Abstract
Rationale
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) produces anxiety-like and aversive effects when infused directly into the various regions of the brain, including the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST). However, the CRF receptor subtypes within the BNST mediating these phenomena have not been established.
Objectives
We used selective CRF receptor antagonists to determine the receptor subtypes involved in the anxiogenic-like and aversive effects CRF in the BNST.
Materials and methods
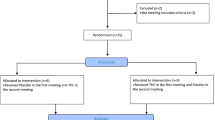
Male Long–Evans rats were bilaterally infused with CRF (0.2 or 1.0 nmol) either alone or in combination with the CRF1 receptor antagonist CP154,526 or the CRF2 receptor antagonist anti-sauvagine 30 (AS30) before behavioral testing in the elevated plus maze or place conditioning paradigms.
Results
Intra-BNST administration of CRF produced a dose-dependent reduction in open arm entries and open arm time in the elevated plus maze, indicating an anxiogenic-like effect. These effects were inhibited by co-infusion of CP154,526 but not of AS30, indicating that the anxiogenic-like effects of CRF in the BNST are mediated by CRF1 receptors. Place conditioning with intra-BNST administration of CRF produced a dose-dependent aversion to the CRF-paired environment that was prevented by co-infusion of either CP154,526 or AS30, indicating that both CRF receptor subtypes mediate the aversive effects of this peptide. Intra-BNST infusions of the CRF receptor antagonists alone produced no effects in either behavioral paradigm.
Conclusions
CRF1 receptors in the BNST mediate the anxiogenic-like effects of CRF in this region, whereas both CRF1 and CRF2 receptor subtypes mediate the conditioned aversive effects of this peptide within the BNST.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alheid GF (2003) Extended amygdala and basal forebrain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:185–205
Alheid GF, de Olmos JS, Beltramino CA (1995) Amygdala and extended amygdala. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic, San Diego, CA, pp 495–578
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Andrews N, File SE (1993) Handling history of rats modifies behavioural effects of drugs in the elevated plus-maze test of anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 235:109–112
Bakshi VP, Smith-Roe S, Newman SM, Grigoriadis DE, Kalin NH (2002) Reduction of stress-induced behavior by antagonism of corticotropin-releasing hormone 2 (CRH2) receptors in lateral septum or CRH1 receptors in amygdala. J Neurosci 22:2926–2935
Bale TL, Vale WW (2004) CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:525–557
Bale TL, Contarino A, Smith GW, Chan R, Gold LH, Sawchenko PE, Koob GF, Vale WW, Lee K-F (2000) Mice deficient for corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2 display anxiety-like behaviour and are hypersensitive to stress. Nat Genet 24:410–414
Bangasser DA, Santollo J, Shors TJ (2005) The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis is critically involved in enhancing associative learning after stressful experience. Behav Neurosci 119:1459–1466
Blank T, Nijholt I, Eckart K, Spiess J (2002) Priming of long-term potentiation in mouse hippocampus by corticotropin-releasing factor and acute stress: implications for hippocampus-dependent learning. J Neurosci 22:3788–3794
Bonaz B, Tache Y (1994) Induction of Fos immunoreactivity in the rat brain after cold-restraint induced gastric lesions and fecal excretion. Brain Res 652:56–64
Cador M, Ahmed SH, Koob GF, Le Moal M, Stinus L (1992) Corticotropin-releasing factor induces a place aversion independent of its neuroendocrine role. Brain Res 597:304–309
Campeau S, Watson SJ (1997) Neuroendocrine and behavioral responses and brain pattern of c-fos induction associated with audiogenic stress. J Neuroendocrinol 9:577–588
Casada JH, Dafny N (1991) Restraint and stimulation of bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produce similar stress-like behaviors. Brain Res Bull 27:207–212
Chalmers DT, Lovenberg TW, De Souza EB (1995) Localization of novel corticotropin-releasing factor receptor (CRF2) mRNA expression to specific subcortical nuclei in rat brain: comparison with CRF1 receptor mRNA expression. J Neurosci 15:6340–6350
Chappell PB, Smith MA, Kilts CD, Bissette G, Ritchie J, Anderson C, Nemeroff CB (1986) Alterations in corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in discrete rat brain regions after acute and chronic stress. J Neurosci 6:2908–2914
Chen YL, Mansbach RS, Winter SM, Brooks E, Collins J, Corman ML, Dunaiskis AR, Faraci WS, Gallaschun RJ, Schmidt A, Schulz DW (1997) Synthesis and oral efficacy of a 4-(butylethylamino)pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine: a centrally active corticotropin-releasing factor1 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 40:1749–1754
Chen Y, Brunson KL, Müller MB, Cariaga W, Baram TZ (2000) Immunocytochemical distribution of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type-1 (CRF1)-like immunoreactivity in the mouse brain: light microscopy analysis using an antibody directed against the C-terminus. J Comp Neurol 420:305–323
Ciccocioppo R, Fedeli A, Economidou D, Policani F, Weiss F, Massi M (2003) The bed nucleus is a neuroanatomical substrate for the anorectic effect of corticotropin-releasing factor and for its reversal by nociceptin/orphanin FQ. J Neurosci 23:9445–9451
Contarino A, Dellu F, Koob GF, Smith GW, Lee K-F, Vale W, Gold LH (1999) Reduced anxiety-like and cognitive performance in mice lacking the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1. Brain Res 835:1–9
Cooper MA, Huhman KL (2005) Corticotropin-releasing factor type II (CRF2) receptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis modulate conditioned defeat in Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus). Behav Neurosci 119:1042–1051
Coste SC, Kesterson RA, Heldwein KA, Stevens SL, Heard AD, Hollis JH, Murray SE, Hill JK, Pantely GA, Hohimer AR, Hatton DC, Phillips TJ, Finn DA, Low MJ, Rittenberg MB, Stenzel P, Stenzel-Poore MP (2000) Abnormal adaptations to stress and impaired cardiovascular function in mice lacking corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2. Nat Genet 24:403–409
Cummings S, Elde R, Ells J, Lindall A (1983) Corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity is widely distributed within the central nervous system of the rat: an immunohistochemical study. J Neurosci 3:1355–1368
Davis M (1998) Are different parts of the extended amygdala involved in fear versus anxiety? Biol Psychiatry 44:1239–1247
Davis M, Walker DL, Lee Y (1997) Roles of the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in fear and anxiety measured with the acoustic startle reflex. Possible relevance to PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci 821:305–331
Deak T, Nguyen KT, Ehrlich AL, Watkins LR, Spencer RL, Maier SF, Licinio J, Wong ML, Chrousos GP, Webster E, Gold PW (1999) The impact of the nonpeptide corticotropin-releasing hormone antagonist antalarmin on behavioral and endocrine responses to stress. Endocrinology 140:79–86
Dunn JD (1987) Plasma corticosterone responses to electrical stimulation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Brain Res 407:321–327
Erb S, Stewart J (1999) A role for the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, but not the amygdala, in the effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 19(RC35):1–6
Erb S, Salmaso N, Rodaros D, Stewart J (2001) A role for the CRF-containing pathway from central nucleus of the amygdala to bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 158:360–365
Fendt M, Endres T, Apfelbach R (2003) Temporary inactivation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis but not of the amygdala blocks freezing induced by trimethylthiazoline, a component of fox feces. J Neurosci 23:23–28
Garcia-Lecumberri C, Ambrosio E (2000) Differential effect of low doses of intracerebroventricular corticotropin-releasing factor in forced swimming test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:519–525
Gewirtz JC, McNish KA, Davis M (1998) Lesions of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis block sensitization of the acoustic startle reflex produced by repeated stress, but not fear-potentiated startle. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 22:625–648
Gray TS, Piechowski RA, Yracheta JM, Rittenhouse PA, Bethea CL, Van de Kar LD (1993) Ibotenic acid lesions in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis attenuate conditioned stress-induced increases in prolactin, ACTH and corticosterone. Neuroendocrinology 57:517–524
Greenwell TN, Zorrilla EP, Koob GF (2004) Microinfusion of a corticotropin-releasing factor receptor antagonist into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis attenuates defensive burying behavior (Online). Program No 1027.12. 2004 Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner. Society for Neuroscience, Washington, DC
Griebel G, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (1998) Characterization of the behavioral profile of the non-peptide CRF receptor antagonist CP-154,526 in anxiety models in rodents: comparison with diazepam and buspirone. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 138:55–66
Griebel G, Simiand J, Steinberg R, Jung M, Gully D, Roger P, Geslin M, Scatton B, Maffrand JP, Soubrie P (2002) 4-(2-chloro-4-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)-N-[(1S)-2-cyclopropyl-1-(3-fluoro-4-methylphenyl)ethyl]5-methyl-N-(2-propynyl)-1, 3-Thiazol-2-amine hydrochloride (SSR125543A), a potent and selective corticotrophin-releasing factor(1) receptor antagonist. II. Characterization in rodent models of stress-related disorders. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:333–345
Hammack SE, Richey KJ, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2004) Chemical lesion of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis blocks the behavioral consequences of uncontrollable stress. Behav Neurosci 118:443–448
Heimer L (2003) A new anatomical framework for neuropsychiatric disorders and drug abuse. Am J Psychiatry 160:1726–1739
Heinrichs SC (2003) Modulation of social learning in rats by brain corticotropin-releasing factor. Brain Res 994:107–114
Heinrichs SC, Lapsansky J, Lovenberg TW, De Souza EB, Chalmers DT (1997a) Corticotropin-releasing factor CRF1, but not CRF2, receptors mediate anxiogenic-like behavior. Regul Pept 71:15–21
Heinrichs SC, Vale EA, Lapsansky J, Behan DP, McClure LV, Ling N, De Souza EB, Schulteis G (1997b) Enhancement of performance in multiple learning tasks by corticotropin-releasing factor-binding protein ligand inhibitors. Peptides 18:711–716
Henke PG (1984) The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and immobilization-stress: unit activity, escape behaviour, and gastric pathology in rats. Behav Brain Res 11:35–45
Hogg S (1996) A review of the validity and variability of the elevated plus-maze as an animal model of anxiety. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:21–30
Hung HC, Chou CK, Chiu TH, Lee EH (1992) CRF increases protein phosphorylation and enhances retention performance in rats. Neuroreport 3:181–184
Jasnow AM, Davis M, Huhman KL (2004) Involvement of central amygdalar and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis corticotropin-releasing factor in behavioral responses to social defeat. Behav Neurosci 118:1052–1061
Ju G, Swanson LW, Simerly RB (1989) Studies on the cellular architecture of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis in the rat. II. Chemoarchitecture. J Comp Neurol 280:603–621
Kishimoto T, Radulovic J, Radulovic M, Lin CR, Schrick C, Hooshmand F, Hermanson O, Rosenfeld MG, Spiess J (2000) Deletion of Crhr2 reveals an anxiolytic role for corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2. Nat Genet 24:415–419
Kollack-Walker S, Watson SJ, Akil H (1997) Social stress in hamsters: defeat activates specific neurocircuits within the brain. J Neurosci 17:8842–8855
Lee EH (1995) Corticotropin-releasing factor injected into the lateral septum improves memory function in rats. Chin J Physiol 38:125–129
Lee Y, Davis M (1997) Role of the hippocampus, the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, and the amygdala in the excitatory effect of corticotropin-releasing hormone on the acoustic startle reflex. J Neurosci 17:6434–6446
Lee EH, Sung YJ (1989) Differential influences of corticotropin-releasing factor on memory retention of aversive learning and appetitive learning in rats. Behav Neural Biol 52:285–294
Liang KC, Lee EH (1988) Intra-amygdala injections of corticotropin releasing factor facilitate inhibitory avoidance learning and reduce exploratory behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 96:232–236
Liang KC, Chen H-C, Chen D-Y (2001) Posttraining infusion of norepinephrine and corticotropin releasing factor into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis enhanced retention in an inhibitory avoidance task. Chin J Physiol 44:33–43
Ma YL, Chen KY, Wei CL, Lee EH (1999) Corticotropin-releasing factor enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression to facilitate memory retention in rats. Chin J Physiol 42:73–81
Martinez M, Phillips PJ, Herbert J (1998) Adaptation in patterns of c-fos expression in the brain associated with exposure to either single or repeated social stress in male rats. Eur J Neurosci 10:20–33
Martinez M, Calvo-Torrent A, Herbert J (2002) Mapping brain response to social stress in rodents with c-fos expression: a review. Stress 5:3–13
Moga MM, Saper CB, Gray TS (1989) Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: cytoarchitecture, immunohistochemistry, and projection to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 283:315–332
Morin SM, Ling N, Liu X-J, Kahl SD, Gehlert DR (1999) Differential distribution of urocortin- and corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivities in the rat brain. Neuroscience 92:281–291
Muller MB, Zimmermann S, Sillaber I, Hagemeyer TP, Deussing JM, Timpl P, Kormann MS, Droste SK, Kuhn R, Reul JM, Holsboer F, Wurst W (2003) Limbic corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 mediates anxiety-related behavior and hormonal adaptation to stress. Nat Neurosci 6:1100–1107
National Research Council (2003) Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in neuroscience and behavioral research. National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Nijsen MJ, Croiset G, Diamant M, De Wied D, Wiegant VM (2001) CRH signalling in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis is involved in stress-induced cardiac vagal activation in conscious rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:1–10
Olive MF, Koenig HN, Nannini MA, Hodge CW (2002) Elevated extracellular CRF levels in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis during ethanol withdrawal and reduction by subsequent ethanol intake. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:213–220
Olschowka JA, O’Donohue TL, Mueller GP, Jacobowitz DM (1982) The distribution of corticotropin releasing factor-like immunoreactive neurons in rat brain. Peptides 3:995–1015
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 5th edn. Academic, San Diego, CA
Pelleymounter MA, Joppa M, Ling N, Foster AC (2002) Pharmacological evidence supporting a role for central corticotropin-releasing factor2 receptors in behavioral, but not endocrine, response to environmental stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:145–152
Pelleymounter MA, Joppa M, Ling N, Foster AC (2004) Behavioral and neuroendocrine effects of the selective CRF2 receptor agonists urocortin II and urocortin III. Peptides 25:659–666
Radulovic J, Rühmann A, Liepold T, Spiess J (1999) Modulation of learning and anxiety by corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and stress: differential roles of CRF receptors 1 and 2. J Neurosci 19:5016–5025
Risbrough VB, Hauger RL, Pelleymounter MA, Geyer MA (2003) Role of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptors 1 and 2 in CRF-potentiated acoustic startle in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 170:178–187
Risbrough VB, Hauger RL, Roberts AL, Vale WW, Geyer MA (2004) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors CRF1 and CRF2 exert both additive and opposing influences on defensive startle behavior. J Neurosci 24:6545–6552
Rominger DH, Rominger CM, Fitzgerald LW, Grzanna R, Largent BL, Zaczek R (1998) Characterization of [125I]sauvagine binding to CRH2 receptors: membrane homogenate and autoradiographic studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:459–468
Ruhmann A, Bonk I, Lin CR, Rosenfeld MG, Spiess J (1998) Structural requirements for peptidic antagonists of the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor (CRFR): development of CRFR2β-selective antisauvagine-30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15264–15269
Rybnikova EA, Pelto-Huikko M, Rakitskaya VV, Shalyapina VG (2003) Localization of corticoliberin receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci Behav Physiol 33:399–404
Sahuque LL, Mcgeehan AJ, Kinder JR, Janak PH, Olive MF (2004) Anxiogenic and aversive effects of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (Online). Program No. 5789.15. 2004. Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner. Society for Neuroscience, Washington, DC
Sakanaka M, Shibasaki T, Lederis K (1986) Distribution and efferent projections of corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in the rat amygdaloid complex. Brain Res 382:213–238
Sakanaka M, Shibasaki T, Lederis K (1987) Corticotropin releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain as revealed by a modified cobalt-glucose oxidase-diaminobenzidine method. J Comp Neurol 260:256–298
Schulkin J, Morgan MA, Rosen JB (2005) A neuroendocrine mechanism for sustaining fear. Trends Neurosci 28:629–635
Schulz D, Canbeyli R (1999) Freezing behavior in BNST-lesioned Wistar rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:728–731
Schulz D, Canbeyli RS (2000) Lesion of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis enhances learned despair. Brain Res Bull 52:83–87
Schulz DW, Mansbach RS, Sprouse J, Braselton JP, Collins J, Corman M, Dunaiskis A, Faraci S, Schmidt AW, Seeger T, Seymour P, Tingley FD, Winston EN, Chen YL, Heym J (1996) CP-154,526: a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of corticotropin releasing factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10477–10482
Seymour PA, Schmidt AW, Schulz DW (2003) The pharmacology of CP-154,526, a non-peptide antagonist of the CRH1 receptor: a review. CNS Drug Rev 9:57–96
Smith GW, Aubry JM, Dellu F, Contarino A, Bilezikjian LM, Gold LH, Chen R, Marchuk Y, Hauser C, Bentley CA, Sawchenko PE, Koob GF, Vale W, Lee KF (1998) Corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1-deficient mice display decreased anxiety, impaired stress response, and aberrant neuroendocrine development. Neuron 20:1093–1102
Stout SC, Mortas P, Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB, Moreau J (2000) Increased corticotropin-releasing factor concentrations in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of anhedonic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 401:39–46
Sullivan GM, Apergis J, Bush DEA, Johnson LR, Hou M, LeDoux JE (2004) Lesions in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis disrupt corticosterone and freezing responses elicited by a contextual but not by a specific cue-conditioned fear stimulus. Neuroscience 128:7–14
Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW (1983) Organization of ovine corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactive cells and fibers in the rat brain: an immunohistochemical study. Neuroendocrinology 36:165–186
Takahashi LK, Ho SP, Livanov V, Graciani N, Arneric SP (2001) Antagonism of CRF2 receptors produces anxiolytic behavior in animal models of anxiety. Brain Res 902:135–142
Tezval H, Jahn O, Todorovic C, Sasse A, Eckart K, Spiess J (2004) Cortagine, a specific agonist of corticotropin- releasing factor receptor subtype 1, is anxiogenic and antidepressive in the mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9468–9473
Timpl P, Spanagel R, Sillaber I, Kresse A, Reul JMHM, Stalla GK, Blanquet V, Steckler T, Holsboer F, Wurst W (1998) Impaired stress response and reduced anxiety in mice lacking a functional corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1. Nat Genet 19:162–166
Todorovic C, Jahn O, Tezval H, Hippel C, Spiess J (2005) The role of CRF receptors in anxiety and depression: implications of the novel CRF1 agonist cortagine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1323–1333
Treit D, Aujla H, Menard J (1998) Does the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis mediate fear behaviors? Behav Neurosci 112:379–386
Valdez GR, Inoue K, Koob GF, Rivier J, Vale W, Zorrilla EP (2002) Human urocortin II: mild locomotor suppressive and delayed anxiolytic-like effects of a novel corticotropin-releasing factor related peptide. Brain Res 943:142–150
Valdez GR, Zorrilla EP, Rivier J, Vale WW, Koob GF (2003) Locomotor suppressive and anxiolytic-like effects of urocortin 3, and highy selective type 2 corticotropoin releasing factor agonist. Brain Res 980:206–212
Valdez GR, Sabino V, Koob GF (2004) Increased anxiety-like behavior and ethanol self-administration in dependent rats: reversal via corticotropin-releasing factor-2 receptor activation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:865–872
Van Pett K, Viau V, Bittencourt JC, Chan RK, Li HY, Arias C, Prins GS, Perrin M, Vale W, Sawchenko PE (2000) Distribution of mRNAs encoding CRF receptors in brain and pituitary of rat and mouse. J Comp Neurol 428:191–212
Vaughan J, Donaldson C, Bittencourt J, Perrin MH, Lewis K, Sutton S, Chan R, Turnbull AV, Lovejoy D, Rivier C, Rivier J, Sawchenko PE, Vale W (1995) Urocortin, a mammalian neuropeptide related to fish urotensin I and to corticotropin-releasing factor. Nature 378:287–292
Venihaki M, Sakihara S, Subramanian S, Dikkes P, Weninger SC, Liapakis G, Graf T, Majzoub JA (2004) Urocortin III, a brain neuropeptide of the corticotropin-releasing hormone family: modulation by stress and attenuation of some anxiety-like behaviours. J Neuroendocrinol 16:411–422
Walker DL, Davis M (1997) Double dissociation between the involvement of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and the central nucleus of the amygdala in startle increases produced by conditioned versus unconditioned fear. J Neurosci 17:9375–9383
Walker DL, Toufexis DJ, Davis M (2003) Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis versus the amygdala in fear, stress and anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 463:199–216
Wang HL, Wayner MJ, Chai CY, Lee EH (1998) Corticotrophin-releasing factor produces a long-lasting enhancement of synaptic efficacy in the hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 10:3428–3437
Wang HL, Tsai LY, Lee EH (2000) Corticotropin-releasing factor produces a protein synthesis–dependent long-lasting potentiation in dentate gyrus neurons. J Neurophysiol 83:343–349
Wang J, Fang Q, Liu Z, Lu L (2006) Region-specific effects of brain corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 1 blockade on footshock-stress- or drug-priming-induced reinstatement of morphine conditioned place preference in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 185:19–28
Zorrilla EP, Schulteis G, Ormsby A, Klaassen A, Ling N, McCarthy JR, Koob GF, De Souza EB (2002) Urocortin shares the memory modulating effects of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF): mediation by CRF1 receptors. Brain Res 952:200–210
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Public Health Service grants AA13276 and AA013852 to MFO, the Charleston Alcohol Research Center (AA010761), and funds provided by the State of California for medical research on alcohol and substance abuse through the University of California at San Francisco. The authors wish to thank Dr. Tom Greenberg and Dr. Eric Zorrilla of The Scripps Research Institute for technical advice on elevated plus maze procedures. The experiments described herein were conducted in accordance with the current laws of the Food and Drug Administration of the United States of America. Portions of these data have been presented previously in abstract form (Sahuque et al. 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahuque, L.L., Kullberg, E.F., Mcgeehan, A.J. et al. Anxiogenic and aversive effects of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat: role of CRF receptor subtypes. Psychopharmacology 186, 122–132 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0362-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0362-y