Abstract
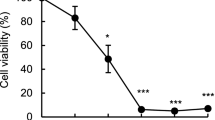
It has been reported that sorbitol induces apoptosis in several cancer cell lines. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the sorbitol-induced apoptotic process is not yet clearly understood. In the present study, the intracellular signaling pathways of sorbitol-induced apoptosis in human K562 cells were investigated using both morphological analysis and DNA fragmentation technique. In this study, we demonstrated that sorbitol-induced apoptosis in human K562 cells is a concentration- and time-dependent manner. This sorbitol-induced apoptosis in human K562 cells was also accompanied by the up-regulation of Bax, and down-regulation of p-Bcl-2, but no effect on the levels of Bcl-XL. Moreover, the sorbitol treatment resulted in a significant reduction of mitochondria membrane potential, increase in the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c (cyt c), and activation of caspase 3. Furthermore, treatment with caspase 3 inhibitor (z-DEVD-fmk) was capable of preventing the sorbitol-induced caspase 3 activity and cell death. These results clearly demonstrate that the induction of apoptosis by sorbitol involves multiple cellular/molecular pathways and strongly suggest that pro- and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial cyt c, and caspase 3, they all participate in sorbitol-induced apoptotic process in human K562 cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonsson B, Martinou IC (2000) The Bcl-2 protein family. Exp Cell Res 256:50–57
Aquilano K, Filomeni G, Di Renzo L, Vito M, Stefano C, Salimei PS, Ciriolo MR, Marfè G (2007) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species are involved in sorbitol-induced apoptosis of human erithroleukaemia cells K562. Free Radic Res 41:452–460
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X (1999) Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:269–290
Cheng AC, Jian CB, Huang YT, Lai CS, Hsu PC, Pan MH (2007) Induction of apoptosis by Uncaria tomentosa through reactive oxygen species production, cytochrome c release, and caspases activation in human leukemia cells. Food Chem Toxicol 45:2206–2218
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioner of apoptosis. Biochem J 326:1–16
Deveraux QL, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Van Arsdale T, Zhou Q, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1998) IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase-8 and cytochrome c by direct inhibition of distinct caspases. EMBO J 17:2215–2223
Eskes R, Desagher S, Antonsson B, Martinou JC (2000) Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mol Cell Biol 20:929–935
Galvez AS, Ulloa JA, Chiong M, Criollo A, Eisner V, Barros LF, Lavandero S (2003) Aldose reductase induced by hyperosmotic stress mediates cardiomyocyte apoptosis: differential effects of sorbitol and mannitol. J Biol Chem 278:38484–38494
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondrial in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Herrmann M, Lorenz HM, Voll R, Grunke M, Woith W, Kalden JR (1994) A rapid and simple method for the isolation of apoptotic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 22:5506–5507
Jow GM, Wu YC, Guh JH, Teng CM (2004) Armepavine oxalate induces cell death on CCRF-CEM leukemia cell line through an apoptotic pathway. Life Sci 75:549–557
Kantrow SP, Piantasdosi CA (1997) Release of cytochrome c from liver mitochondria during permeability transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 232:669–671
Kaufmann SH, Hengartner MO (2001) Programmed cell death: alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol 11:526–534
Koyama AH, Arakawa T, Adachi A (2000) Characterization of apoptosis induced by sorbitol: a unique system for the detection of antiapoptotic activities of viruses. Microbes Infect 2:599–606
Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD (2003) Bcl-2-family proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:691–699
Murata T, Goshima F, Yamauchi Y, Koshizuka T, Takakuwa H, Nishiyama Y (2002) Herpes simplex virus type 2 US3 blocks apoptosis induced by sorbitol treatment. Microbes Infect 4:707–712
Reed JC (2001) Apoptosis-regulating proteins as targets for drug discovery. Trends Mol Med 7:314–319
Salvesen G, Dixit V (1999) Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10964–10967
Scaduto RC Jr, Grotyohann LW (1999) Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J 76:469–477
Sinibaldi-Salimei P, Marfe G, Di Renzo L, Di Stefano C, Giganti MG, Filomeni G, Ciriolo MR (2007) The interference of rosmarinic acid in the DNA fragmentation induced by osmotic shock. Front Biosci 12:1308–1317
Solange D, Martinou JC (2000) Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 10:369–377
Stoothoff WH, Johnson GV (2001) Hyperosmotic stress-induced apoptosis and tau phosphorylation in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci Res 65:573–582
Teramachi K, Izawa M (2000) Rapid induction of apoptosis in human gastric cancer cell lines by sorbitol. Apoptosis 5:181–187
Vander Heiden MG, Thompson CB (1999) Bcl-2 proteins: regulators of apoptosis or of mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Cell Biol 1:E209–E216
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96:245–254
Wood DE, Newcomb EW (2000) Cleavage of Bax enhances its cell death function. Exp Cell Res 256:375–382
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP, Wang X (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2 release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275:1129–1132
Zhang L, Yu J, Park BH, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (2000) Role of Bax in the apoptotic response to anticancer agents. Science 290:989–992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The present study focused on K562 cells, a bcr-abl-exspressing human chronic myelogenous leukemia line that has been reported to resistent induction of apoptosis by many of same stimuli. Sorbitol can induce apoptosis in cultured cells: (1) apoptosis is induced simply by the addition of the reagent to the culture medium and following withdrawal from the medium, (2) apoptotic response is quick and efficient.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marfè, G., Morgante, E., Di Stefano, C. et al. Sorbitol-induced apoptosis of human leukemia is mediated by caspase activation and cytochrome c release. Arch Toxicol 82, 371–377 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0261-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0261-y