek DR, Lane SD (2000) Fenfluramine effects impulsivity in a sample of adults with and without a history of conduct disorder. Psychopharmacology 152:149–156
Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR (1993) A psycho-biological model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:590–975
Collier DA, Arranz MJ, Li T, Mupita D, Brown N, Treasure J (1997) Association between 5-HT gene promoter polymorphism and anorexia nervosa. Lancet 350:412
Damasio AR (2000) A neural basis for sociopathy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:128–130
Damasio AR, Tranel D, Damasio H (1990) Individuals with sociopathic behaviour caused by frontal damage fail to respond autonomically to social stimuli. Behav Brain Res 41:81–94
Goyer PF, Andreason PJ, Semple WE, Clayton AH, King AC, Compton-Toth BA, Schulz SC, Cohen RM (1994) Positron-emission tomography and personality disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 10:21–28
Grafman J, Schwab K, Warden D, Pridgen A, Brown HR, Salazar AM (1996) Frontal lobe injuries, violence, and aggression: a report of the Vietnam Head Injury Study. Neurology 46:1231–1238
Hart SD, Dempster RJ (1997) Impulsivity and psychopathy. In: Webster CD, Jackson MA (eds) Impulsivity; theory, assessment and treatment. Guilford, New York, pp 212–232
Kaye WH, Frank GK, Meltzer CC, Price JC, McConaha CW, Crossan PJ, Klump KL, Rhodes L (2001) Altered serotonin 2A receptor activity in women who have recovered from bulimia nervosa. Am J Psychiatr 158:1152–1155
Kijima N, Saito R, Takeuchi M, Yoshino A, Ono Y, Kato M, Kitamura T (1996) Cloninger’s seven-factor model of temperament and character and Japanese version of Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI). Jpn J Psychiatry Diagn 7:379–399
Kindlon D, Mezzacappa E, Earls F (1995) Psychometric properties of impulsivity measures: temporal stability, validity and factor structure. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 36:645–661
Kouzmenko AP, Scaffidi A, Pereira AM, Hayes WL, Copolov DL, Dean B (1999) No correlation between A(-1438):G polymorphism in 5-HT2A receptor gene promoter and the density of frontal cortical 5-HT2A receptors in schizophrenia. Hum Hered 49:103–105
Kusumi I, Suzuki K, Sasaki Y, Kameda K, Sasaki T, Koyama T (2002) Serotonin 5-HT receptor gene polymorphism, 5-HT receptor 2A function and personality traits in healthy subjects: a negative study. J Affect Disord 68:235–241
LeMarquand DG, Pihl RO, Palmour RM, Young SN, Tremblay RE, Seguin JR, Palmour RM, Benkelfat C (1998) Tryptophan depletion, executive functions disinhibition in aggressive, adolescent males. Neuropsychopharmachology 19:333–341
LeMarquand DG, Benkelfat C, Pihl RO, Palmour RM, Young SN (1999) Behavioral disinhibition induced by tryptophan depletion in nonalcoholic young men with multigenerational family histories of paternal alcoholism. Am J Psychiatr 156:1771–1779
Leyton M, Okazawa H, Diksic M, Paris J, Rosa P, Mzengeza S, Young SN, Blier P, Benkelfat C (2001) Brain regional α-[11C]methyl-l-tryptophan trapping in impulsive subjects with borderline personality disorder. Am J Psychiatr 158:775–782
McMurran M, Blair M, Egan V (2002) An investigation of the correlations between aggression, impulsiveness, social problem-solving, and alcohol use. Aggress Behav 28:439–445
Meltzer HY (1990) Role of serotonin in depression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 600:486–500
Morgan MJ (1998) Recreational use of “ecstasy” (MDMA) is associated with elevated impulsivity. Neuropsychopharmacology 19:252–264
Newman JP, Kosson DS (1986) Passive avoidance learning in psychopathic and non psychopathic offenders. J Abnorm Psychology 95:252–256
Newman JP, Widom CS, Nathan S (1985) Passive avoidance in syndromes of disinhibition: psychopathy and extraversion. J Pers Soc Psychol 48:1316–1327
Newman JP, Patterson CM, Howland EW, Nichols SL (1990) Passive avoidance in psychopaths: the effects of reward. Pers Individ Differ 11:1101–1114
Nishiguchi N, Matsushita S, Suzuki K, Murayama M, Shirakawa O, Higuchi S (2001) Association between 5HT2A receptor gene promoter region polymorphism and eating disorders in Japanese patients. Biol Psychiatry 50:123–128
Ozaki N, Manji H, Lubierman V, Lu SJ, Lappalainen J, Rosenthal NE, Goldman D (1997) A naturally occurring amino acid substitution of the human serotonin 5-HT2A receptor influences amplitude and timing of intracellular calcium mobilization. J Neurochem 68:2186–2193
Paradiso S, Robinson RG, Andreasen NC, Downhill JE, Davidson RJ, Kirchner PT, Watkins GL, Boles Ponto LL, Hichwa RD (1997) Emotional activation of limbic circuitry in elderly normal subjects in a PET study. Am J Psychiatr 154:384–389
Patterson CM, Kosson DS, Newman JP (1987) Reaction to punishment, reflectivity, and passive avoidance learning in extraverts. J Pers Soc Psychol 52:565–575
Plutchik R, Van Praag HM (1995) The nature of impulsivity: definitions, ontology, genetics, and relations to aggression. In: Hollander E, Stein D (eds) Impulsivity and aggression. Wiley, New York, pp 7–24
Preuss UW, Koller G, Bondy B, Bahlmann M, Soyka M (2001) Impulsive traits and 5-HT2A receptor promoter polymorphism in alcohol dependents: possible association but no influence of personality disorders. Neuropsychobiology 43:186–191
Ricca V, Nacmias B, Boldrini M, Cellini E, di Bernardo M, Ravaldi C, Tedde A, Bagnoli S, Placidi GF, Rotella CM, Sorbi S (2004) Psychopathological traits and 5-HT2A receptor promoter polymorphism (-1438 G/A) in patients suffering from anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Neurosci Lett 365:92–96
Rubia K, Taylor E, Smith AB, Oksanen H, Overmeyer S, Newman S (2001) Neuropsychological analyses of impulsiveness in childhood hyperactivity. Br J Psychiatry 179:138–143
Rubia K, Lee F, Cleare AJ, Tunstall N, Fu CH, Brammer M, McGuire P (2005) Tryptophan depletion reduces right inferior prefrontal activation during response inhibition in fast, event-related fMRI. Psychopharmacology 179:791–803
Stein DJ, Hollander E, Liebowit MR (1993) Neurobiology of impulsivity and the impulse control disorders. J Neuropsychiatry 5:9–17
Tremblay RE, Pihl RO, Vitaro F, Dobkin PL (1994) Predicting early onset of male antisocial behavior from preschool behavior. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:732–739
Walderhaug E, Lunde H, Nordvik JE, Landro NI, Refsum H, Magnusson A (2002) Lowering of serotonin by rapid tryptophan depletion increases impulsiveness in normal individuals. Psychopharmacology 164:385–391
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Marco Leyton for comment on this article. This work was supported by grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nomura, M., Kusumi, I., Kaneko, M. et al. Involvement of a polymorphism in the 5-HT2A receptor gene in impulsive behavior. Psychopharmacology 187, 30–35 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0398-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0398-z