Abstract
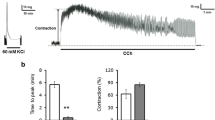
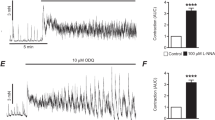
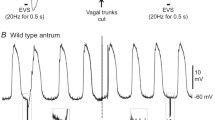
To elucidate the roles played by the interstitial cells of Cajal in the myenteric layer (ICC-MY) in cholinergic neuromuscular transmission, we recorded mechanical and electrical activities in response to electrical field stimulation (EFS) of the ileal longitudinal muscle strips from WBB6F1-W/WV (W/WV) mutant mice, that lacked ICC-MY and compared with those in WBB6F1-+/+ (+/+) control mice. In +/+ muscle strips, EFS induced phasic contractions, which were abolished or strongly attenuated by atropine or tetrodotoxin. In W/WV preparations, EFS induced similar phasic contractions, but the cholinergic component was smaller than that in +/+ strips. This was despite of the fact that the contractions because of exogenous applications of carbachol and high K+ solution in W/WV strips were comparable to or rather greater than those in the +/+ preparations. EFS induced atropine-sensitive excitatory junction potentials (EJPs) in the +/+ longitudinal smooth muscle cells but not in W/WV cells. In the presence of eserine, EFS induced atropine-sensitive EJPs in W/WV cells. These results suggest that ICC-MY mediate the cholinergic neuromuscular transmission in mouse ileal longitudinal smooth muscles. In addition, the other pathway in which ICC-MY are not involved can operate concomitantly.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- CCh:
-
Carbamylcholine chloride
- EFS:
-
Electrical field stimulation
- EJP:
-
Excitatory junction potential
- ICC:
-
Interstitial cells of Cajal
- ICC-DMP:
-
ICC that exist in the deep muscular plexus
- ICC-MY:
-
ICC that exist in the myenteric plexus
- IJP:
-
Inhibitory junction potential
- PGP9.5:
-
Protein gene product 9.5
- TTX:
-
Tetrodotoxin
References
Bayguinov PO, Hennig GW, Smith TK (2010) Ca2+ imaging of activity in ICC-MY during local mucosal reflexes and the colonic migrating motor complex in the murine large intestine. J Physiol 588:4453–4474. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2010.196824
Chen H, Redelman D, Ro S, Ward SM, Ordog T, Sanders KM (2007) Selective labeling and isolation of functional classes of interstitial cells of Cajal of human and murine small intestine. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C497–C507
Cheung DW, Daniel EE (1980) Comparative study of the smooth muscle layers of the rabbit duodenum. J Physiol 309:13–27
Chi MM, Powley TL (2003) c-Kit mutant mouse behavioral phenotype: altered meal patterns and CCK sensitivity but normal daily food intake and body weight. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:R1170–R1183
Choi K, Winston J, Chen J, Shi X-Z, Sarna Sushil K (2011) Mast cell deficiency, rather than deficiency of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), impairs smooth muscle function in W/Wv mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23(suppl s1):50–51
Cousins HM, Edwards FR, Hirst GD, Wendt IR (1993) Cholinergic neuromuscular transmission in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol 471:61–86
Cousins HM, Edwards FR, Hirst GD (1995) Neuronally released and applied acetylcholine on the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience 65:193–207
Crist JR, He XD, Goyal RK (1992) Both ATP and the peptide VIP are inhibitory neurotransmitters in guinea-pig ileum circular muscle. J Physiol 447:119–131
Der-Silaphet T, Malysz J, Hagel S, Larry Arsenault A, Huizinga JD (1998) Interstitial cells of Cajal direct normal propulsive contractile activity in the mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 114:724–736
Dickson EJ, Heredia DJ, McCann CJ, Hennig GW, Smith TK (2010) The mechanisms underlying the generation of the colonic migrating motor complex in both wild-type and nNOS knockout mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G222–G232. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00399.2009
Epperson A, Hatton WJ, Callaghan B, Doherty P, Walker RL, Sanders KM et al (2000) Molecular markers expressed in cultured and freshly isolated interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C529–C539
Flanagan JG, Chan DC, Leder P (1991) Transmembrane form of the kit ligand growth factor is determined by alternative splicing and is missing in the Sld mutant. Cell 64:1025–1035
Fujita A, Okishio Y, Fujinami K, Nakagawa M, Takeuchi T, Takewaki T, Hata F (2004) Role of the interstitial cells distributed in the myenteric plexus in neural reflexes in the mouse ileum. J Pharmacol Sci 96:483–492
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A (1995) W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 373:347–349
Iino S, Horiguchi K (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal are involved in neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Acta Histochem Cytochem 39:145–153
Iino S, Nojyo Y (2006) Muscarinic M2 acetylcholine receptor distribution in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience 138:549–559
Iino S, Horiguchi S, Horiguchi K, Nojyo Y (2007) Interstitial cells of Cajal in the gastrointestinal musculature of W mutant mice. Arch Histol Cytol 70:163–173
Iino S, Ward SM, Sanders KM (2004) Interstitial cells of Cajal are functionally innervated by excitatory motor neurones in the murine intestine. J Physiol 556:521–530
Kitamura Y, Go S, Hatanaka K (1978) Decrease of mast cells in W/Wv mice and their increase by bone marrow transplantation. Blood 52:447–452
Kito Y, Suzuki H (2003) Properties of pacemaker potentials recorded from myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal distributed in the mouse small intestine. J Physiol 553:803–818
Kito Y, Ward SM, Sanders KM (2005) Pacemaker potentials generated by interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine intestine. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C710–C720
Klemm MF (1995) Neuromuscular junctions made by nerve fibres supplying the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Auton Nerv Syst 55:155–164
Klein S, Seidler B, Kettenberger A, Sibaev A, Rohn M, Feil R, Allescher HD, Vanderwinden JM, Hofmann F, Schemann M, Rad R, Storr MA, Schmid RM, Schneider G, Saur D (2013) Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave activity. Nat Commun 4:1630–1638. doi:10.1038/ncomms2626
Llewellyn Smith IJ, Costa M, Furness JB, Bornstein JC (1993) Structure of the tertiary component of the myenteric plexus in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 1272:509–516
Matsuyama H, Tanahashi Y, Kitazawa T, Yamada M, Komori S, Unno T (2013) Evidence for M2 and M3 muscarinic receptor involvement in cholinergic excitatory junction potentials through synergistic activation of cation channels in the longitudinal muscle of mouse ileum. J Pharmacol Sci 121:227–236
McKay CM, Huizinga JD (2006) Muscarinic regulation of ether-a-go-go-related gene K+ currents in interstitial cells of Cajal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1112–1123
Nakagawa T, Misawa H, Nakajima Y, Takaki M (2005) Absence of peristalsis in the ileum of W/W(V) mutant mice that are selectively deficient in myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal. J Smooth Muscle Res 41:141–151
Nocka K, Tan JC, Chiu E, Chu TY, Ray P, Traktman P, Besmer P (1990) Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J 9:1805–1813
Okishio Y, Takeuchi T, Fujita A, Suenaga K, Fujinami K, Munakata S, Hata F (2005) Examination of the role of cholinergic myenteric neurons with the impairment of neural reflexes in the ileum of c-kit mutant mice. J Smooth Muscle Res 41:49–60
Sanders KM, Ordog T, Koh SD, Torihashi S, Ward SM (1999) Development and plasticity of interstitial cells of Cajal. Neurogastroenterol Motil 11:311–338
Sperelakis N (1991) Electric field model: an alternative mechanism for cell-to-cell propagation in cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Neurogastroenterol Motil 3:64–83. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.1991.tb00050.x
Tanahashi Y, Unno T, Matsuyama H, Ishii T, Yamada M, Wess J, Komori S (2009) Multiple muscarinic pathways mediate the suppression of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in mouse intestinal smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 158:1874–1883
Tanahashi Y, Waki N, Unno T, Matsuyama H, Iino S, Kitazawa T, Yamada M, Komori S (2013) Roles of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in the generation of rhythmic motor activity in mouse small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:e687–e697. doi:10.1111/nmo.12194
Thuneberg L, Peters S (2001) Toward a concept of stretch-coupling in smooth muscle. I. Anatomy of intestinal segmentation and sleeve contractions. Anat Rec 262:110–124
Tomita T (1981) Electrical activity (spikes and slow waves) in gastrointestinal smooth muscle. In: Bülbring E, Brading AF, Jones AW, Tomita T (eds) Smooth muscle. An assessment of current knowledge. Edward Arnold, London, pp 127–156
Torihashi S, Ward SM, Nishikawa S, Nishi K, Kobayashi S, Sanders KM (1995) c-Kit-dependent development of interstitial cells and electrical activity in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 280:97–111
Unno T, Kwon SC, Okamoto H, Irie Y, Kato Y, Matsuyama H, Komori S (2003) Receptor signaling mechanisms underlying muscarinic agonist-evoked contraction in guinea-pig ileal longitudinal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 139:337–350
Unno T, Matsuyama H, Izumi Y, Yamada M, Wess J, Komori S (2006) Roles of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in cholinergic nerve-induced contractions in mouse ileum studied with receptor knockout mice. Br J Pharmacol 149:1022–1030
Vannucchi MG, Faussone Pellegrini MS (2000) NK1, NK2 and NK3 tachykinin receptor localization and tachykinin distribution in the ileum of the mouse. Anat Embryol (Berl) 202:247–255
Vigmond EJ, Bardakjian BL, Thuneberg L, Huizinga JD (2000) Intercellular coupling mediated by potassium accumulation in peg-and-socket junctions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 47:1576–1583
Wang XY, Sanders KM, Ward SM (1999) Intimate relationship between interstitial cells of Cajal and enteric nerves in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 295:247–256
Wang XY, Vannucchi MG, Nieuwmeyer F, Ye J, Faussone Pellegrini MS, Huizinga JD (2005) Changes in interstitial cells of Cajal at the deep muscular plexus are associated with loss of distention-induced burst-type muscle activity in mice infected by Trichinella spiralis. Am J Pathol 167:437–453
Ward SM, Burns AJ, Torihashi S, Sanders KM (1994) Mutation of the proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine. J Physiol 480:91–97
Ward SM, Burns AJ, Torihashi S, Harney SC, Sanders KM (1995) Impaired development of interstitial cells and intestinal electrical rhythmicity in steel mutants. Am J Physiol 269:C1577–C1585
Ward SM, McLaren GJ, Sanders KM (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal in the deep muscular plexus mediate enteric motor neurotransmission in the mouse small intestine. J Physiol 573:147–159
Xue L, Farrugia G, Sarr MG, Szurszewski JH (1999) ATP is a mediator of the fast inhibitory junction potential in human jejunal circular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 276:G1373–G1379
Young HM, McConalogue K, Furness JB, De Vente J (1993) Nitric oxide targets in the guinea-pig intestine identified by induction of cyclic GMP immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 55:583–596
Zhu MH, Sung IK, Zheng H, Sung TS, Britton FC, O’Driscoll K et al (2011) Muscarinic activation of Ca2+-activated Cl− current in interstitial cells of Cajal. J Physiol 589:4565–4582. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.211094
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the JSPS Research Fellows for Young Scientists (no. 203080) and JSPS KAKENHI grant nos. 22380159 and 25870891 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanahashi, Y., Ichimura, Y., Kimura, K. et al. Cholinergic neuromuscular transmission mediated by interstitial cells of Cajal in the myenteric layer in mouse ileal longitudinal smooth muscles. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 387, 377–388 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0944-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0944-2