Abstract
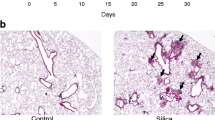
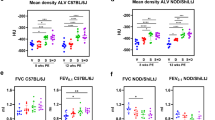
Current epidemiological studies suggest that crystalline silica exposure is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular and renal disease; however, the potential pathological damage of the heart and kidney and its underlying mechanisms have not been completely elucidated. This study tried to investigate the silica-induced inflammatory and fibrotic changes in the heart and kidney and evaluate the role of interleukin (IL)-1 beta (β) in silica-induced cardiac and renal damage. In this study, a silica-exposed model was generated by intratracheally instilling silica dust in mice. The anti-IL-1β monoclonal antibody (mAb) was used to neutralise IL-1β in the pulmonary alveolus and serum. The real-time PCR studies showed that (1) inhalational silica induced inflammatory responses in the heart and kidney by elevated mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and MCP-1; (2) early fibrotic responses in the heart were observed as elevated mRNA levels of collagen I and fibronectin. What is more, fibrosis of the kidney was demonstrated by pathological results and significantly increased mRNA levels of TGF-β, collagen I, collagen III and fibronectin. Further studies showed that usage of anti-IL-1β mAb decreased the inflammatory response of the heart and kidney induced by inhalational silica and also attenuated fibrosis in the mouse kidney. In conclusion, this study found that inhaled silica induced inflammatory and early fibrotic responses in the mouse heart and inflammatory response and fibrosis in the mouse kidney. Neutralisation of IL-1β attenuated the silica-induced inflammatory response of the heart and kidney and decreased fibrosis in the mouse kidney.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bickel C, Rupprecht HJ, Blankenberg S, Espiniola-Klein C, Schlitt A, Rippin G, Hafner G, Treude R, Othman H, Hofmann KP, Meyer J (2002) Relation of markers of inflammation (C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, and leukocyte count) and statin therapy to long-term mortality in patients with angiographically proven coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 89:901–908
Boor P, Casper S, Celec P, Hurbankova M, Beno M, Heidland A, Amann K, Sebekova K (2009) Renal, vascular and cardiac fibrosis in rats exposed to passive smoking and industrial dust fibre amosite. J Cell Mol Med 13:4484–4491
Cassel SL, Eisenbarth SC, Iyer SS, Sadler JJ, Colegio OR, Tephly LA, Carter AB, Rothman PB, Flavell RA, Sutterwala FS (2008) The Nalp3 inflammasome is essential for the development of silicosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9035–9040
Chen W, Liu Y, Wang H, Hnizdo E, Sun Y, Su L, Zhang X, Weng S, Bochmann F, Hearl FJ, Chen J, Wu T (2012) Long-term exposure to silica dust and risk of total and cause-specific mortality in Chinese workers: a cohort study. PLoS Med 9:e1001206
Cheng W, Rong Y, Shi T, Zhou T, Liu Y, Chen W (2014) Size-dependent biological effects on vascular endothelial cells induced by different particulate matters. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci] 34:314–321
Cho WS, Choi M, Han BS, Cho M, Oh J, Park K, Kim SJ, Kim SH, Jeong J (2007) Inflammatory mediators induced by intratracheal instillation of ultrafine amorphous silica particles. Toxicol Lett 175:24–33
Dinarello CA, Donath MY, Mandrup-Poulsen T (2010) Role of IL-1beta in type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:314–321
Dostert C, Petrilli V, Van Bruggen R, Steele C, Mossman BT, Tschopp J (2008) Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 320:674–677
Du Z, Zhao D, Jing L, Cui G, Jin M, Li Y, Liu X, Liu Y, Du H, Guo C, Zhou X, Sun Z (2013) Cardiovascular toxicity of different sizes amorphous silica nanoparticles in rats after intratracheal instillation. Cardiovasc Toxicol 13:194–207
Gluba A, Bielecka A, Mikhailidis DP, Wong ND, Franklin SS, Rysz J, Banach M (2012) An update on biomarkers of heart failure in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 30:1681–1689
Gui S, Zhang Z, Zheng L, Cui Y, Liu X, Li N, Sang X, Sun Q, Gao G, Cheng Z, Cheng J, Wang L, Tang M, Hong F (2011) Molecular mechanism of kidney injury of mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 195:365–370
Guo J, Gu N, Chen J, Shi T, Zhou Y, Rong Y, Zhou T, Yang W, Cui X, Chen W (2013) Neutralization of interleukin-1 beta attenuates silica-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice. Arch Toxicol 87:1963–1973
Huaux F (2007) New developments in the understanding of immunology in silicosis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 7:168–173
Jia X, Liu B, Shi X, Ye M, Zhang F, Liu H (2011) Roles of the ERK, JNK/AP-1/cyclin D1-CDK4 pathway in silica-induced cell cycle changes in human embryo lung fibroblast cells. Cell Biol Int 35:697–704
Kubota T, McTiernan CF, Frye CS, Slawson SE, Lemster BH, Koretsky AP, Demetris AJ, Feldman AM (1997) Dilated cardiomyopathy in transgenic mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ Res 81:627–635
Landen DD, Wassell JT, McWilliams L, Patel A (2011) Coal dust exposure and mortality from ischemic heart disease among a cohort of U.S. coal miners. Am J Ind Med 54:727–733
Leung CC, Yu IT, Chen W (2012) Silicosis. Lancet 379:2008–2018
Liu Y (2006) Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int 69:213–217
Liu F, Liu J, Weng D, Chen Y, Song L, He Q, Chen J (2010) CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells depletion may attenuate the development of silica-induced lung fibrosis in mice. PLoS One 5:e15404
Liu L, Kou P, Zeng Q, Pei G, Li Y, Liang H, Xu G, Chen S (2012a) CD4 + T Lymphocytes, especially Th2 cells, contribute to the progress of renal fibrosis. Am J Nephrol 36:386–396
Liu X, Xue Y, Ding T, Sun J (2012b) Enhancement of proinflammatory and procoagulant responses to silica particles by monocyte–endothelial cell interactions. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:36
Liu Y, Steenland K, Rong Y, Hnizdo E, Huang X, Zhang H, Shi T, Sun Y, Wu T, Chen W (2013) Exposure-response analysis and risk assessment for lung cancer in relationship to silica exposure: a 44-year cohort study of 34,018 workers. Am J Epidemiol 178:1424–1433
Mann DL (2002) Inflammatory mediators and the failing heart: past, present, and the foreseeable future. Circ Res 91:988–998
Medugorac I, Jacob R (1983) Characterisation of left ventricular collagen in the rat. Cardiovasc Res 17:15–21
Mendall MA, Patel P, Asante M, Ballam L, Morris J, Strachan DP, Camm AJ, Northfield TC (1997) Relation of serum cytokine concentrations to cardiovascular risk factors and coronary heart disease. Heart 78:273–277
Morozova OA (2012) Gender differences in death causes and survival rate of silicosis patients. Med Tr Prom Ekol 9:32–36
Nemmar A, Vanbilloen H, Hoylaerts MF, Hoet PH, Verbruggen A, Nemery B (2001) Passage of intratracheally instilled ultrafine particles from the lung into the systemic circulation in hamster. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1665–1668
Olsen GW, Andres KL, Johnson RA, Buehrer BD, Holen BM, Morey SZ, Logan PW, Hewett P (2012) Cohort mortality study of roofing granule mine and mill workers. Part II. Epidemiologic analysis, 1945–2004. J Occup Environ Hyg 9:257–268
Passagne I, Morille M, Rousset M, Pujalte I, L’Azou B (2012) Implication of oxidative stress in size-dependent toxicity of silica nanoparticles in kidney cells. Toxicology 299:112–124
Rimal B, Greenberg AK, Rom WN (2005) Basic pathogenetic mechanisms in silicosis: current understanding. Curr Opin Pulm Med 11:169–173
Schindler R, Clark BD, Dinarello CA (1990) Dissociation between interleukin-1 beta mRNA and protein synthesis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Biol Chem 265:10232–10237
Schnaper HW, Hayashida T, Hubchak SC, Poncelet AC (2003) TGF-beta signal transduction and mesangial cell fibrogenesis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F243–F252
Seaton A, MacNee W, Donaldson K, Godden D (1995) Particulate air pollution and acute health effects. Lancet 345:176–178
Seta Y, Shan K, Bozkurt B, Oral H, Mann DL (1996) Basic mechanisms in heart failure: the cytokine hypothesis. J Card Fail 2:243–249
Shao DD, Suresh R, Vakil V, Gomer RH, Pilling D (2008) Pivotal advance: Th-1 cytokines inhibit, and Th-2 cytokines promote fibrocyte differentiation. J Leukoc Biol 83:1323–1333
Shen F, Fan X, Liu B, Jia X, Du H, You B, Ye M, Huang C, Shi X (2006) Overexpression of cyclin D1-CDK4 in silica-induced transformed cells is due to activation of ERKs, JNKs/AP-1 pathway. Toxicol Lett 160:185–195
Steenland K, Ward E (2014) Silica: a lung carcinogen. CA Cancer J Clin 64:63–69
Sun YB, Qu X, Li X, David JN, Li J (2013) Endothelial dysfunction exacerbates renal interstitial fibrosis through enhancing fibroblast Smad3 linker phosphorylation in the mouse obstructed kidney. PLoS One 8:e84063
Testa M, Yeh M, Lee P, Fanelli R, Loperfido F, Berman JW, LeJemtel TH (1996) Circulating levels of cytokines and their endogenous modulators in patients with mild to severe congestive heart failure due to coronary artery disease or hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:964–971
Vupputuri S, Parks CG, Nylander-French LA, Owen-Smith A, Hogan SL, Sandler DP (2012) Occupational silica exposure and chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail 34:40–46
Wang Y, Cao Q, Zheng G, Lee VW, Zheng D, Li X, Tan TK, Harris DC (2008) By homing to the kidney, activated macrophages potently exacerbate renal injury. Am J Pathol 172:1491–1499
Weber KT, Janicki JS, Shroff SG, Pick R, Chen RM, Bashey RI (1988) Collagen remodeling of the pressure-overloaded, hypertrophied nonhuman primate myocardium. Circ Res 62:757–765
Zhou T, Rong Y, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Guo J, Cheng W, Wang H, Chen W (2012) Association between proinflammatory responses of respirable silica dust and adverse health effects among dust-exposed workers. J Occup Environ Med 54:459–465
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Grants from National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB503804) and the National Natural Science Foundations of China (81372967 and 81402657). We are indebted to Dr. Paul Borm at the Zuyd University in the Netherlands for providing valuable suggestions and comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jiali Guo and Tingming Shi have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Shi, T., Cui, X. et al. Effects of silica exposure on the cardiac and renal inflammatory and fibrotic response and the antagonistic role of interleukin-1 beta in C57BL/6 mice. Arch Toxicol 90, 247–258 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1405-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1405-5