Abstract
Rationale
Noradrenergic system plays a critical role in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis regulation and the stress response. A dysregulated HPA axis may be indicative of an increased biological vulnerability for depression. In addition, a variety of studies have focused on specific alterations of α2-adrenoceptors as a mechanism involved in the pathogenesis of mood disorders and antidepressant response.
Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of subchronic corticosterone administration on rat brain α2-adrenoceptor functionality by in vitro [35S]GTPγS binding stimulation assays and in vivo dual-probe microdialysis determination of extracellular noradrenaline concentrations.
Results
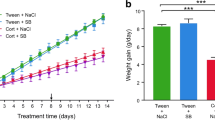
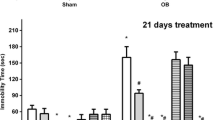
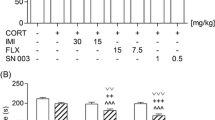
Implantation of a time release corticosterone pellet during 14 days induced sustained changes in endocrine function. However, there were no differences in α2-adrenoceptor agonist UK14304-induced stimulation of [35S]GTPγS binding in prefrontal cortex (PFC) between corticosterone-treated and control rats. In the same way, the in vivo evaluation of α2-adrenoceptor-mediated noradrenaline release responses to the α2-adrenoceptor agonist clonidine local administration into the locus coeruleus (LC), and the PFC did not show differences between the groups.
Conclusions
The present results show that subchronic corticosterone administration does not induce changes on functionality of α2-adrenoceptors neither in the LC nor in noradrenergic cortical terminal areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Southwick SM, Charney DS (1996) Noradrenergic mechanisms in stress and anxiety: II. Clinical studies. Synapse 23:39–51
Callado LF, Stamford JA (1999) α2A- but not α2B/C-adrenoceptors modulate noradrenaline release in rat locus coeruleus: voltammetric data. Eur J Pharmacol 366:35–39
Callado LF, Meana JJ, Grijalba B, Pazos A, Sastre M, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1998) Selective increase of α2A-adrenoceptor agonist binding sites in brains of depressed suicide victims. J Neurochem 70:1114–1123
Charmandari E, Tsigos C, Chrousos G (2005) Endocrinology of the stress response. Annu Rev Physiol 67:259–284
De Paermentier F, Mauger JM, Lowther S, Crompton MR, Katona CL, Horton RW (1997) Brain α-adrenoceptors in depressed suicides. Brain Res 757:60–68
Fernandez-Pastor B, Meana JJ (2002) In vivo tonic modulation of the noradrenaline release in the rat cortex by locus coeruleus somatodendritic α2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 442:225–229
Fernandez-Pastor B, Ortega JE, Meana JJ (2013) Involvement of serotonin 5-HT3 receptors in the modulation of noradrenergic transmission by serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a microdialysis study in rat brain. Psychopharmacology 229:331–344
Flugge G (1996) Alterations in the central nervous α2-adrenoceptor system under chronic psychosocial stress. Neuroscience 75:187–196
Flugge G (1999) Effects of cortisol on brain α2-adrenoceptors: potential role in stress. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:949–956
Garcia-Sevilla JA, Padro D, Giralt MT, Guimon J, Areso P (1990) α2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of platelet adenylate cyclase and induction of aggregation in major depression. Effect of long-term cyclic antidepressant drug treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:125–132
Garcia-Sevilla JA, Ventayol P, Perez V, Rubovszky G, Puigdemont D, Ferrer-Alcon M, Andreoli A, Guimon J, Alvarez E (2004) Regulation of platelet α2A-adrenoceptors, Gi proteins and receptor kinases in major depression: effects of mirtazapine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:580–588
Gartside SE, Leitch MM, Young AH (2003) Altered glucocorticoid rhythm attenuates the ability of a chronic SSRI to elevate forebrain 5-HT: implications for the treatment of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1572–1578
Gonzalez-Maeso J, Rodriguez-Puertas R, Gabilondo AM, Meana JJ (2000) Characterization of receptor-mediated [35S]GTPgammaS binding to cortical membranes from postmortem human brain. Eur J Pharmacol 390:25–36
Hill MN, Hellemans KG, Verma P, Gorzalka BB, Weinberg J (2012) Neurobiology of chronic mild stress: parallels to major depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:2085–2117
Invernizzi RW, Parini S, Sacchetti G, Fracasso C, Caccia S, Annoni K, Samanin R (2001) Chronic treatment with reboxetine by osmotic pumps facilitates its effect on extracellular noradrenaline and may desensitize α2-adrenoceptors in the prefrontal cortex. Br J Pharmacol 132:183–188
Jedema HP, Gold SJ, Gonzalez-Burgos G, Sved AF, Tobe BJ, Wensel T, Grace AA (2008) Chronic cold exposure increases RGS7 expression and decreases α2-autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. Eur J Neurosci 27:2433–2443
Leitch MM, Ingram CD, Young AH, McQuade R, Gartside SE (2003) Flattening the corticosterone rhythm attenuates 5-HT1A autoreceptor function in the rat: relevance for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:119–125
Mateo Y, Meana JJ (1999) Determination of the somatodendritic α2-adrenoceptor subtype located in rat locus coeruleus that modulates cortical noradrenaline release in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 379:53–57
Mateo Y, Pineda J, Meana JJ (1998) Somatodendritic α2-adrenoceptors in the locus coeruleus are involved in the in vivo modulation of cortical noradrenaline release by the antidepressant desipramine. J Neurochem 71:790–798
Mateo Y, Fernandez-Pastor B, Meana JJ (2001) Acute and chronic effects of desipramine and clorgyline on α2-adrenoceptors regulating noradrenergic transmission in the rat brain: a dual-probe microdialysis study. Br J Pharmacol 133:1362–1370
Ortega JE, Mendiguren A, Pineda J, Meana JJ (2012) Regulation of central noradrenergic activity by 5-HT3 receptors located in the locus coeruleus of the rat. Neuropharmacology 62:2472–2479
Parini S, Renoldi G, Battaglia A, Invernizzi RW (2005) Chronic reboxetine desensitizes terminal but not somatodendritic α2-adrenoceptors controlling noradrenaline release in the rat dorsal hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1048–1055
Stanford SC (1995) Central noradrenergic neurones and stress. Pharmacol Ther 68:297–242
Sterner EY, Kalynchuk LE (2010) Behavioral and neurobiological consequences of prolonged glucocorticoid exposure in rats: relevance to depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:777–790
Valdizan EM, Diez-Alarcia R, Gonzalez-Maeso J, Pilar-Cuellar F, Garcia-Sevilla JA, Meana JJ, Pazos A (2010) α2-adrenoceptor functionality in postmortem frontal cortex of depressed suicide victims. Biol Psychiatry 68:869–872
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Spanish MICINN (SAF 04/02784), MINECO (SAF2009-08460, SAF2013-48586-R), ERDF Funds and the Basque Government (IT-616-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal care and all experimental protocols were performed in agreement with the European Ethical Standards (European Union Directive 2010/63/EU) and translation into Spanish legislation (RD 53/2013) and approved by the UPV/EHU Ethical Board for Animal Welfare (CEEA)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horrillo, I., Ortega, J.E., Diez-Alarcia, R. et al. Effect of subchronic corticosterone administration on α2-adrenoceptor functionality in rat brain: an in vivo and in vitro study. Psychopharmacology 233, 3861–3867 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4418-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4418-3