Abstract
Rationale
Adolescents differ from adults in their sensitivity to a variety of psychoactive drugs. For example, adolescent rats are less sensitive to locomotor stimulant and stereotypic effects of amphetamine as well as to motor-impairing and hypnotic effects of ethanol while more sensitive to ethanol-induced disruption of brain plasticity.
Objective
The current study further explored age differences in psychopharmacological sensitivity by examining the effects of d-amphetamine (1.0 and 4.0 mg/kg) or ethanol (0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 g/kg) given interperitoneally on the acoustic startle response (ASR) and prepulse inhibition (PPI) in male adolescent and adult Sprague–Dawley rats.
Materials and methods
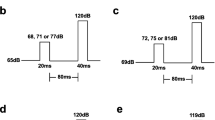
The animals were given five startle trials (120 dB for 40 ms) before semi-randomized presentation of 12 startle trials interspersed with ten trials at each prepulse intensity (40 ms pulse of 5, 10, or 20 dB above background; 100 ms before the startle stimulus).
Results
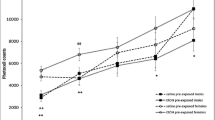
Adolescent controls showed significantly less PPI than adults, replicating previous ontogenetic findings. The higher dose of amphetamine disrupted PPI in adult but not in adolescent animals, extending previous reports of an adolescent insensitivity to amphetamine to include this measure of sensorimotor gating. Ethanol exposure failed to alter PPI at either age, although both the 1.0 and 1.5 g/kg doses of ethanol significantly suppressed the magnitude of the ASR at both ages, potentially reflecting sedative or anxiolytic effects.
Conclusion
These data provide further evidence of the relative insensitivity of adolescent animals to amphetamine, although no age effects were found in terms of ethanol sensitivity using these measures of startle and sensorimotor gating.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1999) Ontogeny of isolation rearing-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating in rats. Physiol Behav 67:385–392
Bell R, Rodd Z, Hsu C, Lumeng L, Murphy J, McBride W (2003) Amphetamine-modified acoustic startle responding and prepulse inhibition in adult and adolescent alcohol-preferring and -nonpreferring rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:163–171
Bolanos C, Glatt S, Jackson D (1998) Subsensitivity to dopaminergic drugs in periadolescent rats: a behavioral and neurochemical analysis. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 111:25–33
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Brunell SC, Spear LP (2005) Effect of stress on the voluntary intake of a sweetened ethanol solution in pair-housed adolescent and adult rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1641–1653
Canal NM, Gourevitch R, Sandner G (2001) Non-monotonic dependency of PPI on temporal parameters: differential alteration by ketamine and MK-801 as opposed to apomorphine and DOI. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156:169–176
Caster JM, Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2005) Enhanced behavioral response to repeated-dose cocaine in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:218–225
Celentano JJ, Gibbs TT, Farb DH (1988) Ethanol potentiates GABA- and glycine-induced chloride currents in chick spinal cord neurons. Brain Res 455:377–380
Curtin J, Lang A, Patrick C, Stritzke W (1998) Alcohol and fear-potentiated startle: the role of competing cognitive demands in the stress-reducing effects of intoxication. J Abnorm Psychol 107:547–557
Doremus TL, Brunell SC, Rajendran P, Spear LP (2005) Factors influencing elevated ethanol consumption in adolescent relative to adult rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1796–1808
Eckardt M, File S, Gessa G, Grant K, Guerri C, Hoffman P, Kalant H, Koob G, Li T-K, Tabakoff B (1998) Effects of moderate alcohol consumption on the central nervous system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:998–1040
Ellwanger J, Geyer MA, Braff DL (2003) The relationship of age to prepulse inhibition and habituation of the acoustic startle response. Biol Psychol 62:175–195
Elmer GI, Sydnor J, Guard H, Hercher E, Vogel MW (2004) Altered prepulse inhibition in rats treated prenatally with the anitmitotic Ara-C: an animal model for sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 174:177–189
Feifel D, Reza TL, Robeck SL (1997) Pro-dopamine effects of neurotensin on sensorimotor gating deficits. Peptides 18:1457–1460
Fletcher PJ, Selhi ZF, Azampanah A, Sills TL (2001) Reduced brain serotonin activity disrupts prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Effects of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine and p-chlorophenylalanine. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:399–409
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Grillon C, Sinha R, O’Malley SS (1994) Effects of ethanol on the acoustic startle reflex in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 114:167–171
Grillon C, Sinha R, Ameli R, O’Malley SS (2000) Effects of alcohol on baseline startle and prepulse inhibition in young men at risk for alcoholism and/or anxiety disorders. J Stud Alcohol 61:46–54
Hsieh MA, Swerdlow NR, Braff DL (2006) Effects of background and prepulse characteristics on prepulse inhibition and facilitation: implications for neuropsychiatric research. Biol Psychiatry 59:555–559
Hutchison K, McGeary J, Wooden A, Blumenthal T, Ito T (2003) Startle magnitude and prepulse inhibition: effects of alcohol and attention. Psychopharmacology 167:235–241
Johnston L, O’Malley P, Bachman J (2002) Monitoring the future: national survey results on drug use, 1975–2001, vol I. Secondary school students. National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda, MD
Jones A, McBride W, Murphy J, Lumeng L, Li T-K, Shekhar A, McKinzie D (2000) Effects of ethanol on startle responding in alcohol-preferring and -non-preferring rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:313–318
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59:107–128
Koch M, Schnitzler H-U (1997) The acoustic startle response in rats—circuits mediating evocation, inhibition and potentiation. Behav Brain Res 89:35–49
Laviola G, Wood RD, Kuhn C, Fancis R, Spear LP (1995) Cocaine sensitization in periadolescent and adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:345–357
Laviola G, Adriani W, Terranova ML, Gerra G (1999) Psychobiological risk factors for vulverability to psychostimulants in human adolescents and animal models. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:993–1010
Langen B, Dietze S, Fink H (2002) Acute effect of ethanol on anxiety and 5-HT in the prefrontal cortex of rats. Alcohol 27:135–141
Lipska BK, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Jaskiw GE, Braff DL, Weinberger DR (1995) Neonatal excitotoxic hippocampal damage in rats causes post-pubertal changes in prepulse inhibition of startle and its disruption by apomorphine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 122:35–43
Marable BR, Maurissen JP (2004) Validation of an auditory startle response system using chemicals or parametric modulation as positive controls. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26:231–237
Markwiese B, Acheson S, Levin E, Wilson W, Swartzwelder H (1998) Differential effects of ethanol on memory in adolescent and adult rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:416–421
Martin S, Lawrence AJ, van den Buuse M (2004) Prepulse inhibition in fawn-hooded rats: increased sensitivity to 5-HT1A receptor stimulation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 14:373–379
Martinez ZA, Platten A, Pollack E, Shoemaker J, Ro H, Pitcher L, Geyer M, Swerdlow NR (2002) “Typical” but not “atypical” antipsychotic effects on startle gating deficits in prepubertal rats. Psychopharmacology 161:38–46
Nevo I, Hamon M (1995) Neurotransmitter and neuromodulatory mechanisms involved in alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Neurochem Int 26:305–336
Niculescu M, Ehrlich ME, Unterwald EM (2005) Age-specific behavioral responses to psychostimulants in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:280–288
Pohorecky LA, Cagan M, Jaffe LS (1976) The startle response in rats: effect of ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:311–316
Rassnick S, Koob GF, Geyer MA (1992) Responding to acoustic startle during chronic ethanol intoxication and withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106:351–358
Schmid A, Koch M, Schnitzler H-U (1995) Conditioned pleasure attenuates the startle response in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 64:1–3
Silveri MM, Spear LP (1998) Decreased sensitivity to the hypnotic effects of ethanol early in ontogeny. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:670–676
Silveri MM, Spear LP (2001) Acute, rapid and chronic tolerance during ontogeny: observations when equating ethanol perturbation across age. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1301–1308
Silveri MM, Spear LP (2002) The effects of NMDA and GABAA pharmacological manipulations on ethanol sensitivity in immature and mature animals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:449–456
Sills TL (1999) Amphetamine dose dependently disrupts prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response in rats within a narrow time window. Brain Res Bull 4:445–448
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Spear LP, Brake S (1983) Periadolescence: age-dependent behavior and psychopharmacological responsivity in rats. Dev Psychobiol 16:83–109
Stritzke WG, Patrick CJ, Lang AR (1995) Alcohol and human emotion: a multidimensional analysis incorporating startle-probe methodology. J Abnorm Psychol 104:114–122
Swartzwelder HS, Wilson W, Tayyeb M (1995a) Age-dependent inhibition of long-term potentiation by ethanol in immature versus mature hippocampus. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:1480–1485
Swartzwelder HS, Wilson WA, Tayyeb MI (1995b) Differential sensitivity of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic potentials to ethanol in immature versus mature hippocampus. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:320–323
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) GABAergic projection from nucleus accumbens to ventral pallidum mediates dopamine-induced sensorimotor gating deficits of acoustic startle in rats. Brain Res 532:146–150
Swerdlow NR, Benbow CH, Zisook S, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1993) A preliminary assessment of sensorimotor gating in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 33:298–301
Tirelli E, Laviola G, Adrianai W (2003) Ontogenesis of behavioral sensitization and conditioned place preference induced by psychostimulants in laboratory rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:163–178
Van den Buuse M, Garner B, Koch M (2003) Neurodevelopmental animal models of schizophrenia: effects on prepulse inhibition. Curr Mol Med 3:459–471
Varlinskaya E, Spear LP (2002) Acute effects of ethanol on social behavior of adolescent and adult rats: role of familiarity of the test situation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:1502–1511
Varty GB, Walters N, Cohen-Williams M, Carey GJ (2001) Comparison of apomorphine, amphetamine and dizocilpine disruptions of prepulse inhibition in inbred and outbred mice strains. Eur J Pharmacol 424:27–36
Walker D, Cassella J, Lee Y, de lima T, Davis M (1997) Opposing roles of the amygdala and dorsolateral periaqueductal gray in fear-potentiated startle. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:743–753
White A, Truesdale M, Bae J, Ahmad S, Wilson W, Best P, Swartzwelder H (2002) Differential effects of ethanol on motor coordination in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:673–677
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants R37 AA12525 and R01 DA019071.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunell, S.C., Spear, L.P. Effects of acute ethanol or amphetamine administration on the acoustic startle response and prepulse inhibition in adolescent and adult rats. Psychopharmacology 186, 579–586 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0380-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0380-9