Abstract.
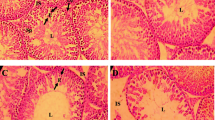
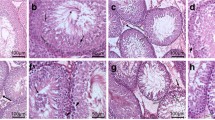
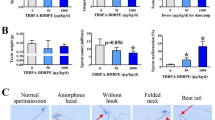
Male F344/DuCrj (Fischer) rats were given bisphenol A (BPA) in the diet at levels of 0 (control), 0.25, 0.50 and 1.00%, equivalent to 0, 235, 466 and 950 mg/kg per day, respectively, for 44 days. Body weight gains were depressed dose-dependently in BPA-treated rats, and those of 0.50 and 1.00% groups were significant. Testis and epididymis weights were not significantly decreased. Both absolute and relative weights of dorsolateral prostate and preputial glands were reduced in a dose-related fashion. Absolute weights of seminal vesicles and hypophysis were also decreased. Histopathologically, seminiferous tubule degeneration and loss of elongated spermatids were observed, the severity being related to BPA dose. The disorganization, distortion and degeneration of late spermatids, and the atrophy of seminiferous tubules were found even in the 0.25% BPA group. Serum testosterone concentrations were not decreased in BPA-treated groups. These results indicate that BPA even at a level of 0.25% (235 mg/kg per day) is clearly toxic to male reproductive organs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, O., Oishi, S. Testicular toxicity of dietary 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane (bisphenol A) in F344 rats. Arch Toxicol 75, 42–51 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000204
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000204