Abstract
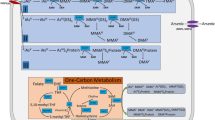
Human exposure to arsenicals is associated with inflammatory-related diseases including different kinds of cancer as well as non-cancerous diseases like neuro-degenerative diseases, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes. Interindividual susceptibility has been mainly addressed by evaluating the role of genetic polymorphism in metabolic enzymes in inorganic arsenic (iAs) metabolism. Glutathione S-transferase omega 1-1 (GSTO1-1), which had been associated with iAs metabolism, is also known to participate in inflammatory and apoptotic cellular responses. The polymorphism A140D of GSTO1-1 has been not only associated with distinct urinary profile of arsenic metabolites in populations chronically exposed to iAs in drinking water, but also with higher risk of childhood leukemia and lung disease in non-exposed populations, suggesting that GSTO1-1 involvement in other physiologic processes different from toxics metabolism could be more relevant than is thought. We evaluated the association of the presence of A140D and E208K polymorphisms of GSTO1-1 gene with the expression of genes codifying for proteins involved in the inflammatory and apoptotic response in a human population chronically exposed to iAs through drinking water. A140D polymorphism was associated with higher expression of genes codifying for IL-8 and Apaf-1 mainly in heterozygous individuals, while E208K was associated with higher expression of IL-8 and TGF-β gene, in both cases, the association was independently of iAs exposure level; however, the exposure to iAs increased slightly but significantly the influence of A140D and E208K polymorphisms on such genes expression. These results suggest an important role of GSTO1-1 in the inflammatory response and the apoptotic process and indicate that A140D and E208K polymorphisms could increase the risk of developing inflammatory and apoptosis-related diseases in As-exposed populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Bañuelos P, Escudero-Lourdes C, Sanchez-Peña LC, Del Razo LM, Perez-Urizar J (2008) Inorganic arsenic exposure affects pain behavior and inflammatory response in rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 229:374–385
Agusa T, Kunito T, Kubota R, Inoue S, Fujihara J, Minh TB, Ha NN, Tu NP, Trang PT, Chamnan C, Takeshita H, Iwata H, Tuyen BC, Viet PH, Tana TS, Tanabe S (2010) Exposure, metabolism, and health effects of arsenic in residents from arsenic-contaminated groundwater areas of Vietnam and Cambodia: a review. Rev Environ Health 25:193–220
Apostolakis S, Vogiatzi K, Amanatidou V, Spandidos DA (2009) Interleukin 8 and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res 84:353–360
Balkwill F (2003) Chemokine biology in cancer. Review. Semin Immunol 15:49–55
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Review. Lancet 357:539–545
Beard NA, Wei L, Dulhunty AF (2009) Control of muscle ryanodine receptor calcium release channels by proteins in the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:340–345
Berglund M, Lindberg AL, Rahman M, Yunus M, Grandér M, Lönnerdal B, Vahter M (2011) Gender and age differences in mixed metal exposure and urinary excretion. Environ Res 111(8):1271–1279
Black PC, Dinney CP (2007) Bladder cancer angiogenesis and metastasis–translation from murine model to clinical trial. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:623–634
Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF (2000) Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N Engl J Med 342:1350–1358
Board PG, Coggan M, Cappello J, Zhou H, Oakley AJ, Anders MW (2008) S-(4-Nitrophenacyl) glutathione is a specific substrate for glutathione transferase omega 1-1. Anal Biochem 374:25–30
Bretz F, Hothorn T, Westfall PH (2011) Multiple comparisons using R. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Bunderson M, Brooks DM, Walker DL, Rosenfeld ME, Coffin JD, Beall HD (2004) Arsenic exposure exacerbates atherosclerotic plaque formation and increases nitrotyrosine and leukotriene biosynthesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 201:32–39
Cáceres DD, Werlinger F, Orellana M, Jara M, Rocha R, Alvarado SA, Luis Q (2010) Polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase (GST) variants and its effect on distribution of urinary arsenic species in people exposed to low inorganic arsenic in tap water: an exploratory study. Arch Environ Occup Health 65:140–147
Cain K (2003) Chemical-induced apoptosis: formation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Drug Metab Rev 35:337–363
Caroppi P, Sinibaldi F, Fiorucci L, Santucci R (2009) Apoptosis and human diseases: mitochondrion damage and lethal role of released cytochrome C as proapoptotic protein. Curr Med Chem 16:4058–4065
Chen YC, Guo YL, Su HJ, Hsueh YM, Smith TJ, Ryan LM (2003a) Arsenic methylation and skin cancer risk in south-western Taiwan. J Occup Environ Med 45:241–248
Chen YC, Su HJ, Guo YL, Hsueh YM, Smith TJ, Ryan LM (2003b) Arsenic methylation and bladder cancer risk in Taiwan. Cancer Causes Control 14:303–310
Chikazawa M, Inoue K, Fukata S, Karashima T, Shuin T (2008) Expression of angiogenesis-related genes regulates different steps in the process of tumor growth and metastasis in human urothelial cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Pathobiology 75:335–345
Dani SU (2010) Arsenic for the fool: an exponential connection. Sci Total Environ 408:1842–1846
De Vizcaya-Ruiz A, Barbier O, Ruiz-Ramos R, Cebrian ME (2009) Biomarkers of oxidative stress and damage in human populations exposed to arsenic. Mutat Res 674:85–92
Del Razo LM, Arellano MA, Cebrián ME (1990) The oxidation states of arsenic in well-water from a chronic arsenicism area of northern Mexico. Environ Pollut 64:143–153
Del Razo LM, Styblo M, Cullen WR, Thomas DJ (2001) Determination of trivalent methylated arsenicals in biological matrices. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 174:282–293
Drobná Z, Walton FS, Paul DS, Xing W, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M (2010) Metabolism of arsenic in human liver: the role of membrane transporters. Arch Toxicol 84:3–16
Dulhunty A, Gage P, Curtis S, Chelvanayagam G, Board P (2001) The glutathione transferase structural family includes a nuclear chloride channel and a ryanodine receptor calcium release channel modulator. J Biol Chem 276:3319–3323
Engel RR, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Receveur O, Smith AH (1994) Vascular effects of chronic arsenic exposure: a review. Epidemiol Rev 16:184–209
Escudero-Lourdes C, Medeiros MK, Cárdenas-González MC, Wnek SM, Gandolfi JA (2010) Low level exposure to monomethyl arsonous acid-induced the over-production of inflammation-related cytokines and the activation of cell signals associated with tumor progression in a urothelial cell model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244:162–173
Guha Mazumder DN (2008) Chronic arsenic toxicity & human health. Indian J Med Res 128:436–447
Gustafson B (2010) Adipose tissue, inflammation and atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 17(4):332–341
Huang C, Ke Q, Costa M, Shi X (2004) Molecular mechanisms of arsenic carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 255:57–66
Jiang X, McDermott JR, Ajees AA, Rosen BP, Liu Z (2010) Trivalent arsenicals and glucose use different translocation pathways in mammalian GLUT1. Metallomics 2:211–219
Kalman DA, Hughes J, van Belle G, Burbacher T, Bolgiano D, Coble K, Mottet NK, Polissar L (1990) The effect of variable environmental arsenic contamination on urinary concentrations of arsenic species. Environ Health Perspect 89:145–151
Karagas MR, Tosteson TD, Morris JS, Demidenko E, Mott LA, Heaney J (2004) Incidence of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder and arsenic exposure in New Hampshire. Cancer Causes Control 15:465–472
Kile ML, Hoffman E, Hsueh YM, Afroz S, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Mahiuddin G, Ryan L, Christiani DC (2009) Variability in biomarkers of arsenic exposure and metabolism in adults over time. Environ Health Perspect 117:455–460
Kumagai Y, Sumi D (2007) Arsenic: signal transduction, transcription factor, and biotransformation involved in cellular response and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:243–462
Kurttio P, Komulainen H, Hakala E, Kahelin H, Pekkanen J (1998) Urinary excretion of arsenic species after exposure to arsenic present in drinking water. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 34(3):297–305
Laliberte RE, Perregaux DG, Hoth LR, Rosner PJ, Jordan CK, Peese KM, Eggler JF, Dombroski MA, Geoghegan KF, Gabel CA (2005) Glutathione s transferase omega 1-1 is a target of cytokine release inhibitory drug and may be responsible for their effect on interleukin 1 posttranslational processing. J Biol Chem 278:16567–16578
Lantz RC, Hays AM (2006) Role of oxidative stress in arsenic-induced toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 38:791–804
Lemarie A, Morzadec C, Bourdonnay E, Fardel O, Vernhet L (2006) Human macrophages constitute targets for immunotoxic inorganic arsenic. J Immunol 177:3019–3027
Li YJ, Scott WK, Zhang L, Lin PI, Oliveira SA, Skelly T, Doraiswamy MP, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Martin ER, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (2006) Revealing the role of glutathione S-transferase omega in age-at-onset of Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Neurobiol Aging 27:1087–1093
Marahatta SB, Punyarit P, Bhudisawasdi V, Paupairoj A, Wongkham S, Petmitr S (2006) Polymorphism of glutathione-S-transferase omega gene and risk of cancer. Cancer Lett 236:276–281
Marnell LL, Garcia-Vargas GG, Chowdhury UK, Zakharyan RA, Walsh B, Avram MD, Kopplin MJ, Cebrian ME, Silbergeld EK, Aposhian HV (2003) Polymorphisms in the human Monomethyl arsonic Acid (MMAV) reductase/hGSTO1 gene and changes in urinary arsenic profiles. Chem Res Toxicol 16:1507–1513
Meliker JR, Wahl RL, Cameron LL, Nriagu JO (2007) Arsenic in drinking water and cerebrovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease in Michigan: a standardized mortality ratio analysis. Environ Health 6(4):1–11
Méndez-Gómez J, García-Vargas GG, López-Carrillo L, Calderón-Aranda ES, Gómez A, Vera E, Valverde M, Cebrián ME, Rojas E (2008) Genotoxic effects of environmental exposure to arsenic and lead on children in region Lagunera, Mexico. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1140:358–367
Mukherjee B, Salavaggione OE, Pelleymounter LL, Moon I, Eckloff BW, Schaid DJ, Wieben ED, Weinshilboum RM (2006) Glutathione S-transferase omega 1 and omega 2 pharmacogenomics. Drug Metab Dispos 7:1237–1246
Piaggi S, Raggi C, Corti A, Pitzalis E, Mascherpa MC, Saviozzi M, Pompella A, Casini AF (2010) Glutathione transferase omega 1-1 (GSTO1-1) plays an anti-apoptotic role in cell resistance to cisplatin toxicity. Carcinogenesis 31(5):804–811
Pongstaporn W, Pakakasama S, Sanguansin S, Hongeng S, Petmitr S (2009) Polymorphism of glutathione S-Transferase Omega gene: association with risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135:673–678
Rahman MM, Ng JC, Naidu R (2009) Chronic exposure of arsenic via drinking water and its adverse health impacts on humans. Environ Geochem Health Suppl 1:189–200
Sampayo-Reyes A, Hernández A, El-Yamani N, López-Campos C, Mayet-Machado E, Rincón-Castañeda CB, Limones-Aguilar Mde L, López-Campos JE, de León MB, González-Hernández S, Hinojosa-Garza D, Marcos R (2010) Arsenic induces DNA damage in environmentally exposed Mexican children and adults. Influence of GSTO1 and AS3MT polymorphisms. Toxicol Sci 117(1):63–71
Schläwicke Engström K, Broberg K, Concha G, Nermell B, Warholm M, Vahter M (2007) Genetic polymorphisms influencing arsenic metabolism: evidence from Argentina. Environ Health Perspect 115(4):599–605
Shi H, Xianglin S, Ke J (2004) Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 255:67–78
Siegel PM, Massague J (2003) Cytostatic and apoptotic actions of TGF-βeta in homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:807–821
Simeonova PP, Hulderman T, Harki D, Luster MI (2003) Arsenic exposure accelerates atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E(−/−) mice. Environ Health Perspect 111(14):1744–1748
Tanaka-Kagawa T, Jinno H, Hasegawa T, Makino Y, Seko Y, Hanioka N, Ando M (2003) Functional characterization of two variant human GSTO 1-1 s (Ala140Asp and Thr217Asn). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:516–520
Thomas DJ (2007) Molecular processes in cellular arsenic metabolism. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222(3):365–373
Trouba KJ, Germolec DR (2004) Micromolar concentrations of sodium arsenite induce cyclooxygenase-2 expression and stimulate p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Toxicol Sci 79(2):248–257
Tseng CH (2008) Arsenic exposure and diabetes mellitus in the United States. JAMA 300(23):2728
Tseng CH (2009) A review on environmental factors regulating arsenic methylation in humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 235(3):338–350
Tseng CH, Huang YK, Huang YL, Chung CJ, Yang MH, Chen CJ, Hsueh YM (2005) Arsenic exposure, urinary arsenic speciation, and peripheral vascular disease in blackfoot disease-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206(3):299–308. Erratum in: Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 1;211(2):175
Wang XJ, Sun Z, Chen W, Eblin KE, Gandolfi JA, Zhang DD (2007) Nrf2 protects human bladder urothelial cells from arsenite and monomethylarsonous acid toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 225:206–213
Waugh DJ, Wilson C (2008) The interleukin-8 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(21):6735–6741
Wnek SM, Medeiros MK, Eblin KE, Gandolfi AJ (2009) Persistence of DNA damage following exposure of human bladder cells to chronic monomethylarsonous acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 241(2):202–209
Wu J, Liu J, Waalkes MP, Cheng ML, Li L, Li CX, Yang Q (2008) High dietary fat exacerbates arsenic-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233(3):377–384
Xi S, Jin Y, Lv X, Sun G (2010) Distribution and speciation of arsenic by transplacental and early life exposure to inorganic arsenic in offspring rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 134(1):84–97
Xie K (2001) Interleukin-8 and human cancer biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 12(4):375–391
Yanbaeva DG, Wouters EF, Dentener MA, Spruit MA, Reynaert NL (2009) Association of glutathione-S-transferase omega haplotypes with susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Free Radic Res 43(8):738–743
Yu L, Kalla K, Guthrie E, Vidrine A, Klimecki WT (2003) Genetic variation in genes associated with arsenic metabolism glutathione S transferase Omega 1-1 and purine nucleoside phosphorylase polymorphisms in European and indigenous Americans. Environ Health Perspect 111:1421–1427
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by SEP-CONACYT grant M-44051 to Claudia Escudero-Lourdes. Diana M Escobar received a partial scholarship through this grant. We thank Maggie Brunner, M.A., for reviewing the English translation.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Escobar-García, D.M., Del Razo, L.M., Sanchez-Peña, L.C. et al. Association of glutathione S-transferase Ω 1-1 polymorphisms (A140D and E208K) with the expression of interleukin-8 (IL-8), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), and apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) in humans chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water. Arch Toxicol 86, 857–868 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0802-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0802-x