Abstract
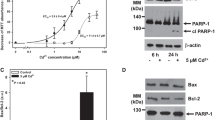
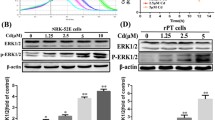
Cadmium exposure is known to cause endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In our current study, we examined the effects of salubrinal, a selective inhibitor of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit α (eIF2α) dephosphorylation, on apoptotic cell death and ER stress-signaling events in HK-2 human renal proximal tubular cells exposed to cadmium chloride (CdCl2). Using phase-contrast microscopy and a cell viability assay, we observed that salubrinal suppressed CdCl2-induced cellular damage and cell death. Treatment with salubrinal reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells and the cleavages of caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, but not the cleavage of light chain 3B, indicating protection from CdCl2-induced apoptosis but not autophagy. Although eIF2α remained phosphorylated after CdCl2 exposure to salubrinal-treated HK-2 cells, the expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and the 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) was not increased. On the other hand, CdCl2-induced expression of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) was reduced by salubrinal treatment. Expression of ATF4, an upstream regulator of GRP78 and CHOP, appeared to be a prerequisite for full protection by salubrinal against cadmium cytotoxicity, because CdCl2-induced cellular damage was not fully suppressed in ATF4-deficient cells. Phosphorylated forms of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), p38, and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), increased after CdCl2 exposure, whereas salubrinal suppressed the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 but not ERK. These results suggest that salubrinal protects CdCl2-exposed HK-2 cells from apoptosis by suppressing cell death signal transduction pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biagioli M, Pifferi S, Ragghianti M, Bucci S, Rizzuto R, Pinton P (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and alteration in calcium homeostasis are involved in cadmium-induced apoptosis. Cell Calcium 43:184–195
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K, Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D, Yuan J (2005) A selective inhibitor of eIF2α dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 307:935–939
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR (2010) The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell 37:299–310
Chou YH, Chao PL, Tsai MJ, Cheng HH, Chen KB, Yang DM, Yang CH, Lin AMY (2008) Arsenite-induced cytotoxicity in dorsal root ganglion explants. Free Radic Biol Med 44:1553–1561
Croute F, Beau B, Murat J-C, Vincent C, Komatsu H, Obata F, Soleilhavoup J-P (2005) Expression of stress-related genes in a cadmium-resistant A549 human cell line. J Toxicol Environ Health A 68:703–718
Gardarin A, Chédin S, Lagniel G, Aude J-C, Godat E, Catty P, Labarre J (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum is a major target of cadmium toxicity in yeast. Mol Microbiol 76:1034–1048
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek R, Schapira M, Ron D (2000) Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 6:1099–1108
He CH, Gong P, Hu B, Stewart D, Choi ME, Choi AMK, Alam J (2001) Identification of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) as an Nrf2-interacting protein: implication for heme oxygenase-1 gene regulation. J Biol Chem 276:20858–20865
Homma K, Katagiri K, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H (2009) Targeting ASK1 in ER stress-related neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13:653–664
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140:900–917
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, Takagi M, Matsumoto K, Miyazono K, Gotoh Y (1997) Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 275:90–94
Inagi R (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a progression factor for kidney injury. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10:156–165
Iwatsuki M, Inageda K, Matsuoka M (2011) Cadmium induces phosphorylation and stabilization of c-Fos in HK-2 renal proximal tubular cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:209–216
Lee AS (2001) The glucose-regulated proteins: stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci 26:504–510
Liu F, Inageda K, Nishitai G, Matsuoka M (2006) Cadmium induces the expression of Grp78, an endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone, in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells. Environ Health Perspect 114:859–864
Long K, Boyce M, Lin H, Yuan J, Ma D (2005) Structure-activity relationship studies of salubrinal lead to its active biotinylated derivative. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:3849–3852
Luo S, Baumeister P, Yang S, Abcouwer SF, Lee AS (2003) Induction of Grp78/BiP by translational block: activation of the Grp78 promoter by ATF4 through an upstream ATF/CRE site independent of the endoplasmic reticulum stress elements. J Biol Chem 278:37375–37385
Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2008) Redox control of cell fate by MAP kinase: physiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase pathway in stress signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:1325–1336
Nordberg GF, Nogawa K, Nordberg M, Friberg LT (2007) Cadmium. In: Nordberg GF, Fowler BA, Nordberg M, Friberg LT (eds) Handbook on the toxicology of metals, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Burlington, pp 445–486
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH (2007) Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 26:3100–3112
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:519–529
Schröder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res 569:29–63
Sugisawa N, Matsuoka M, Okuno T, Igisu H (2004) Suppression of cadmium-induced JNK/p38 activation and HSP70 family gene expression by LL-Z1640–2 in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:206–214
Templeton DM, Liu Y (2010) Multiple roles of cadmium in cell death and survival. Chem Biol Interact 188:267–275
Wada T, Penninger JM (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 23:2838–2849
Wang S-H, Shih Y-L, Lee C–C, Chen W-L, Lin C-J, Lin Y-S, Wu K-H, Shih C-M (2009) The role of endoplasmic reticulum in cadmium-induced mesangial cell apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact 181:45–51
Wang Q, Jiang H, Fan Y, Huang X, Shen J, Qi H, Li Q, Lu X, Shao J (2011) Phosphorylation of the α-subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF2α) alleviates benzo[a]pyrene-7, 8-diol-9, 10-epoxide induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 31:18–24
Yang W, Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Koh HC, Son Il-H (2009) Paraquat activates the IRE1/ASK1/JNK cascade associated with apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol Lett 191:203–210
Yokouchi M, Hiramatsu N, Hayakawa K, Kasai A, Takano Y, Yao J, Kitamura M (2007) Atypical, bidirectional regulation of cadmium-induced apoptosis via distinct signaling of unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ 14:1467–1474
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (21510073) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komoike, Y., Inamura, H. & Matsuoka, M. Effects of salubrinal on cadmium-induced apoptosis in HK-2 human renal proximal tubular cells. Arch Toxicol 86, 37–44 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0742-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0742-x