Abstract
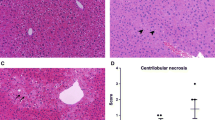
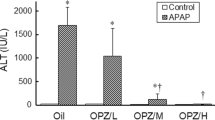
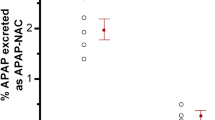
N-acetyl-meta-aminophenol (AMAP) is generally considered as a non-toxic regioisomer of the well-known hepatotoxicant acetaminophen (APAP). However, so far, AMAP has only been shown to be non-toxic in mice and hamsters. To investigate whether AMAP could also be used as non-toxic analog of APAP in rat and human, the toxicity of APAP and AMAP was tested ex vivo in precision-cut liver slices (PCLS) of mouse, rat and human. Based on ATP content and histomorphology, APAP was more toxic in mouse than in rat and human PCLS. Surprisingly, although AMAP showed a much lower toxicity than APAP in mouse PCLS, AMAP was equally toxic as or even more toxic than APAP at all concentrations tested in both rat and human PCLS. The profile of proteins released into the medium of AMAP-treated rat PCLS was similar to that of APAP, whereas in the medium of mouse PCLS, it was similar to the control. Metabolite profiling indicated that mouse PCLS produced the highest amount of glutathione conjugate of APAP, while no glutathione conjugate of AMAP was detected in all three species. Mouse also produced ten times more hydroquinone metabolites of AMAP, the assumed proximate reactive metabolites, than rat or human. In conclusion, AMAP is toxic in rat and human liver and cannot be used as non-toxic isomer of APAP. The marked species differences in APAP and AMAP toxicity and metabolism underline the importance of using human tissues for better prediction of toxicity in man.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albano E, Rundgren M, Harvison PJ, Nelson SD, Moldeus P (1985) Mechanisms of N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine cytotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol 28:306–311
Boess F, Kamber M, Romer S, Gasser R, Muller D, Albertini S, Suter L (2003) Gene expression in two hepatic cell lines, cultured primary hepatocytes, and liver slices compared to the in vivo liver gene expression in rats: possible implications for toxicogenomics use of in vitro systems. Toxicol Sci 73:386–402
Copple IM, Goldring CE, Jenkins RE, Chia AJ, Randle LE, Hayes JD, Kitteringham NR, Park BK (2008) The hepatotoxic metabolite of acetaminophen directly activates the Keap1-Nrf2 cell defense system. Hepatology 48:1292–1301
Cummings AJ, King ML, Martin BK (1967) A kinetic study of drug elimination: the excretion of paracetamol and its metabolites in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 29:150–157
Dalmadi B, Leibinger J, Szeberenyi S, Borbas T, Farkas S, Szombathelyi Z, Tihanyi K (2003) Identification of metabolic pathways involved in the biotransformation of tolperisone by human microsomal enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos 31:631–636
de Graaf IA, van der Voort D, Brits JH, Koster HJ (2000) Increased post-thaw viability and phase I and II biotransformation activity in cryopreserved rat liver slices after improvement of a fast-freezing method. Drug Metab Dispos 28:1100–1106
De Graaf IA, Van Meijeren CE, Pektas F, Koster HJ (2002) Comparison of in vitro preparations for semi-quantitative prediction of in vivo drug metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos 30:1129–1136
de Graaf IA, Olinga P, de Jager MH, Merema MT, de Kanter R, van de Kerkhof EG, Groothuis GM (2010) Preparation and incubation of precision-cut liver and intestinal slices for application in drug metabolism and toxicity studies. Nat Protoc 5:1540–1551
Dragovic S, Boerma JS, van Bergen L, Vermeulen NP, Commandeur JN (2010) Role of human glutathione S-transferases in the inactivation of reactive metabolites of clozapine. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1467–1476
Elferink MG, Olinga P, Draaisma AL, Merema MT, Bauerschmidt S, Polman J, Schoonen WG, Groothuis GM (2008) Microarray analysis in rat liver slices correctly predicts in vivo hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 229:300–309
Elferink MG, Olinga P, van Leeuwen EM, Bauerschmidt S, Polman J, Schoonen WG, Heisterkamp SH, Groothuis GM (2011) Gene expression analysis of precision-cut human liver slices indicates stable expression of ADME-Tox related genes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 253:57–69
Evdokimova E, Taper H, Buc Calderon P (2001) Role of ATP and glycogen reserves in both paracetamol sulfation and glucuronidation by cultured precision-cut rat liver slices. Toxicol In Vitro 15:683–690
Ferrero JL, Brendel K (1997) Liver slices as a model in drug metabolism. Adv Pharmacol 43:131–169
Fiedler GM, Baumann S, Leichtle A, Oltmann A, Kase J, Thiery J, Ceglarek U (2007) Standardized peptidome profiling of human urine by magnetic bead separation and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 53:421–428
Fountoulakis M, Berndt P, Boelsterli UA, Crameri F, Winter M, Albertini S, Suter L (2000) Two-dimensional database of mouse liver proteins: changes in hepatic protein levels following treatment with acetaminophen or its nontoxic regioisomer 3-acetamidophenol. Electrophoresis 21:2148–2161
Goldring CE, Kitteringham NR, Elsby R, Randle LE, Clement YN, Williams DP, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Park BK (2004) Activation of hepatic Nrf2 in vivo by acetaminophen in CD-1 mice. Hepatology 39:1267–1276
Graaf IA, Groothuis GM, Olinga P (2007) Precision-cut tissue slices as a tool to predict metabolism of novel drugs. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 3:879–898
Halmes NC, Samokyszyn VM, Hinton TW, Hinson JA, Pumford NR (1998) The acetaminophen regioisomer 3′-hydroxyacetanilide inhibits and covalently binds to cytochrome P450 2E1. Toxicol Lett 94:65–71
Holme JA, Hongslo JK, Bjorge C, Nelson SD (1991) Comparative cytotoxic effects of acetaminophen (N-acetyl-p-aminophenol), a non-hepatotoxic regioisomer acetyl-m-aminophenol and their postulated reactive hydroquinone and quinone metabolites in monolayer cultures of mouse hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 42:1137–1142
Howie D, Adriaenssens PI, Prescott LF (1977) Paracetamol metabolism following overdosage: application of high performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Pharmacol 29:235–237
Jemnitz K, Veres Z, Monostory K, Kobori L, Vereczkey L (2008) Interspecies differences in acetaminophen sensitivity of human, rat, and mouse primary hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 22:961–967
Ju C, Reilly TP, Bourdi M, Radonovich MF, Brady JN, George JW, Pohl LR (2002) Protective role of Kupffer cells in acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury in mice. Chem Res Toxicol 15:1504–1513
Kenneke JF, Mazur CS, Ritger SE, Sack TJ (2008) Mechanistic investigation of the noncytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of triadimefon to triadimenol in hepatic microsomes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1997–2004
Lerche-Langrand C, Toutain HJ (2000) Precision-cut liver slices: characteristics and use for in vitro pharmaco-toxicology. Toxicology 153:221–253
Matthews AM, Hinson JA, Roberts DW, Pumford NR (1997) Comparison of covalent binding of acetaminophen and the regioisomer 3′-hydroxyacetanilide to mouse liver protein. Toxicol Lett 90:77–82
McGill MR, Yan HM, Ramachandran A, Murray GJ, Rollins DE, Jaeschke H (2011) HepaRG cells: a human model to study mechanisms of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 53:974–982
McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Williams CD, Taha M, Curry SC, Jaeschke H (2012) The mechanism underlying acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Clin Invest 122(4):1574–1583
Michael SL, Pumford NR, Mayeux PR, Niesman MR, Hinson JA (1999) Pretreatment of mice with macrophage inactivators decreases acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and the formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Hepatology 30:186–195
Nelson EB (1980) The pharmacology and toxicology of meta-substituted acetanilide I: acute toxicity of 3-hydroxyacetanilide in mice. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 28:447–456
Newton JF, Hoefle D, Gemborys MW, Mudge GH, Hook JB (1986) Metabolism and excretion of a glutathione conjugate of acetaminophen in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:519–524
Neyrinck A, Eeckhoudt SL, Meunier CJ, Pampfer S, Taper HS, Verbeeck RK, Delzenne N (1999) Modulation of paracetamol metabolism by Kupffer cells: a study on rat liver slices. Life Sci 65:2851–2859
Olinga P, Meijer DK, Slooff MJ, Groothuis GM (1997) Liver slices in in vitro pharmacotoxicology with special reference to the use of human liver tissue. Toxicol In Vitro 12:77–100
Olson H, Betton G, Robinson D, Thomas K, Monro A, Kolaja G, Lilly P, Sanders J, Sipes G, Bracken W, Dorato M, Van Deun K, Smith P, Berger B, Heller A (2000) Concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in humans and in animals. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 32:56–67
Pumford NR, Halmes NC (1997) Protein targets of xenobiotic reactive intermediates. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:91–117
Pumford NR, Hinson JA, Benson RW, Roberts DW (1990) Immunoblot analysis of protein containing 3-(cystein-S-yl)acetaminophen adducts in serum and subcellular liver fractions from acetaminophen-treated mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 104:521–532
Rashed MS, Nelson SD (1989) Characterization of glutathione conjugates of reactive metabolites of 3′-hydroxyacetanilide, a nonhepatotoxic positional isomer of acetaminophen. Chem Res Toxicol 2:41–45
Rashed MS, Myers TG, Nelson SD (1990) Hepatic protein arylation, glutathione depletion, and metabolite profiles of acetaminophen and a non-hepatotoxic regioisomer, 3′-hydroxyacetanilide, in the mouse. Drug Metab Dispos 18:765–770
Roberts SA, Price VF, Jollow DJ (1990) Acetaminophen structure-toxicity studies: in vivo covalent binding of a nonhepatotoxic analog, 3-hydroxyacetanilide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 105:195–208
Smith SW, Howland MA, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS (2008) Acetaminophen overdose with altered acetaminophen pharmacokinetics and hepatotoxicity associated with premature cessation of intravenous N-acetylcysteine therapy. Ann Pharmacother 42:1333–1339
Stamper BD, Bammler TK, Beyer RP, Farin FM, Nelson SD (2010) Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by acetaminophen and its nonhepatotoxic regioisomer 3′-hydroxyacetanilide in TAMH cells. Toxicol Sci 116:164–173
Sun Q, Harper TW, Dierks EA, Zhang L, Chang S, Rodrigues AD, Marathe P (2011) 1-Aminobenzotriazole, a known cytochrome P450 inhibitor, is a substrate and inhibitor of N-acetyltransferase. Drug Metab Dispos 39:1674–1679
Tirmenstein MA, Nelson SD (1989) Subcellular binding and effects on calcium homeostasis produced by acetaminophen and a nonhepatotoxic regioisomer, 3′-hydroxyacetanilide, in mouse liver. J Biol Chem 264:9814–9819
Tirmenstein MA, Nelson SD (1991) Hepatotoxicity after 3′-hydroxyacetanilide administration to buthionine sulfoximine pretreated mice. Chem Res Toxicol 4:214–217
van Midwoud PM, Janssen J, Merema MT, de Graaf IA, Groothuis GM, Verpoorte E (2011) On-line HPLC analysis system for metabolism and inhibition studies in precision-cut liver slices. Anal Chem 83:84–91
Vickers AE, Fisher RL (2004) Organ slices for the evaluation of human drug toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 150:87–96
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Dutch Top Institute Pharma, project D3-201-1 (Towards novel translational safety biomarkers for adverse drug toxicity). The authors would like to thank Dr. Inge de Graaf for making the microscopic images and scoring all the histomorphology data. We also thank Coby Laarakkers and Dr. Roos Masereeuw for providing valuable assistance and discussion in generating the protein profiling data. The authors are very grateful to Prof. Robert Porte (Dept. Surgery, UMCG) for providing human liver samples and Dr.ir. Arjen Lommen for providing APAP-glucuronide, APAP-sulfate and APAP-GSH standard solutions. Dr. Kevin Augustijn is also thanked for his help in managing this collaborative project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadi, M., Dragovic, S., van Swelm, R. et al. AMAP, the alleged non-toxic isomer of acetaminophen, is toxic in rat and human liver. Arch Toxicol 87, 155–165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0924-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0924-1