Abstract
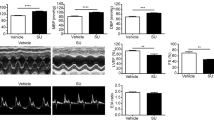
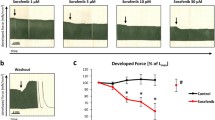
Sunitinib (SNT) is a multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has been approved by the FDA for cancer therapy. However, its cardiotoxicity has limited the clinical applicability with no effective therapeutic approach available. As a broadband kinase inhibitor, the function of several kinases that are essential to cardiac function might also be affected by SNT, such as calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMKII), cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinases (PKA), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K). In this study, we investigated whether SNT-induced cardiotoxicity could be prevented by blocking SNT-induced alteration in the corresponding signaling pathways. In human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, SNT (0.5–20 µmol/L) inhibited contractility of cardiomyocytes in a concentration-dependent manner, and the inhibitory effect was prevented either by PIP3 (1 µmol/L) application or PI3K overexpression. On the contrary, the CaMKII inhibitor KN-93 (50 nmol/L), PKA inhibitor H89 (1 µmol/L), and AMPK activators metformin (2 mmol/L) and 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide 1-b-d-ribofuranoside (2 mmol/L) presented negligible effects. Oral SNT administration (40 mg/kg/day) in mice progressively decreased the PI3K activity and cardiac function in 2 weeks with a significant decrease in the expression and activity of Cav1.2 and SERCA. Cardiac-specific PI3K overexpression through adeno-associated virus 9-mediated gene delivery in mice prevented SNT-induced reduction in cardiac function, calcium transient, calcium current, and Cav1.2 expression. In summary, our data indicate that increased PI3K activity is protective against SNT-induced calcium mishandling and contractile dysfunction. Cardiac-specific PI3K activation could be an effective therapeutic approach to treat SNT cardiotoxicity in patients with cancer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre SA, Heyen JR, Collette W, Bobrowski W, Blasi ER (2010) Cardiovascular effects in rats following exposure to a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Toxicol Pathol 38(3):416–428
Ballou LM, Lin RZ, Cohen IS (2015) Control of cardiac repolarization by phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling to ion channels. Circ Res 116(1):127–137
Barr LA, Makarewich CA, Berretta RM, Gao H, Troupes CD, Woitek F, Recchia F, Kubo H, Force T, Houser SR (2014) Imatinib activates pathological hypertrophy by altering myocyte calcium regulation. Clin Transl Sci 7(5):360–367
Catino AB, Hubbard RA, Chirinos JA, Townsend R, Keefe S, Haas NB, Puzanov I, Fang JC, Agarwal N, Hyman D, Smith AM, Gordon M, Plappert T, Englefield V, Narayan V, Ewer S, ElAmm C, Lenihan D, Ky B (2018) Longitudinal assessment of vascular function with sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Circ Heart Fail 11:e004408
Chen Y, Zhao J, Du J, Xu G, Tang C, Geng B (2012) Hydrogen sulfide regulates cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake via KATP channel and PI3K/Akt pathway. Life Sci 91:271–278
Chu TFB, Rupnick MAM, Kerkela RM, Dallabrida SMP, Zurakowski DP, Nguyen LB, Woulfe KB, Pravda EB, Cassiola FP, Desai JM, George SM, Harris DMP, Ismail NSB, Chen JM, Schoen FJM, Van den Abbeele ADM, Demetri GDM, Force TM, Chen MHM (2007) Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Lancet 370(9604):2011–2019
Cohen JD, Babiarz JE, Abrams RM, Guo L, Kameoka S, Chiao E, Taunton J, Kolaja KL (2011) Use of human stem cell derived cardiomyocytes to examine sunitinib mediated cardiotoxicity and electrophysiological alterations. Toxicol Appl Pharm 257(1):74–83
Demetri GD, Reichardt P, Kang Y, Blay J, Rutkowski P, Gelderblom H, Hohenberger P, Leahy M, von Mehren M, Joensuu H, Badalamenti G, Blackstein M, Le Cesne A, Schöffski P, Maki RG, Bauer S, Nguyen BB, Xu J, Nishida T, Chung J, Kappeler C, Kuss I, Laurent D, Casali PG (2013) Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (GRID): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 381(9863):295–302
Doerr L, Thomas U, Guinot DR, Bot CT, Stoelzle-Feix S, Beckler M, George M, Fertig N (2015) New easy-to-use hybrid system for extracellular potential and impedance recordings. J Lab Autom 20(2):175–188
Eschenhagen T (2018) Exaggerated cardiotoxicity of sunitinib in stressed 3-dimensional heart muscles. JACC Basic Transl Sci 2(3):277–279
Faivre S, Delbaldo C, Vera K, Robert C, Lozahic S, Lassau N, Bello C, Deprimo S, Brega N, Massimini G, Armand J, Scigalla P, Raymond E (2006) Safety, pharmacokinetic, and antitumor activity of SU11248, a Novel oral multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(1):25–35
Force T, Krause DS, Van Etten RA (2007) Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer 7(5):332–344
Garg P, Garg V, Shrestha R, Sanguinetti MC, Kamp TJ, Wu JC (2018) Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes as models for cardiac channelopathies. Circ Res 123(2):224–243
Gharwan H, Groninger H (2016) Kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies in oncology: clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13(4):209–227
Ghigo A, Laffargue M, Li M, Hirsch E (2017) PI3K and calcium signaling in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 121(3):282–292
Giamas G, Man YL, Hirner H, Bischof J, Kramer K, Khan K, Lavina Ahmed SS, Stebbing J, Knippschild U (2010) Kinases as targets in the treatment of solid tumors. Cell Signal 22(7):984–1002
Jessup M, Greenberg B, Mancini D, Cappola T, Pauly DF, Jaski B, Yaroshinsky A, Zsebo KM, Dittrich H, Hajjar RJ (2011) Calcium upregulation by percutaneous administration of gene therapy in cardiac disease (CUPID) a phase 2 trial of intracoronary gene therapy of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation 124:304–313
Kerkela R, Woulfe KC, Durand J, Vagnozzi R, Kramer D, Chu TF, Beahm C, Chen MH, Force T (2009) Sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity is mediated by off-target inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase. Clin Transl Sci 2(1):15–25
Kerkelä R, Grazette L, Yacobi R, Iliescu C, Patten R, Beahm C, Walters B, Shevtsov S, Pesant S, Clubb FJ, Rosenzweig A, Salomon RN, Van Etten RA, Alroy J, Durand J, Force T (2006) Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib mesylate. Nat Med 12(8):908–916
Lu Z, Jiang Y, Wang W, Xu X, Mathias RT, Entcheva E, Ballou LM, Cohen IS, Lin RZ (2009) Loss of cardiac phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110α results in contractile dysfunction. Circulation 120(4):318–325
Lu Z, Yu CY, Jiang YP, Ballou LM, Clausen C, Cohen IS, Lin RZ (2012) Suppression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling and alteration of multiple ion currents in drug-induced long QT syndrome. Sci Transl Med 131(4):1–20
Marx SO, Reiken S, Hisamatsu Y, Jayaraman T, Burkhoff D, Rosemblit N, Marks AR (2000) PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell 101:365–376
Mellor HR, Bell AR, Valentin J, Roberts RRA (2011) Cardiotoxicity associated with targeting kinase pathways in cancer. Toxicol Sci 120(1):14–32
Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG, Christensen JG, Li G, Schreck RE, Abrams TJ, Ngai TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Carver J, Chan E, Moss KG, Haznedar JO, Sukbuntherng J, Blake RA, Sun L, Tang C, Miller T, Shirazian S, McMahon G, Cherrington JM (2003) In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res 9:327–337
Molkentin JD, Lu J, Antos CL, Markham B, Richardson J, Robbins J, Grant SR, Olson EN (1998) A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 93(2):215–228
Mooney L, Skinner M, Coker SJ, Currie S (2015) Effects of acute and chronic sunitinib treatment on cardiac function and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Br J Pharmacol 172(17):4342–4354
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Gannon A, Figlin RA (2017) Sunitinib: ten years of successful clinical use and study in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist 22(1):41–52
Rainer PP, Doleschal B, Kirk JA, Sivakumaran V, Saad Z, Groschner K, Maechler H, Hoefler G, Bauernhofer T, Samonigg H, Hutterer G, Kass DA, Pieske B, von Lewinski D, Pichler M (2012) Sunitinib causes dose-dependent negative functional effects on myocardium and cardiomyocytes. BJU Int 110(10):1455–1462
Respress JL, van Oort RJ, Li N, Rolim N, Dixit SS, Dealmeida A, Voigt N, Lawrence WS, Skapura DG, Skårdal K, Wisløff U, Wieland T, Ai X, Pogwizd SM, Dobrev D, Wehrens XHT (2012) Role of RyR2 phosphorylation at S2814 during heart failure progression. Circ Res 110(11):1474–1483
Sag CM, Wadsack DP, Khabbazzadeh S, Abesser M, Grefe C, Neumann K, Opiela M, Backs J, Olson EN, Brown JH, Neef S, Maier SKG, Maier LS (2009) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II contributes to cardiac arrhythmogenesis in heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2(6):664–675
Sayed-Ahmed MM, Alrufaiq BI, Alrikabi A, Abdullah ML, Hafez MM, Al-Shabanah OA (2019) Carnitine supplementation attenuates sunitinib-induced inhibition of amp-activated protein kinase downstream signals in cardiac tissues. Cardiovasc Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-9500-0
Schneider C, Wallner M, Kolesnik E, Herbst V, Mächler H, Pichler M, von Lewinski D, Sedej S, Rainer PP (2018) The anti-cancer multikinase inhibitor sorafenib impairs cardiac contractility by reducing phospholamban phosphorylation and sarcoplasmic calcium transients. Sci Rep 8(1):5295
Sharma A, Burridge PW, McKeithan WL, Serrano R, Shukla P, Sayed N, Churko JM, Kitani T, Wu H, Holmström A, Matsa E, Zhang Y, Kumar A, Fan AC, Del Álamo JC, Wu SM, Moslehi JJ, Mercola M, Wu JC (2017) High-throughput screening of tyrosine kinase inhibitor cardiotoxicity with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Transl Med 9(377):f2584
Shim JV, Chun B, van Hasselt JGC, Birtwistle MR, Saucerman JJ, Sobie EA (2017) Mechanistic systems modeling to improve understanding and prediction of cardiotoxicity caused by targeted cancer therapeutics. Front Physiol 8:651
Singh AP, Glennon MS, Umbarkar P, Gupte M, Galindo CL, Zhang Q, Force T, Becker JR, Lal H (2019) Ponatinib-induced cardiotoxicity: delineating the signaling mechanisms and potential rescue strategies. Cardiovasc Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz006
Talbert DR, Doherty KR, Trusk PB, Moran DM, Shell SA, Bacus S (2015) A multi-parameter in vitro screen in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes identifies ponatinib-induced structural and functional cardiac toxicity. Toxicol Sci 143(1):147–155
Telli ML, Witteles RM, Fisher GA, Srinivas S (2008) Cardiotoxicity associated with the cancer therapeutic agent sunitinib malate. Ann Oncol 19(9):1613–1618
Truitt R, Mu A, Corbin EA, Vite A, Brandimarto J, Ky B, Margulies KB (2018) Increased afterload augments sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity in an engineered cardiac microtissue model. JACC Basic Transl Sci 2(3):265–276
Wehrens XH, Lehnart SE, Huang F, Vest JA, Reiken SR, Mohler PJ, Sun J, Guatimosim S, Song LS, Rosemblit N, D'Armiento JM, Napolitano C, Memmi M, Priori SG, Lederer WJ, Marks AR (2003) FKBP12.6 deficiency and defective calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function linked to exercise-induced sudden cardiac death. Cell 113:829–840
Yang K, Foeger NC, Marionneau C, Jay PY, McMullen JR, Nerbonne JM (2010) Homeostatic regulation of electrical excitability in physiological cardiac hypertrophy. J Physiol 588(24):5015–5032
Yano N, Tseng A, Zhao TC, Robbins J, Padbury JF, Tseng Y (2008) Temporally controlled overexpression of cardiac-specific PI3Kα induces enhanced myocardial contractility—a new transgenic model. Am J Physiol Heart C 295(4):H1690–H1694
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31771259 to Y. X., 81670370 to W. W.), the Science and Technology Foundation of Hebei Province (17274803D to Y. X.), the Outstanding Youth Foundations of Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2017206381 to W. W.), the Office of Education Foundation of Hebei Province of China (SLRC2017046 to W. W., CY201618 to W. W.), and the Hebei Province Graduate Student Innovation Project (CXZZBS2018063 to C. L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL, RZ, HZ, YW, and SQ performed the research, YX and WW designed the research study, CL, WW, and BQ analyzed the data. CL, WW, and YX wrote the paper.Compliance with ethical standards
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Zou, R., Zhang, H. et al. Upregulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase prevents sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol 93, 1697–1712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02448-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02448-z