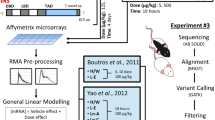
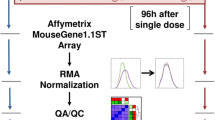
Abstract
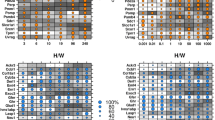
Dioxins exert their major toxicologic effects by binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and altering gene transcription. Numerous dioxin-responsive genes previously were identified both by conventional biochemical and molecular techniques and by recent mRNA expression microarray studies. However, of the large set of dioxin-responsive genes the specific genes whose dysregulation leads to death remain unknown. To identify specific genes that may be involved in dioxin lethality we compared changes in liver mRNA levels following exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in three strains/lines of dioxin-sensitive rats with changes in three dioxin-resistant rat strains/lines. The three dioxin-resistant strains/lines all harbor a large deletion in the transactivation domain of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). Despite this deletion, many genes exhibited a “Type-I” response—that is, their responses were similar in dioxin-sensitive and dioxin-resistant rats. Several genes that previously were well established as being dioxin-responsive or under AHR regulation emerged as Type-I responses (e.g. CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1 and Gsta3). In contrast, a relatively small number of genes exhibited a Type-II response—defined as a difference in responsiveness between dioxin-sensitive and dioxin-resistant rat strains. Type-II genes include: malic enzyme 1, ubiquitin C, cathepsin L, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and ferritin light chain 1. In silico searches revealed that AH response elements are conserved in the 5′-flanking regions of several genes that respond to TCDD in both the Type-I and Type-II categories. The vast majority of changes in mRNA levels in response to 100 μg/kg TCDD were strain-specific; over 75% of the dioxin-responsive clones were affected in only one of the six strains/lines. Selected genes were assessed by quantitative RT-PCR in dose-response and time-course experiments and responses of some genes were assessed in Ahr-null mice to determine if their response was AHR-dependent. Type-II genes may lie in pathways that are central to the difference in susceptibility to TCDD lethality in this animal model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott BD, Buckalew AR, DeVito MJ, Ross D, Bryant PL, Schmid JE (2003) EGF and TGF-alpha expression influence the developmental toxicity of TCDD: dose response and AhR phenotype in EGF, TGF-alpha, and EGF + TGF-alpha knockout mice. Toxicol Sci 71:84–95
Bock KW, Kohle C (2005a) Ah receptor- and TCDD-mediated liver tumor promotion: clonal selection and expansion of cells evading growth arrest and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 69:1403–1408
Bock KW, Kohle C (2005b) UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A6: structural, functional, and regulatory aspects. Methods Enzymol 400:57–75
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19:185–193
Boutros PC, Moffat ID, Franc MA, Tijet N, Tuomisto J, Pohjanvirta R, Okey AB (2004) Dioxin-responsive AHRE-II gene battery: identification by phylogenetic footprinting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321:707–715
Boverhof DR, Tam E, Harney AS, Crawford RB, Kaminski NE, Zacharewski TR (2004) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induces suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 in murine B cells. Mol Pharmacol 66:1662–1670
Boverhof DR, Burgoon LD, Tashiro C, Chittim B, Harkema JR, Jump DB, Zacharewski TR (2005) Temporal and dose-dependent hepatic gene expression patterns in mice provide new insights into TCDD-mediated hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 85:1048–1063
Boverhof DR, Burgoon LD, Tashiro C, Sharratt B, Chittim B, Harkema JR, Mendrick DL, Zacharewski TR (2006) Comparative toxicogenomic analysis of the hepatotoxic effects of TCDD in Sprague Dawley rats and C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Sci 94:398–416
Bunger MK, Moran SM, Glover E, Thomae TL, Lahvis GP, Lin BC, Bradfield CA (2003) Resistance to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin toxicity and abnormal liver development in mice carrying a mutation in the nuclear localization sequence of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. J Biol Chem 278:17767–17774
Croutch CR, Lebofsky M, Schramm KW, Terranova PF, Rozman KK (2005) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (HxCDD) alter body weight by decreasing insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) signaling. Toxicol Sci 85:560–571
Denison MS, Whitlock JP Jr (1995) Xenobiotic-inducible transcription of cytochrome P450 genes. J Biol Chem 270:18175–18178
Dragin N, Dalton TP, Miller ML, Shertzer HG, Nebert DW (2006) For dioxin-induced birth defects, mouse or human CYP1A2 in maternal liver protects whereas mouse CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 are inconsequential. J Biol Chem 281:18591–18600
Fernandez-Salguero P, Pineau T, Hilbert DM, McPhail T, Lee SS, Kimura S, Nebert DW, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (1995) Immune system impairment and hepatic fibrosis in mice lacking the dioxin-binding Ah receptor (see comments). Science 268:722–726
Fernandez-Salguero PM, Hilbert DM, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (1996) Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 140:173–179
Fletcher N, Wahlstrom D, Lundberg R, Nilsson CB, Nilsson KC, Stockling K, Hellmold H, Hakansson H (2005) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) alters the mRNA expression of critical genes associated with cholesterol metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, and bile transport in rat liver: a microarray study. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:1–24
Frericks M, Temchura VV, Majora M, Stutte S, Esser C (2006) Transcriptional signatures of immune cells in aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-proficient and AHR-deficient mice. Biol Chem 387:1219–1226
Fried KW, Bazzi R, Levy Lopez W, Corsten C, Schramm KW, Bell DR, Rozman KK (2007) Relationship between aryl hydrocarbon receptor-affinity and the induction of EROD activity by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorinated phenothiazine and derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 224:147–155
Frueh FW, Hayashibara KC, Brown PO, Whitlock JP (2001) Use of cDNA microarrays to analyze dioxin-induced changes in human liver gene expression. Toxicol Lett 122:189–203
Gibbs RA, Weinstock GM, Metzker ML, Muzny DM, Sodergren EJ, Scherer S, Scott G, Steffen D, Worley KC, Burch PE, Okwuonu G, Hines S, Lewis L, DeRamo C, Delgado O, Dugan-Rocha S, Miner G, Morgan M, Hawes A, Gill R, Celera, Holt RA, Adams MD, Amanatides PG, Baden-Tillson H, Barnstead M, Chin S, Evans CA, Ferriera S, Fosler C, Glodek A, Gu Z, Jennings D, Kraft CL, Nguyen T, Pfannkoch CM, Sitter C, Sutton GG, Venter JC, Woodage T, Smith D, Lee HM, Gustafson E, Cahill P, Kana A, Doucette-Stamm L, Weinstock K, Fechtel K, Weiss RB, Dunn DM, Green ED, Blakesley RW, Bouffard GG, De Jong PJ, Osoegawa K, Zhu B, Marra M, Schein J, Bosdet I, Fjell C, Jones S, Krzywinski M, Mathewson C, Siddiqui A, Wye N, McPherson J, Zhao S, Fraser CM, Shetty J, Shatsman S, Geer K, Chen Y, Abramzon S, Nierman WC, Havlak PH, Chen R, Durbin KJ, Egan A, Ren Y, Song XZ, Li B, Liu Y, Qin X, Cawley S, Cooney AJ, D’Souza LM, Martin K, Wu JQ, Gonzalez-Garay ML, Jackson AR, Kalafus KJ, McLeod MP, Milosavljevic A, Virk D, Volkov A, Wheeler DA, Zhang Z, Bailey JA, Eichler EE, Tuzun E, Birney E, Mongin E, Ureta-Vidal A, Woodwark C, Zdobnov E, Bork P, Suyama M, Torrents D, Alexandersson M, Trask BJ, Young JM, Huang H, Wang H, Xing H, Daniels S, Gietzen D, Schmidt J, Stevens K, Vitt U, Wingrove J, Camara F, Mar Alba M, Abril JF, Guigo R, Smit A, Dubchak I, Rubin EM, Couronne O, Poliakov A, Hubner N, Ganten D, Goesele C, Hummel O, Kreitler T, Lee YA, Monti J, Schulz H, Zimdahl H, Himmelbauer H, Lehrach H, Jacob HJ, Bromberg S, Gullings-Handley J, Jensen-Seaman MI, Kwitek AE, Lazar J, Pasko D, Tonellato PJ, Twigger S, Ponting CP, Duarte JM, Rice S, Goodstadt L, Beatson SA, Emes RD, Winter EE, Webber C, Brandt P, Nyakatura G, Adetobi M, Chiaromonte F, Elnitski L, Eswara P, Hardison RC, Hou M, Kolbe D, Makova K, Miller W, Nekrutenko A, Riemer C, Schwartz S, Taylor J, Yang S, Zhang Y, Lindpaintner K, Andrews TD, Caccamo M, Clamp M, Clarke L, Curwen V, Durbin R, Eyras E, Searle SM, Cooper GM, Batzoglou S, Brudno M, Sidow A, Stone EA, Payseur BA, Bourque G, Lopez-Otin C, Puente XS, Chakrabarti K, Chatterji S, Dewey C, Pachter L, Bray N, Yap VB, Caspi A, Tesler G, Pevzner PA, Haussler D, Roskin KM, Baertsch R, Clawson H, Furey TS, Hinrichs AS, Karolchik D, Kent WJ, Rosenbloom KR, Trumbower H, Weirauch M, Cooper DN, Stenson PD, Ma B, Brent M, Arumugam M, Shteynberg D, Copley RR, Taylor MS, Riethman H, Mudunuri U, Peterson J, Guyer M, Felsenfeld A, Old S, Mockrin S, Collins F (2004) Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature 428:493–521
Gu YZ, Hogenesch JB, Bradfield CA (2000) The PAS superfamily: sensors of environmental and developmental signals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:519–561
Hayes KR, Vollrath AL, Zastrow GM, McMillan BJ, Craven MW, Jovanovich SB, Walisser JA, Rank DR, Penn SG, Reddy JK, Thomas RS, Bradfield CA (2005) EDGE: a centralized resource for the comparison, analysis and distribution of toxicogenomic information. Mol Pharmacol 67:1360–1368
Hayes KR, Zastrow GM, Nukaya M, Pande K, Glover E, Maufort JP, Liss AL, Liu Y, Moran SM, Vollrath AL, Bradfield CA (2007) Hepatic transcriptional networks induced by exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Chem Res Toxicol
Hudson RC, Daniel RM (1993) l-glutamate dehydrogenases: distribution, properties and mechanism. Comp Biochem Physiol B 106:767–792
Ilian MA, Sparrow BR, Ryu BW, Selivonchick DP, Schaup HW (1996) Expression of hepatic pyruvate carboxylase mRNA in C57BL/6J Ah(b/b) and congenic Ah((d/d)) mice exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biochem Toxicol 11:51–56
Karlsen RL, Grofova I, Malthe-Sorenssen D, Fonnum F (1981) Morphological changes in rat brain induced by l-cysteine injection in newborn animals. Brain Res 208:167–180
Karyala S, Guo J, Sartor M, Medvedovic M, Kann S, Puga A, Ryan P, Tomlinson CR (2004) Different global gene expression profiles in benzo[a]pyrene- and dioxin-treated vascular smooth muscle cells of AHR-knockout and wild-type mice. Cardiovasc Toxicol 4:47–74
Kattainen H, Tuukkanen J, Simanainen U, Tuomisto JT, Kovero O, Lukinmaa PL, Alaluusua S, Tuomisto J, Viluksela M (2001) In utero/lactational 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure impairs molar tooth development in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 174:216–224
Kohle C, Bock KW (2006) Activation of coupled Ah receptor and Nrf2 gene batteries by dietary phytochemicals in relation to chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol 72:795–805
Kolluri SK, Weiss C, Koff A, Gottlicher M (1999) p27(Kip1) induction and inhibition of proliferation by the intracellular Ah receptor in developing thymus and hepatoma cells. Genes Dev 13:1742–1753
Kondraganti SR, Muthiah K, Jiang W, Barrios R, Moorthy B (2005) Effects of 3-methylcholanthrene on gene expression profiling in the rat using cDNA microarray analyses. Chem Res Toxicol 18:1634–1641
Kooperberg C, Fazzio TG, Delrow JJ, Tsukiyama T (2002) Improved background correction for spotted DNA microarrays. J Comput Biol 9:55–66
Lee K, Burgoon LD, Lamb L, Dere E, Zacharewski TR, Hogenesch JB, Lapres JJ (2006) Identification and characterization of genes susceptible to transcriptional cross-talk between the hypoxia and dioxin signaling cascades. Chem Res Toxicol 19:1284–1293
Lin TM, Ko K, Moore RW, Buchanan DL, Cooke PS, Peterson RE (2001) Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the development of control and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-exposed male mice. J Toxicol Environ Health A 64:327–342
Martinez JM, Afshari CA, Bushel PR, Masuda A, Takahashi T, Walker NJ (2002) Differential toxicogenomic responses to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in malignant and nonmalignant human airway epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci 69:409–423
Miao W, Hu L, Scrivens PJ, Batist G (2005) Transcriptional regulation of NF-E2 p45-related factor (NRF2) expression by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor–xenobiotic response element signaling pathway: direct cross-talk between phase I and II drug-metabolizing enzymes. J Biol Chem 280:20340–20348
Michel C, Roberts RA, Desdouets C, Isaacs KR, Boitier E (2005) Characterization of an acute molecular marker of nongenotoxic rodent hepatocarcinogenesis by gene expression profiling in a long term clofibric acid study. Chem Res Toxicol 18:611–618
Miettinen HM, Alaluusua S, Tuomisto J, Viluksela M (2002) Effect of in utero and lactational 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure on rat molar development: the role of exposure time. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 184:57–66
Mimura J, Yamashita K, Nakamura K, Morita M, Takagi TN, Nakao K, Ema M, Sogawa K, Yasuda M, Katsuki M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1997) Loss of teratogenic response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in mice lacking the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Genes Cells 2:645–654
Moffat ID, Roblin S, Harper PA, Okey AB, Pohjanvirta R (2007) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor splice variants in the dioxin-resistant rat: tissue expression and transactivational activity. Mol Pharmacol 72:956–966
Nebert DW, Dalton TP, Okey AB, Gonzalez FJ (2004) Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the CYP1 enzymes in environmental toxicity and cancer. J Biol Chem 279:23847–23850
Nishimura N, Miyabara Y, Suzuki JS, Sato M, Aoki Y, Satoh M, Yonemoto J, Tohyama C (2001) Induction of metallothionein in the livers of female Sprague–Dawley rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Life Sci 69:1291–1303
Okey AB (1990) Enzyme induction in the cytochrome P-450 system. Pharmacol Ther 45:241–98
Okey AB (2007) An aryl hydrocarbon receptor Odyssey to the Shores of Toxicology: the Deichmann lecture, International Congress of Toxicology-XI. Toxicol Sci 98:5–38
Okey AB, Franc MA, Moffat ID, Tijet N, Boutros PC, Korkalainen M, Tuomisto J, Pohjanvirta R (2005) Toxicological implications of polymorphisms in receptors for xenobiotic chemicals: the case of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:S43–S51
Ovando BJ, Vezina CM, McGarrigle BP, Olson JR (2006) Hepatic gene downregulation following acute and subchronic exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Sci 94:428–438
Pande K, Moran SM, Bradfield CA (2005) Aspects of dioxin toxicity are mediated by interleukin 1-like cytokines. Mol Pharmacol 67:1393–1398
Parsons RB, Ramsden DB, Waring RH, Barber PC, Williams AC (1998) Hepatic localisation of rat cysteine dioxygenase. J Hepatol 29:595–602
Pastorelli R, Carpi D, Campagna R, Airoldi L, Pohjanvirta R, Viluksela M, Hakansson H, Boutros PC, Moffat ID, Okey AB, Fanelli R (2006) Differential expression profiling of the hepatic proteome in a rat model of dioxin resistance: correlation with genomic and transcriptomic analyses. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:882–894
Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto J (1987) Han/Wistar rats are exceptionally resistant to TCDD. II. Arch Toxicol Suppl 11:344–347
Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto J (1994) Short-term toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in laboratory animals: effects, mechanisms, and animal models. Pharmacol Rev 46:483–549
Pohjanvirta R, Juvonen R, Karenlampi S, Raunio H, Tuomisto J (1988) Hepatic Ah-receptor levels and the effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on hepatic microsomal monooxygenase activities in a TCDD-susceptible and -resistant rat strain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 92:131–140
Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto L, Tuomisto J (1989) The central nervous system may be involved in TCDD toxicity. Toxicology 58:167–174
Pohjanvirta R, Sankari S, Kulju T, Naukkarinen A, Ylinen M, Tuomisto J (1990) Studies on the role of lipid peroxidation in the acute toxicity of TCDD in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 66:399–408
Pohjanvirta R, Wong JMY, Li W, Harper PA, Tuomisto J, Okey AB (1998) Point mutation in intron sequence causes altered carboxyl-terminal structure in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor of the most 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-resistant rat strain. Mol Pharmacol 54:86–93
Pohjanvirta R, Viluksela M, Tuomisto JT, Unkila M, Karasinska J, Franc M-A, Holowenko M, Giannone JV, Harper PA, Tuomisto J, Okey AB (1999) Physicochemical differences in the AH receptors of the most TCDD-susceptible and the most TCDD-resistant rat strains. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 155:82–95
Puga A, Maier A, Medvedovic M (2000) The transcriptional signature of dioxin in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1129–1142
Schwanekamp JA, Sartor MA, Karyala S, Halbleib D, Medvedovic M, Tomlinson CR (2006) Genome-wide analyses show that nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA levels are differentially affected by dioxin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1759:388–402
Siepel A, Haussler D (2004) Combining phylogenetic and hidden Markov models in biosequence analysis. J Comput Biol 11:413–428
Simanainen U, Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J, Viluksela M (2002) Structure–activity relationships and dose responses of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins for short-term effects in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-resistant and -sensitive rat strains. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 181:38–47
Simanainen U, Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J, Viluksela M (2003) Dose–response analysis of short-term effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in three differentially susceptible rat lines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 187:128–136
Slatter JG, Cheng O, Cornwell PD, de Souza A, Rockett J, Rushmore T, Hartley D, Evers R, He Y, Dai X, Hu R, Caguyong M, Roberts CJ, Castle J, Ulrich RG (2006) Microarray-based compendium of hepatic gene expression profiles for prototypical ADME gene-inducing compounds in rats and mice in vivo. Xenobiotica 36:902–937
Smith AG, Clothier B, Robinson S, Scullion MJ, Carthew P, Edwards R, Luo J, Lim CK, Toledano M (1998) Interaction between iron metabolism and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in mice with variants of the Ahr gene: a hepatic oxidative mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 53:52–61
Smyth GK (2003) Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genetics Mol Biol 3:1–26
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9440–9445
Tanaka TS, Jaradat SA, Lim MK, Kargul GJ, Wang X, Grahovac MJ, Pantano S, Sano Y, Piao Y, Nagaraja R, Doi H, Wood WH III, Becker KG, Ko MS (2000) Genome-wide expression profiling of mid-gestation placenta and embryo using a 15,000 mouse developmental cDNA microarray. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9127–9132
Thimmulappa RK, Mai KH, Srisuma S, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S (2002) Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res 62:5196–5203
Thurmond TS, Silverstone AE, Baggs RB, Quimby FW, Staples JE, Gasiewicz TA (1999) A chimeric aryl hydrocarbon receptor knockout mouse model indicates that aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in hematopoietic cells contributes to the hepatic lesions induced by 2,3,7, 8- tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 158:33–40
Tijet N, Boutros PC, Moffat ID, Okey AB, Tuomisto J, Pohjanvirta R (2006) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates distinct dioxin-dependent and dioxin-independent gene batteries. Mol Pharmacol 69:140–153
Tuomisto J (2005) Does mechanistic understanding help in risk assessment-the example of dioxins. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:2–10
Tuomisto JT, Viluksela M, Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto J (1999) The AH receptor and a novel gene determine acute toxic responses to TCDD: segregation of the resistant alleles to different rat lines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 155:71–81
Unkila M (1993) Differential effect of TCDD on brain serotonin metabolism in a TCDD-susceptible and a TCDD-resistant rat strain. Chemosphere 27:401–406
Uno S, Dalton TP, Sinclair PR, Gorman N, Wang B, Smith AG, Miller ML, Shertzer HG, Nebert DW (2004) Cyp1a1(−/−) male mice: protection against high-dose TCDD-induced lethality and wasting syndrome, and resistance to intrahepatocyte lipid accumulation and uroporphyria. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:410–421
Vartiainen T, Lampi P, Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J (1995) Polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and polychlorodibenzofuran concentrations in human fat samples in a village after pollution of drinking water with chlorophenols. Chemosphere 30:1429–1438
Vezina CM, Walker NJ, Olson JR (2004) Subchronic exposure to TCDD, PeCDF, PCB126, and PCB153: effect on hepatic gene expression. Environ Health Perspect 112:1636–1644
Viluksela M, Bager Y, Tuomisto JT, Scheu G, Unkila M, Pohjanvirta R, Flodstrom S, Warngard L, Tuomisto J (1997) Comparison of liver tumor promoting activity of TCDD in a TCDD-sensitive and a TCDD-resistant rat strain. Pharmacol Toxicol 80:152–156
Viluksela M, Unkila M, Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto JT, Stahl BU, Rozman KK, Tuomisto J (1999) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on liver phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) activity, glucose homeostasis and plasma amino acid concentrations in the most TCDD-susceptible and the most TCDD-resistant rat strains. Arch Toxicol 73:323–336
Viluksela M, Bager Y, Tuomisto JT, Scheu G, Unkila M, Pohjanvirta R, Flodstrom S, Kosma VM, Maki-Paakkanen J, Vartiainen T, Klimm C, Schramm KW, Warngard L, Tuomisto J (2000) Liver tumor-promoting activity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in TCDD-sensitive and TCDD-resistant rat strains. Cancer Res 60:6911–6920
Walisser JA, Bunger MK, Glover E, Bradfield CA (2004) Gestational exposure of Ahr and Arnt hypomorphs to dioxin rescues vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16677–16682
Wang P, Ding F, Chiang H, Thompson RC, Watson SJ, Meng F (2002a) ProbeMatchDB—a web database for finding equivalent probes across microarray platforms and species. Bioinformatics 18:488–489
Wang W, Wyckoff JB, Frohlich VC, Oleynikov Y, Huttelmaier S, Zavadil J, Cermak L, Bottinger EP, Singer RH, White JG, Segall JE, Condeelis JS (2002b) Single cell behavior in metastatic primary mammary tumors correlated with gene expression patterns revealed by molecular profiling. Cancer Res 62:6278–6288
Weber LW, Lebofsky M, Stahl BU, Kettrup A, Rozman K (1992) Comparative toxicity of four chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (CDDs) and their mixture. Part II: structure–activity relationships with inhibition of hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, pyruvate carboxylase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activities. Arch Toxicol 66:478–483
Weber LW, Palmer CD, Rozman K (1994) Reduced activity of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase in the liver of rats treated with chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (CDDs): dose–responses and structure–activity relationship. Toxicology 86:63–69
Workman C, Jensen LJ, Jarmer H, Berka R, Gautier L, Nielser HB, Saxild HH, Nielsen C, Brunak S, Knudsen S (2002) A new non-linear normalization method for reducing variability in DNA microarray experiments. Genome Biol 3:research0048
Yang YH, Speed T (2002) Design issues for cDNA microarray experiments. Nat Rev Genet 3:579–588
Yang D, Li Y, Yuan X, Matoney L, Yan B (2001) Regulation of rat carboxylesterase expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD): a dose-dependent decrease in mRNA levels but a biphasic change in protein levels and activity. Toxicol Sci 64:20–27
Zeytun A, McKallip R, Fisher M, Camacho I, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti P (2002) Analysis of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced gene expression profile in vivo using pathway-specific cDNA arrays. Toxicology 178:241
Zhang L, Zheng W, Jefcoate CR (2003) Ah receptor regulation of mouse Cyp1B1 is additionally modulated by a second novel complex that forms at two AhR response elements. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 192:174–190
Acknowledgments
Supported by grant MOP-57903 from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to A.B.O. and by grants 200980 and 211120 from the Academy of Finland to R.P.; M.A.F. and I.D.M. were supported by fellowships from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. We thank Virpi Tiihonen and Arja Tamminen for excellent technical assistance. Experiments reported in this paper comply with the current laws of Canada and of Finland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M.A. Franc and I.D. Moffat contributed equally to this project.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0320-z
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franc, M.A., Moffat, I.D., Boutros, P.C. et al. Patterns of dioxin-altered mRNA expression in livers of dioxin-sensitive versus dioxin-resistant rats. Arch Toxicol 82, 809–830 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0303-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0303-0