Abstract
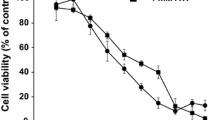
Inorganic arsenic is well known as a carcinogen in human beings. Chronic exposure to inorganic arsenic increases risks of developing some cancers and non-carcinogenic diseases, such as skin lesions in humans. However, the modes of action are not well elucidated. In the present study, HaCaT cells, an immortalized non-tumorigenic human keratinocyte, were continuously exposed to low-dose trivalent arsenic (arsenic trioxide, 0.1 and 0.2 μM) for at least 4 weeks. We proved that low-dose arsenic could stimulate malignant transformation of HaCaT cells, including increase of cellular proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers alteration, matrix metalloproteinases activation, invadopodia formation, migration/invasion activities, and anchorage-independent growth. Surprisingly, low-dose arsenic could also transcriptionally increase TG-interacting factor (TGIF) expression via c-Src/EGFR/AKT/FOXO3A signaling involving superoxide production from NADPH oxidase. Moreover, stable overexpression of TGIF could also induce malignant transformation of HaCaT cells. Knockdown of TGIF with its specific shRNA abolished the arsenic-induced effects. Taken together, we suggest that TGIF plays an important role in low-dose arsenic-induced malignant transformation of HaCaT cells, which is regulated by c-Src/EGFR/AKT/FOXO3A pathway and redox signaling.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy CO, Liu YP, Longfellow D et al (1999) Arsenic: health effects, mechanisms of actions, and research issues. Environ Health Perspect 107(7):593–597
Bi X, Gu J, Guo Z et al (2010) Different pathways are involved in arsenic-trioxide-induced cell proliferation and growth inhibition in human keratinocytes. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 23(2):68–78
Biscardi JS, Maa MC, Tice DA, Cox ME, Leu TH, Parsons SJ (1999) c-Src-mediated phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor on Tyr845 and Tyr1101 is associated with modulation of receptor function. J Biol Chem 274(12):8335–8343
Boerner JL, Demory ML, Silva C, Parsons SJ (2004) Phosphorylation of Y845 on the epidermal growth factor receptor mediates binding to the mitochondrial protein cytochrome c oxidase subunit II. Mol Cell Biol 24(16):7059–7071
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE (1988) Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol 106(3):761–771
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296(5573):1655–1657
Chen CJ, Wang SL, Chiou JM et al (2007) Arsenic and diabetes and hypertension in human populations: a review. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222(3):298–304
Chien CW, Chiang MC, Ho IC, Lee TC (2004) Association of chromosomal alterations with arsenite-induced tumorigenicity of human HaCaT keratinocytes in nude mice. Environ Health Perspect 112(17):1704–1710
Cuzick J, Evans S, Gillman M, Price Evans DA (1982) Medicinal arsenic and internal malignancies. Br J Cancer 45(6):904–911
Demory ML, Boerner JL, Davidson R et al (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor translocation to the mitochondria: regulation and effect. J Biol Chem 284(52):36592–36604
Flora SJ (2011) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radic Biol Med 51(2):257–281
Hamann I, Klotz LO (2013) Arsenite-induced stress signaling: modulation of the phosphoinositide 3′-kinase/Akt/FoxO signaling cascade. Redox Biol 1(1):104–109
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ (1993) The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 75(4):805–816
Huang HS, Chang WC, Chen CJ (2002) Involvement of reactive oxygen species in arsenite-induced downregulation of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 33(6):864–873
Huang HS, Liu ZM, Ding L et al (2006) Opposite effect of ERK1/2 and JNK on p53-independent p21WAF1/CIP1 activation involved in the arsenic trioxide-induced human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cellular cytotoxicity. J Biomed Sci 13(1):113–125
Huang HS, Liu ZM, Hong DY (2010) Blockage of JNK pathway enhances arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244(2):234–241
Huang HS, Liu ZM, Cheng YL (2011) Involvement of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in arsenic trioxide-induced p21 expression. Toxicol Sci 121(1):101–109
Huang HS, Liu ZM, Chen PC, Tseng HY, Yeh BW (2012) TG-interacting factor-induced superoxide production from NADPH oxidase contributes to the migration/invasion of urothelial carcinoma. Free Radic Biol Med 53(4):769–778
Hughes MF, Beck BD, Chen Y, Lewis AS, Thomas DJ (2011) Arsenic exposure and toxicology: a historical perspective. Toxicol Sci 123(2):305–332
Hwang BJ, Utti C, Steinberg M (2006) Induction of cyclin D1 by submicromolar concentrations of arsenite in human epidermal keratinocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217(2):161–167
Koedrith P, Seo YR (2011) Advances in carcinogenic metal toxicity and potential molecular markers. Int J Mol Sci 12(12):9576–9595
Li Y, Jiang R, Zhao Y et al (2012) Opposed arsenite-mediated regulation of p53-survivin is involved in neoplastic transformation, DNA damage, or apoptosis in human keratinocytes. Toxicology 300(3):121–131
Liao WT, Chang KL, Yu CL, Chen GS, Chang LW, Yu HS (2004) Arsenic induces human keratinocyte apoptosis by the FAS/FAS ligand pathway, which correlates with alterations in nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein-1 activity. J Invest Dermatol 122(1):125–129
Lin HK, Bergmann S, Pandolfi PP (2004) Cytoplasmic PML function in TGF-beta signalling. Nature 431(7005):205–211
Liu ZM, Huang HS (2006) As2O3-induced c-Src/EGFR/ERK signaling is via Sp1 binding sites to stimulate p21WAF1/CIP1 expression in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Cell Signal 18(2):244–255
Liu ZM, Huang HS (2008a) Arsenic trioxide phosphorylates c-Fos to transactivate p21WAF1/CIP1 expression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 233(2):297–307
Liu ZM, Huang HS (2008b) Inhibitory role of TGIF in the As2O3-regulated p21WAF1/CIP1 expression. J Biomed Sci 15(3):333–342
Liu B, Pan S, Dong X et al (2006) Opposing effects of arsenic trioxide on hepatocellular carcinomas in mice. Cancer Sci 97(7):675–681
Liu ZM, Tseng JT, Hong DY, Huang HS (2011) Suppression of TG-interacting factor sensitizes arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem J 438:349–358
Lo RS, Wotton D, Massague J (2001) Epidermal growth factor signaling via Ras controls the Smad transcriptional co-repressor TGIF. EMBO J 20(1–2):128–136
Massague J (2004) G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature 432(7015):298–306
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer J, Waxman S (2002) Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res 62(14):3893–3903
Murphy DA, Courtneidge SA (2011) The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of podosomes and invadopodia: characteristics, formation and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(7):413–426
Myatt SS, Lam EW (2007) The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(11):847–859
Ouyang W, Luo W, Zhang D et al (2008) PI-3K/Akt pathway-dependent cyclin D1 expression is responsible for arsenite-induced human keratinocyte transformation. Environ Health Perspect 116(1):1–6
Pettersson HM, Karlsson J, Pietras A, Ora I, Pahlman S (2007) Arsenic trioxide and neuroblastoma cytotoxicity. J Bioenerg Biomembr 39(1):35–41
Pi J, Diwan BA, Sun Y et al (2008) Arsenic-induced malignant transformation of human keratinocytes: involvement of Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med 45(5):651–658
Platanias LC (2009) Biological responses to arsenic compounds. J Biol Chem 284(28):18583–18587
Ren X, McHale CM, Skibola CF, Smith AH, Smith MT, Zhang L (2011) An emerging role for epigenetic dysregulation in arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect 119(1):11–19
Seo SR, Lallemand F, Ferrand N et al (2004) The novel E3 ubiquitin ligase Tiul1 associates with TGIF to target Smad2 for degradation. EMBO J 23(19):3780–3792
Seo SR, Ferrand N, Faresse N et al (2006) Nuclear retention of the tumor suppressor cPML by the homeodomain protein TGIF restricts TGF-beta signaling. Mol Cell 23(4):547–559
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13(12):1501–1512
Simeonova PP, Luster MI (2002) Arsenic carcinogenicity: relevance of c-Src activation. Mol Cell Biochem 234–235(1–2):277–282
Soucy NV, Ihnat MA, Kamat CD et al (2003) Arsenic stimulates angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in vivo. Toxicol Sci 76(2):271–279
Straub AC, Stolz DB, Vin H et al (2007) Low level arsenic promotes progressive inflammatory angiogenesis and liver blood vessel remodeling in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222(3):327–336
Stueckle TA, Lu Y, Davis ME et al (2012) Chronic occupational exposure to arsenic induces carcinogenic gene signaling networks and neoplastic transformation in human lung epithelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 261(2):204–216
Takahashi H, Ibe M, Nakamura S, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Hashimoto Y, Iizuka H (2002) Extracellular regulated kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase are activated in psoriatic involved epidermis. J Dermatol Sci 30(2):94–99
Tokar EJ, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Ward JM, Lunn R, Sams RL 2nd, Waalkes MP (2010) Cancer in experimental animals exposed to arsenic and arsenic compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol 40(10):912–927
Tokar EJ, Qu W, Waalkes MP (2011) Arsenic, stem cells, and the developmental basis of adult cancer. Toxicol Sci 120:S192–S203
Tse WP, Cheng CH, Che CT, Lin ZX (2008) Arsenic trioxide, arsenic pentoxide, and arsenic iodide inhibit human keratinocyte proliferation through the induction of apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326(2):388–394
Tse WP, Cheng CH, Che CT, Zhao M, Fan RQ, Lin ZX (2009) Realgar-mediated growth inhibition on HaCaT human keratinocytes is associated with induction of apoptosis. Int J Mol Med 24(2):189–196
Tseng HY, Liu ZM, Huang HS (2012) NADPH oxidase-produced superoxide mediates EGFR transactivation by c-Src in arsenic trioxide-stimulated human keratinocytes. Arch Toxicol 86(6):935–945
Wang CH, Hsiao CK, Chen CL et al (2007) A review of the epidemiologic literature on the role of environmental arsenic exposure and cardiovascular diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222(3):315–326
Wang Z, Yang J, Fisher T, Xiao H, Jiang Y, Yang C (2012) Akt activation is responsible for enhanced migratory and invasive behavior of arsenic-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Environ Health Perspect 120(1):92–97
Wen G, Calaf GM, Partridge MA et al (2008) Neoplastic transformation of human small airway epithelial cells induced by arsenic. Mol Med 14(1–2):2–10
Wotton D, Knoepfler PS, Laherty CD, Eisenman RN, Massague J (2001) The Smad transcriptional corepressor TGIF recruits mSin3. Cell Growth Differ 12(9):457–463
Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell 14(6):818–829
Yeh BW, Wu WJ, Li WM et al (2012) Overexpression of TG-interacting factor is associated with worse prognosis in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Am J Pathol 181(3):1044–1055
Yilmaz M, Christofori G (2009) EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(1–2):15–33
Yu HS, Liao WT, Chai CY (2006) Arsenic carcinogenesis in the skin. J Biomed Sci 13(5):657–666
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants from the National Science Council (Taipei, Taiwan; NSC98-2320-B-006-008-MY3; NSC101-2320-B-006-034; NSC102-2320-B-006-017) and by a Grant from Health and Welfare surcharge of tobacco products, Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW103-TD-B-111-05).
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
204_2014_1445_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. S1 Low-dose ATO increased cellular migration abilities of NIH3T3. NIH3T3 fibroblasts were pretreated with various doses or ATO for 48 h as indicated, then the cellular migration abilities were analyzed by migration assay as described in “Materials and methods” (PDF 80 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZM., Tseng, HY., Yeh, BW. et al. TG-interacting factor mediates arsenic-induced malignant transformation of keratinocytes via c-Src/EGFR/AKT/FOXO3A and redox signalings. Arch Toxicol 89, 2229–2241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1445-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1445-x