Abstract
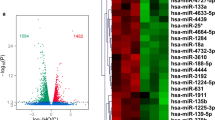
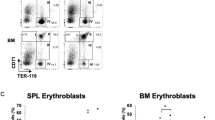
Exposure to high-dose benzene leads to the inhibition of erythroid differentiation. However, whether lower doses of benzene exposure resemble high-dose effects in erythroid differentiation, as well as the underlying mechanisms, remains largely unknown. To identify the microRNAs (miRNAs) specifically responsible for benzene exposure and their regulatory role in erythroid differentiation, we performed miRNA microarray in CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells isolated from human umbilical cord blood after treatment with hydroquinone (HQ), a metabolite of benzene at concentrations of 0, 1.0, 2.5, and 5.0 μM. As a result, HQ treatment inhibited erythroid differentiation in a dose–response manner. miRNA microarray analysis revealed that miRNA-451a, miRNA-486-5p and miRNA-126-3p expression were significantly lower in HQ-treated CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. In vitro studies showed that miRNA-451a and miRNA-486-5p were up-regulated during erythroid differentiation both in CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and K562 cells. The increase in the percentage of benzidine-positive cells and the expression of γ-globin in K562 cells transfected with either miRNA-451a or miRNA-486-5p mimic indicated that both miRNAs played a role in the promotion of erythroid cell differentiation. Overexpression of either miRNA-451a or miRNA-486-5p attenuated the inhibitory effects on erythroid differentiation in HQ-treated K562 cells. In vivo study showed a decreasing count of peripheral red blood cell (RBC) in C57BL/6J male mice treated with aerosol benzene at concentrations of 0, 1, 5, 25 ppm (time weight average, TWA). In addition, the expression of miRNA-451a or miRNA-486-5p was negatively correlated with the concentration of benzene inhalation on erythroid toxicity of C57BL/6J mice. Particularly, the decline in miRNA-451a and miRNA-486-5p expression appeared in male chronic benzene poisoning patients, and was correlated with a constant decrease in their RBC counts over the first 3 months after being diagnosed. These findings indicate that the suppression of miRNA-451a or miRNA-486-5p might be associated with the benzene-induced perturbation of erythroid cell differentiation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernethy DJ, Kleymenova EV, Rose J, Recio L, Faiola B (2004) Human CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitor cells are sensitive targets for toxicity induced by 1,4-benzoquinone. Toxicol Sci 79(1):82–89. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfh095
Andersson LC, Nilsson K, Gahmberg CG (1979) K562—a human erythroleukemic cell line. Int J cancer 23(2):143–147
Arnold SM, Angerer J, Boogaard PJ et al (2013) The use of biomonitoring data in exposure and human health risk assessment: benzene case study. Crit Rev Toxicol 43(2):119–153. doi:10.3109/10408444.2012.756455
Baarson KA, Snyder CA, Albert RE (1984) Repeated exposure of C57Bl mice to inhaled benzene at 10 ppm markedly depressed erythropoietic colony formation. Toxicol Lett 20(3):337–342
Bianchi N, Zuccato C, Finotti A, Lampronti I, Borgatti M, Gambari R (2012) Involvement of miRNA in erythroid differentiation. Epigenomics 4(1):51–65. doi:10.2217/epi.11.104
Choi S, Kim JY, Kim KB et al (2011) Differential gene expression analysis in human leukemia cell line K562 treated with benzene. Epidemiology 22(1):S246. doi:10.1097/01.ede.0000392446.46463.20
Deng QF, Huang SL, Zhang X et al (2014) Plasma microRNA expression and micronuclei frequency in workers exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Health Persp 122(7):719–725. doi:10.1289/ehp.1307080
Faiola B, Bauer AK, Fuller ES et al (2003) Variations in Prkdc and susceptibility to benzene-induced toxicity in mice. Toxicol Sci 75(2):321–332. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfg186
Gao AM, Ke ZP, Wang JN, Yang JY, Chen SY, Chen H (2013) Apigenin sensitizes doxorubicin-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin via inhibiting PI3 K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Carcinogenesis 34(8):1806–1814. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt108
Grabher C, Payne EM, Johnston AB et al (2011) Zebrafish microRNA-126 determines hematopoietic cell fate through c-Myb. Leukemia 25(3):506–514. doi:10.1038/leu.2010.280
Huang X, Gschweng E, Van Handel B, Cheng D, Mikkola HK, Witte ON (2011) Regulated expression of microRNAs-126/126* inhibits erythropoiesis from human embryonic stem cells. Blood 117(7):2157–2165. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-08-302711
Kerzic PJ, Liu WS, Pan MT et al (2010) Analysis of hydroquinone and catechol in peripheral blood of benzene-exposed workers. Chem Biol Interact 184(1–2):182–188. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.12.010
Koh DH, Jeon HK, Lee SG, Ryu HW (2015) The relationship between low-level benzene exposure and blood cell counts in Korean workers. Occup Environ Med 72(6):421–427. doi:10.1136/oemed-2014-102227
Kolde R (2015) pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R package version 1.0.8. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap
Lan Q, Zhang L, Li G et al (2004) Hematotoxicity in workers exposed to low levels of benzene. Science 306(5702):1774–1776. doi:10.1126/science.1102443
Li DC, Wang Q, Liu CX et al (2012) Aberrant expression of miR-638 contributes to benzo(a)pyrene-induced human cell transformation. Toxicol Sci 125(2):382–391. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr299
Li XJ, Ren ZJ, Tang JH (2014) MicroRNA-34a: a potential therapeutic target in human cancer. Cell Death Dis 5:e1327. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.270
McHale CM, Zhang L, Smith MT (2012) Current understanding of the mechanism of benzene-induced leukemia in humans: implications for risk assessment. Carcinogenesis 33(2):240–252. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgr297
Obeidi N, Pourfathollah AA, Soleimani M, Nikougoftar Zarif M, Kouhkan F (2016) The Effect of mir-451 upregulation on erythroid lineage differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells. Cell J 18(2):165–178
Pase L, Layton JE, Kloosterman WP, Carradice D, Waterhouse PM, Lieschke GJ (2009) miR-451 regulates zebrafish erythroid maturation in vivo via its target gata2. Blood 113(8):1794–1804. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-05-155812
Program NT (1986) NTP Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of benzene (CAS No. 71-43-2) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (Gavage Studies). Natl Toxicol Progr Techn Rep Ser 289:1
R Core Team (2015) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Rickert DE, Baker TS, Bus JS, Barrow CS, Irons RD (1979) Benzene disposition in the rat after exposure by inhalation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 49(3):417–423
Rutherford TR, Clegg JB, Weatherall DJ (1979) K562 human leukaemic cells synthesise embryonic haemoglobin in response to haemin. Nature 280(5718):164–165
Seidel HJ, Barthel E, Zinser D (1989) The hematopoietic stem cell compartments in mice during and after long-term inhalation of three doses of benzene. Exp Hematol 17(3):300–303
Sturgeon CM, Chicha L, Ditadi A et al (2012) Primitive erythropoiesis is regulated by miR-126 via nonhematopoietic Vcam-1 + cells. Dev Cell 23(1):45–57. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2012.05.021
Su R, Gong JN, Chen MT et al (2016) c-Myc suppresses miR-451⊣YWTAZ/AKT axis via recruiting HDAC3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 7(47):77430–77443
Svasti S, Masaki S, Penglong T et al (2010) Expression of microRNA-451 in normal and thalassemic erythropoiesis. Ann Hematol 89(10):953–958. doi:10.1007/s00277-010-0980-7
Tang KY, Yu CH, Jiang L et al (2016) Long-term exposure of K562 cells to benzene metabolites inhibited erythroid differentiation and elevated methylation in erythroid specific genes. Toxicol Res 5(5):1284–1297. doi:10.1039/c6tx00143b
Tsai CY, Wang CC, Lai TY et al (2013) Antioxidant effects of diallyl trisulfide on high glucose-induced apoptosis are mediated by the PI3 K/Akt-dependent activation of Nrf2 in cardiomyocytes. Int J Cardiol 168(2):1286–1297. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.12.004
Vacha J, Znojil V, Seidel HJ, Barthel E (1990) Ferrokinetics and erythropoiesis in mice after long-term inhalation of benzene. Blut 60(1):41–47
Vermeulen R, Li G, Lan Q et al (2004) Detailed exposure assessment for a molecular epidemiology study of benzene in two shoe factories in China. Ann Occup Hyg 48(2):105–116
Vian L, Di Carlo M, Pelosi E et al (2014) Transcriptional fine-tuning of microRNA-223 levels directs lineage choice of human hematopoietic progenitors. Cell Death Differ 21(2):290–301. doi:10.1038/cdd.2013.145
Wang LS, Li L, Li L et al (2015) MicroRNA-486 regulates normal erythropoiesis and enhances growth and modulates drug response in CML progenitors. Blood 125(8):1302–1313. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-06-581926
Wei H, Zhang J, Tan K, Sun R, Yin L, Pu Y (2015) Benzene-induced aberrant miRNA expression profile in hematopoietic progenitor cells in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Mol Sci 16(11):27058–27071. doi:10.3390/ijms161126001
Wu XR, Xue M, Li XF et al (2011) Phenolic metabolites of benzene inhibited the erythroid differentiation of K562 cells. Toxicol Lett 203(3):190–199. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.03.012
Yang GH, Wang F, Yu J, Wang XS, Yuan JY, Zhang JW (2009) MicroRNAs are involved in erythroid differentiation control. J Cell Biochem 107(3):548–556. doi:10.1002/jcb.22156
Yi Z, Wang Z, Li H, Liu M (2004) Inhibitory effect of tellimagrandin I on chemically induced differentiation of human leukemia K562 cells. Toxicol Lett 147(2):109–119
Yu D, dos Santos CO, Zhao G et al (2010) miR-451 protects against erythroid oxidant stress by repressing 14-3-3zeta. Genes Dev 24(15):1620–1633. doi:10.1101/gad.1942110
Yuan W, Sun Q, Jiang Y et al (2016) MiR-146a affects the alteration in myeloid differentiation induced by hydroquinone in human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and HL-60 cells. Toxicol Res 5(3):848–858
Zhu Y, Wang DS, Wang F et al (2013) A comprehensive analysis of GATA-1-regulated miRNAs reveals miR-23a to be a positive modulator of erythropoiesis. Nucleic Acids Res 41(7):4129–4143. doi:10.1093/Nar/Gkt093
Ziegler B, Testa U, Condorelli G, Vitelli L, Valtieri M, Peschle C (1998) Unilineage hematopoietic differentiation in bulk and single cell culture. Stem Cells 16(Suppl 1):51–73. doi:10.1002/stem.5530160808
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81430079), regular National Natural Science Foundation of China (81372962, 81402658, 81273099, and 81273116) and National Key Technology Research and Development Program (2014BAI12B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All human and animal studies were approved by the appropriate ethics committees. All procedures performed in the studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. All patients and workers gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, B., Chen, Y., Yuan, W. et al. Down-regulation of miRNA-451a and miRNA-486-5p involved in benzene-induced inhibition on erythroid cell differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol 92, 259–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2033-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2033-7