Abstract
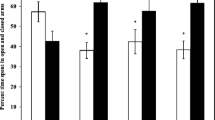
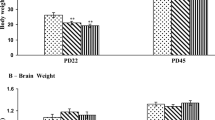
To evaluate the developmental neurotoxicity of arsenic in offspring rats by transplacental and early life exposure to sodium arsenite in drinking water, the pregnant rats or lactating dams, and weaned pups were given free access to drinking water, which contained arsenic at concentrations of 0, 10, 50, 100 mg/L from GD 6 until PND 42. A battery of physical and behavioral tests was applied to evaluate the functional outcome of pups. Pups in arsenic exposed groups weighed less than controls throughout lactation and weaning. Body weight of 10, 50 and 100 mg/L arsenic exposed groups decreased significantly on PND 42, 16 and 12, respectively. Physical development (pinna unfolding, fur appearance, incisor eruption, or eye opening) in pups displayed no significant differences between control and arsenic treated groups. The number of incidences within the 100 mg/L arsenic treated group, in tail hung, auditory startle and visual placing showed significant decrease compared to the control group (p < 0.05). In square water maze test, the trained numbers to finish the trials successfully in 50 and 100 mg/L arsenic exposed groups increased remarkably compared to control group, and there was a dose-related increase (p < 0.01) observed. Taken together, these data show that exposure of inorganic arsenite to pregnant dams and offspring pups at levels up to 100 mg/L in drinking water may affect their learning and memory functions and neuromotor reflex.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolla-Wilson K, Bleecker ML (1987) Neuropsychological impairment following inorganic arsenic exposure. J Occup Med 29:500–503
Calderon J, Navarro ME, Jimenez-Capdeville ME, Santos-Diaz MA, Golden A, Rodriguez-Leyva I, Borja-Aburto V, Diaz-Barriqa F (2001) Exposure to arsenic and lead and neuropsychological development in Mexican children. Environ Res 85:69–76
Delgado JM, Dufour L, Grimaldo JI, Carrizales L, Rodríguez VM, Jiménez-Capdeville ME (2000) Effects of arsenite on central monoamines and plasmatic levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in mice. Toxicol Lett 117:61–67
Dhar P, Jaitley M, Kalaivani M, Mehra RD (2005) Preliminary morphological and histochemical changes in rat spinal cord neurons following arsenic ingestion. Neurotoxicology 26:309–320
Flora SJ, Bhadauria S, Pant SC, Dhaked RK (2005) Arsenic induced blood and brain oxidative stress and its response to some thiol chelators in rats. Life Sci 77:2324–2337
García-Chávez E, Jiménez I, Segura B, Del Razo LM (2006) Lipid oxidative damage and distribution of inorganic arsenic and its metabolites in the rat nervous system after arsenite exposure: Influence of alpha tocopherol supplementation. Neurotoxicology 27:1024–1031
Gerr F, Letz R, Ryan PB, Green RC (2000) Neurological effects of environmental exposure to arsenic in dust and soil among humans. Neurotoxicology 21:475–487
Haque R, Mazumder DN, Samanta S, Ghosh N, Kalman D, Smith MM, Mitra S, Santra A, Lahiri S, Das S, De BK, Smith AH (2003) Arsenic in drinking water and skin lesions: dose-response data from West Bengal, India. Epidemiology 14:174–182
Hood RD, Vedel-Macrander GC, Zaworotko MJ, Tatum FM, Meeks RG (1987) Distribution, metabolism, and fetal uptake of pentavalent arsenic in pregnant mice following oral or intraperitoneal administration. Teratology 35:19–25
Hood RD, Vedel GC, Zaworotko MJ, Tatum FM, Meeks RG (1988) Uptake, distribution, and metabolism of trivalent arsenic in the pregnant mouse. J Toxicol Environ Health 25:423–434
Jin H, Xie H, Wang R, Zhao S (2002) Effects of acrylonitrile exposure on neurobehavioral function in rats. Ind Hlth & Occup Dis 28:209–11 (in Chinese)
Jin Y, Xi S, Li X, Lu C, Li G, Xu Y, Qu C, Niu Y, Sun G (2006) Arsenic speciation transported through the placenta from mother mice to their newborn pups. Environ Res 101:349–355
Kannan GM, Flora SJ (2004) Chronic arsenic poisoning in the rat: treatment with combined administration of succimers and an antioxidant. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 58:37–43
Kannan GM, Tripathi N, Dube SN, Gupta M, Flora SJ (2001) Toxic effects of arsenic (III) on some hematopoietic and central nervous system variables in rats and guinea pigs. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 39:675–682
Kobayashi H, Yuyama A, Ishihara M, Matsusaka N (1987) Effects of arsenic on cholinergic parameters in brain in vitro. Neuropharmacology 26:1707–1713
Li Y, Zhang T (2000) The study methods and experimental technology of developmental toxicology. Beijing Medical University publishing company, Beijing (in Chinese)
Mejía JJ, Diaz-Barriqa F, Calderon J, Rios C, Jimenez Capdeville ME (1997) Effects of lead–arsenic combined exposure on central, monoaminergic systems. Neurotoxicol Teratol 19:489–497
Milton AH, Rahman M (2002) Respiratory effects and arsenic contaminated well water in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Health Res 12:175–179
Nagaraja TN, Desiraju T (1994) Effects on operant learning and brain acetylcholine esterase activity in rats following chronic inorganic arsenic intake. Hum Exp Toxicol 13:353–356
Patlolla AK, Tchounwou PB (2005) Serum acetyl cholinesterase as a biomarker of arsenic induced neurotoxicity in sprague–dawley rats. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2:80–83
Peterson DP, Bhattacharyya MH (1985) Hematological responses to arsine exposure: quantitation of exposure response in mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 5:499–505
Rodriguez VM, Carrizales L, Jimenez-Capdeville ME, Dufour L, Giordano M (2001) The effects of sodium arsenite exposure on behavioral parameters in the rat. Brain Res Bull 55:301–308
Rodriguez VM, Carrizalesb L, Mendozaa MS, Fajardo OR, Giordano M (2002) Effects of sodium arsenite exposure on development and behavior in the rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:743–750
Rosado JL, Ronquillo D, Kordas K, Rojas O, Alatorre J, Lopez P, Garcia-Vargas G, Del Carmen Caamaño M, Cebrián ME, Stoltzfus RJ (2007) Arsenic exposure and cognitive performance in Mexican schoolchildren. Environ Health Perspect 115:1371–1375
Samson FE, Nelson SR (2000) The aging brain, metals and oxygen free radicals. Cell Mol Biol 46:699–707
Shila S, Subathra M, Devi MA, Panneerselvam C (2005) Arsenic intoxication-induced reduction of glutathione level and of the activity of related enzymes in rat brain regions: reversal by DL-alpha-lipoic acid. Arch Toxicol 79:140–146
Tamuras S (1978) Effect of arsenic on the spontaneous motor activity, avoidance conditioning, extinction and swimming record in rats. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi 74:783–795 (in Japanese)
Tayarani I, Cloe¨z I, Clement M, Bourre JM (1989) Antioxidant enzymes and related trace elements in again brain capillaries and choroid plexus. J Neurochem 53:817–824
Tsai SY, Chou HY, The HW, Chen CM, Chen CJ (2003) The effects of chronic arsenic exposure from drinking water on the neurobehavioral development in adolescence. Neurotoxicology 24:747–753
Wang SL, Chiou JM, Chen CJ, Tseng CH, Chou WL, Wang CC, Wu TN, Chang LW (2003) Prevalence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and related vascular diseases in southwestern arseniasis-endemic and nonendemic areas in Taiwan. Environ Health Perspect 111:155–159
Wang CH, Hsiao CK, Chen CL, Hsu LI, Chiou HY, Chen SY, Hsueh YM, Wu MM, Chen CJ (2007) A review of the epidemiologic literature on the role of environmental arsenic exposure and cardiovascular diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:315–326
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Factor-Litvak P, van Geen A, Slavkovich V, LoIacono NJ, Cheng Z, Hussain I, Momotaj H, Graziano JH (2004) Water arsenic exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 112:1329–1333
Xi S, Guo L, Sun W, Qi R, Jin Y, Sun G (2007) Effects of drinking water inorganic arsenic exposure on gene expression of GAD and GABA-T in offspring rat brain. Chin J Endemiol 26:9–11 (in Chinese)
Xi S, Sun G, Sun W, Wang F, Jin Y (2008) Arsemic-induced oxidative damage and histopathological changes in brain of rat offspring. Ind Health Occup Dis 34:89–93 (in Chinese)
Zaidi SM, Banu N (2004) Antioxidant potential of vitamins A, E and C in modulating oxidative stress in rat brain. Clin Chim Acta 340:229–233
Zheng W, Perry DF, Nelson DL, Aposhian HV (1991) Choroid plexus protects cerebrospinal fluid against toxic metals. FASEB J 5:2188–2193
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China through grant number (NSFC) 30530640. We thank Professor Xiaoru Wang, Dr. Xuan Cao in the First Institute of Oceanography State Oceanic Administration, China for measurement of arsenic contents in rat brains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, S., Sun, W., Wang, F. et al. Transplacental and early life exposure to inorganic arsenic affected development and behavior in offspring rats. Arch Toxicol 83, 549–556 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0403-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0403-5