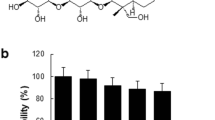
Abstract
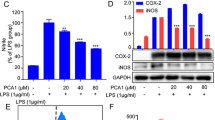
Excessive activation of macrophages has been implicated in various types of inflammatory injury. Suppression of macrophage activation would have therapeutic benefits, leading to the alleviation of the progression of inflammatory diseases. Eburicoic acid (EA) is one of main bioactive components isolated from Laetiporus sulphureus (Bull.:Fr.) Murrill. In our previous study, we found that EA possessed anti-inflammatory activities. However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying its anti-inflammatory activities remain to be poorly understood. The present study aimed to further evaluate its effect on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. We investigated the anti-inflammatory effect by modulating LPS-induced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway in RAW264.7 cells. The results showed that EA caused no obvious cytotoxicity, and its suitable concentrations on RAW264.7 cells were in the range from 0.02 to 0.08 μM. EA significantly inhibited the releases of inflammatory mediators, nitrite oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2); suppressed mRNA and protein expression levels of inducible nitrite oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 COX-2 and pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β; and reduced levels of phosphorylated PI3K, Akt, mTOR, and NF-κBp65 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells in dose- and time-dependent manners. These aforementioned results indicated that EA executed anti-inflammatory effect on LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells, and this effect might be achieved via suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting the LPS-induced productions of inflammatory mediators and pro-inflammatory cytokines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arango Duque G, Descoteaux A (2014) Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front Immunol 5:491. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00491
Bai CH, He HB, Cheng F, Zou K, Wang JZ, Liu GY, Deng W, Chen ZF, Chen X, Chen JF (2014) A steroidal saponin RCE-4 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses via blocking PI3K/Akt-mediated NF-κB activation in RAW264.7 cells. Appl Mech Mater 568-570:1901–1906
Bai CH, Yang XJ, Zou K, He HB, Wang JZ, Qin HL, Yu XQ, Liu CX, Zheng JY, Cheng F, Chen JF (2016) Anti-proliferative effect of RCE-4 from Reineckia carnea on human cervical cancer HeLa cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and NF-κB activation. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 389:573–584
Carneiro AB, Iaciura BM, Nohara LL, Lopes CD, Veas EM, Mariano VS, Bozza PT, Lopes UG, Atella GC, Almeida IC, Silva-Neto MA (2013) Lysophosphatidylcholine triggers TLR2- and TLR4-mediated signaling pathways but counteracts LPS-induced NO synthesis in peritoneal macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB translocation and MAPK/ERK phosphorylation. PLoS One 8:e76233
Deng JS, Huang SS, Lin TH, Lee MM, Kuo CC, Sung PJ, Hou WC, Huang GJ, Kuo YH (2013) Analgesic and anti-inflammatory bioactivities of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid isolated from Antrodia camphorata on the inflammatory mediator expression in mice. J Agric Food Chem 61:5064–50671
Dilshara MG, Jayasooriya RG, Lee S, Jeong JB, Seo YT, Choi YH, Jeong JW, Jang YP, Jeong YK, Kim GY (2013) Water extract of processed Hydrangea macrophylla (Thunb.) Ser. leaf attenuates the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing Akt-mediated NF-κB activation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:311–319
Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE (2007) Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1β generation. Clin Exp Immunol 147:227–235
Gasparini C, Feldmann M (2012) NF-κB as a target for modulating inflammatory responses. Curr Pharm Des 18:5735–5745
Guo C, Yang L, Luo J, Zhang C, Xia YX, Ma T, Kong LY (2016) Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells by targeting PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 38:349–356
Ha TZ, Liu L, Kelley J, Kao R, Williams D, Li CF (2011) Toll-like receptors: new players in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1875–1893
Hawkins PT, Stephens LR (2015) PI3K signalling in inflammation. Biochimi Biophys Acta 1851:882–897
Hu BY, Zhang H, Meng XL, Wang F, Wang P (2014) Aloe-emodin from rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 153:846–853
Huang GJ, Deng JS, Huang SS, Lee CY, Hou WC, Wang SY, Sung PJ, Kuo YH (2013) Hepatoprotective effects of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia camphorata in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury. Food Chem 141:3020–3027
Hwang YJ, Lee SJ, Park JY, Chun W, Nam SJ, Park JM, Park SC, Choi DH, Kang CD (2016) Apocynin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through the inhibition of MAPKinase signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Drug Dev Res 77:271–277
Jiang ZL, Zhu L (2016) Update on the role of alternatively activated macrophages in asthma. J Asthma Allergy 9:101–107
Kikuchi T, Uchiyama E, Ukiya M, Tabata K, Kimura Y, Suzuki T, Akihisa T (2011) Cytotoxic and Apoptosis-Inducing Activities of Triterpene Acids from Poria cocos. J Nat Prod 74(2):137–144
Kim JH, Kim YS, Hwang JW, Han YK, Lee JS, Kim SK, Jeon YJ, Moon SH, Jeon BT, Bahk YY, Park PJ (2014) Sulfated chitosan oligosaccharides suppress LPS-induced NO production via JNK and NF-κB inactivation. Molecules 19:18232–18247
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149:274–293
Lee JH, Jung NH, Lee BH, Kim SH, Jun JH (2013) Suppression of heme oxygenase-1 by prostaglandin E2-protein kinase A-A-kinase anchoring protein signaling is central for augmented cyclooxygenase-2 expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 5:329–336
Li Z, Zheng Z, Ruan J, Li Z, Tzeng CM (2016) Chronic inflammation links cancer and parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 8:126. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2016.00126
Lin HW, Chen YC, Liu CW, Yang DJ, Chen SY, Chang TJ, Chang YY (2014) Regulation of virus-induced inflammatory response by Dunaliella salina alga extract in macrophages. Food Chem Toxicol 71:159–165
Liu JX, Tang JS, Zuo YH, Yu Y, Luo P, Yao XS, Dong Y, Wang PX, Liu L, Zhou H (2016) Stauntoside B inhibits macrophage activation by inhibiting NF-κB and ERK MAPK signalling. Pharmacol Res 111:303–315
Madonna R, Cadeddu C, Deidda M, Giricz Z, Madeddu C, Mele D, Monte I, Novo G, Pagliaro P, Pepe A, Spallarossa P, Tocchetti CG, Varga ZV, Zito C, Geng YJ, Mercuro G, Ferdinandy P (2015) Cardioprotection by gene therapy: a review paper on behalf of the working group on drug cardiotoxicity and cardioprotection of the Italian Society of Cardiology. Int J Cardiol 191:203–210
McCarthy HO, Coulter JA, Robson T, Hirst DG (2008) Gene therapy via inducible nitric oxide synthase: a tool for the treatment of a diverse range of pathological conditions. J Pharm Pharmacol 60:999–1017
Nam YJ, Kim A, Sohn DS, Lee CS (2016) Apocynin inhibits Toll-like receptor-4-mediated activation of NF-κB by suppressing the Akt and mTOR pathways. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 389:1267–1277
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401:82–85
Pannu R, Singh I (2006) Pharmacological strategies for the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase: neurodegenerative versus neuroprotective mechanisms. Neurochem Int 49:170–182
Prasad S, Aggarwal BB (2014) Chronic diseases caused by chronic inflammation require chronic treatment: anti-inflammatory role of dietary apices. J Clin Cell Immunol 5:238
Qi SM, Xin YQ, Guo YT, Diao Y, Kou XJ, Luo L, Yin ZM (2012) Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int Immuno- pharmacol 12:278–287
Qin XY, Jiang XR, Jiang X, Wang YL, Miao ZL, He WG, Yang GZ, Lv ZH, YU YZ, Zheng YJ (2016) Micheliolide inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and protects mice from LPS challenge. Sci Rep 6:23240. doi:10.1038/srepb 23240
Ricciotti E, FitzGerald GA (2011) Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:986–1000
Saba E, Son Y, Jeon BR, Kim SE, Lee IK, Yun BS, Rhee MH (2015) Acetyl eburicoic acid from Laetiporus sulphureus var. miniatus suppresses inflammation in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Mycobiology 43:131–136
Seong YA, Hwang D, Kim GD (2016) The anti-inflammatory effect of Gnaphalium affine through inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and analysis of its phytochemical components. Cell Biochem Biophys 74:407–417
Song G, Ouyang G, Bao S (2005) The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med 9:59–71
Suschek CV, Schnorr O, Kolb-Bachofen V (2004) The role of iNOS in chronic inflammatory processes in vivo: is it damage-promoting, protective, or active at all? Curr Mol Med 4:763–775
Thomson AW, Turnquist HR, Raimondi G (2009) Immunoregulatory functions of mTOR inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol 9:324–337
Wang JZ, Sun WJ, Luo HJ, He HB, Deng WQ, Zou K, Liu C, Song J, Huang WF (2015) Protective effect of eburicoic acid of the chicken of the woods mushroom, Laetiporus sulphureus (higher Basidiomycetes), against gastric ulcers in mice. Int J Med Mushrooms 17:619–626
Wei N, Zhang CC, He HB, Wang T, Liu ZQ, Liu GY, Sun ZW, Zhou ZY, Bai CH, Yuan D (2014) Protective effect of saponins extract from Panax japonicus on myocardial infarction: involvement of NF-κB, Sirt1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways and inhibition of inflammation. J Pharm Pharmacol 66:1641–1651
Yeom MJ, Park JH, Lim CY, Sur BJ, Lee BB, Han JJ, Choi HD, Lee H, Hahm DH (2015) Glucosylceramide attenuates the inflammatory mediator expression in lipopolysaccharide- stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Nutr Res 35:241–250
Zamora Z, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR (2000) Inducible nitric oxide synthase and inflammatory diseases. Mol Med 6:347–373
Zhang GL, Ghosh S (2001) Toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappa B activation: a phyloge- netically conserved paradigm in innate immunity. J Clin Invest 107:13–19
Zhang X, Sun JL, Xin WY, Li YJ, Ni L, Ma XW, Zhang D, Zhang DM, Zhang TT, Du GH (2015) Anti-inflammation effect of methyl salicylate 2-O-β-D-lactoside on adjuvant induced-arthritis rats and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated murine macrophages RAW264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 25:88–95
Zhong LM, Zong Y, Sun L, Guo JZ, Zhang W, He Y, Song R, Wang WM, Xiao CJ, Lu D (2012) Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory responses via the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in cultured LPS-stimulated microglial cells. PLoS One 7:e32195
Zhou LT, Wang KJ, Li L, Li H, Geng M (2015) Pinocembrin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators production in BV2 microglial cells through suppression of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 761:211–216
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Common Projects from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31370373), National Drug Modernization Engineering Technology Research Center Foundation of Hubei Province (no. 20152Y007), and College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Research Foundation of China Three Gorges University (no. Hy1402). We thanked Professor Chengfu Yuan for his valuable comments and suggestions for the revision of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, P., He, H. et al. Eburicoic acid from Laetiporus sulphureus (Bull.:Fr.) Murrill attenuates inflammatory responses through inhibiting LPS-induced activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 845–856 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1382-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1382-3