Abstract.
Hippocampal 5-HT1A receptors have been shown to be suppressed by glucocorticoids in a variety of animal studies, however the molecular mechanism and the functional meaning of this effect are still not well understood.
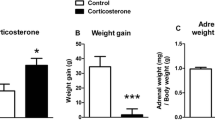
The present study was designed to investigate the impact of repeated administration of corticosterone (10 mg/kg s.c. twice daily for 7 days) on the functional consequences of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation measured electrophysiologically in hippocampal slices. Additionally, the effects of corticosterone on 5-HT1A receptor binding and on receptor mRNA levels in the hippocampus were studied. Prolonged, but not acute treatment with corticosterone attenuated (±)-8-hydroxy-2-di-N-propylamino)tetralin hydrobromide (8-OH-DPAT)-induced inhibition of population spikes, and 8-OH-DPAT-induced hyperpolarization in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. Chronic, but not acute treatment with corticosterone also decreased 5-HT1A receptor binding in the CA1 region (in the ventral part only) and the dentate gyrus. A single dose of corticosterone increased [3H]8-OHDPAT binding in the dentate gyrus and in the CA3 and CA4 hippocampal regions. Only acute, but not prolonged treatment with corticosterone decreased the level of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the CA1 region and dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. 5-HT turnover in the hippocampus was not influenced by chronic corticosterone.
It is concluded that a chronically elevated level of corticosterone can induce functional desensitization of 5-HT1A receptors in the CA1 area of the hippocampus, although this effect is not always followed consequently by decreases in 5-HT1A receptor synthesis in this or other areas of the hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czyrak, A., Maćkowiak, M., Chocyk, A. et al. Prolonged corticosterone treatment alters the responsiveness of 5-HT1A receptors to 8-OH-DPAT in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 366, 357–367 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-002-0586-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-002-0586-2