Abstract
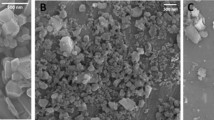
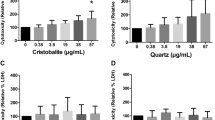
The uptake of respirable quartz particles by alveolar macrophages (AM) is believed to cause an inflammatory response, which is discussed as a crucial step in quartz pathogenicity. However, little is known about the mechanism and the relevance of particle uptake. Therefore, the aim of this study was to analyze the role of the actin cytoskeleton in quartz particle uptake, reactive oxygen species generation (ROS) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) release. Primary rat alveolar and interstitial macrophages (IM) as well as a rat alveolar macrophage cell line (NR8383) were treated with quartz particles at various concentrations and time intervals. Particle uptake was studied using flow cytometry and light/fluorescence microscopy to analyze particle uptake and cytoskeleton recruitment. Intra- as well as extracellular ROS generation was analyzed by flow cytometry and electron spin resonance (ESR). Flow cytometric investigations demonstrated a dose- and time-dependent particle uptake. Primary AM showed a similar uptake indicating that the cell line provides a good model to investigate the mechanisms of particle uptake while primary IM had a lower uptake rate. Inhibition of actin polymerization using cytochalasin-D caused a significant reduction of particle uptake in NR8383 cells. The quartz induced dose-dependent increase of ROS generation and TNF-α release was also blocked by inhibition of actin polymerization. Our results demonstrate an active involvement of the cytoskeleton in uptake of quartz particles and suggest a role of the actin framework and/or the particle uptake in DQ12-induced ROS generation and cytokine release.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht C, Schins RPF, Höhr D, Becker A, Shi T, Knaapen AM, Borm PJA (2004) Inflammation time course after quart instillation. Role of tumor necrosis factor-α and particle surface. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 31:292–301
Albrecht C, Knaapen AM, Becker A, Höhr D, Haberzettl P, van Schooten FJ, Borm PJ, Schins RP (2005) The crucial role of particle surface reactivity in respirable quartz-induced reactive oxygen/nitrogen species formation and APE/Ref-1 induction in rat lung. Respir Res 2(6):129
Ali MH, Pearlstein DP, Mathieu CE, Schumacker PT (2004) Mitochondrial requirement for endothelial response to cyclic strain: implications for mechanotransduction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L486–L496
Allen LA, Adrerem A (1996) Molecular definition of distinct cytoskeletal structures invalved in complement- and Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages. J Exp Med 184(2):627–637
Allen LA, Underhill DM (1999) Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol 17:593–623
Babior BM (1999) NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood 5:1464–1476
Balduzzi M, Diociaiuti M, De Beraedis B, Paradisi S, Paoletti L (2004) In vitro effects on macrophages induced by noncytotoxic doses of silica particles possibly relevant to ambient exposure. Environ Res 96:62–71
Brain JD (1992) Mechanisms, measurement, and significance of lung macrophage function. Environ Health Perspect 97:5–10
Brown DM, Donaldson K, Stone V (2004) Effects of PM10 in human peripheral blood monocytes and J774 macrophages. Respir Res 5:29
Castranova V (2000) From coalmine dust to quartz: mechanisms of pulmonary pathogenicity. Inhal Toxicol 12(3):7–14
Churg A (1996) The uptake of mineral particles by pulmonary epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154:1124–1140
Duffin R, Gilmour PS, Schins RP, Clouter A, Guy K, Brown DM, MacNee W, Borm PJ, Donaldson K, Stone V (2001) Aluminum lactate treatment of DQ12 quartz inhibits its ability to cause inflammation, chemokine expression, and nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 176(1):10–17
Fels AO, Cohn ZA (1986) The alveolar macrophage. J Appl Physiol 60(2):353–369
Franke-Ullmann G, Pförster C, Walter P, Steinmüller C, Lohmann Matthes M, Kobzik L (1996) characterisation of murine lung interstitial macrophages with alveolar macrophages in vitro. J Immunol 157:3097–3104
Fujiwara N, Kobayashi K (2005) Macrophages in inflammation. Current Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:281–286
Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Moldovan L (1999) Stress, superoxide, and signal transduction. Gene Expr 7:255–260
Granfeldt D, Dahlgren C (2001) An intact cytoskeleton is required for prolonged respiratory burst activity during neutrophil phagocytosis. Inflammation 25(3):165–169
Gwinn MR, Vallayathan V (2006) Respiratory burst: role in signaltransduction in alveolar macrophages. J toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 9(1):27–39
Haugen TS, Skjønsberg OH, Kähler H, Lyberg T (1999) Production of oxidants in alveolar macrophages and blood leukocytes. Eur Respir J 14:1100–1105
Hildemann S, Hammer C, Krombach F (1992) Heterogeneity of alveolar macrophages in experimental silicosis. Environ Health Perspect 97:53–57
Hubbard A, Timblin C, Shukla A, Rincón M, Mossman B (2002) Activation of NF-κB-dependent gene expression by silica in lungs of luciferase reporter mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L968–L975
IARC (1997) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans. Silica, some silicates, coal dust and para-aramid fibrills, vol. 68. IRAC Lyon, France
Iles KE, Forman HJ (2002) Macrophage signalling and respiratory burst. Immunol Res 26(1–3):95–105
Imrich A, Ning YY, Kobzik L (1999) Intracellular oxidant production and cytokine response in lung macrophages: evaluation of fluorescent probes. J Leukoc Biol 65:499–507
Kang JL, Go YH, Hur KC, Castranova V (2000) Silica-induced nuclear factor-κB activation: involvement of reactive oxygen species and protein tyrosin kinase activation. J Toxicol Environ Health 60:27–46
Keane MP, Strieter RM (2002) The importance of balanced pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in diffuse lung disease. Respir Res 3(1):5
Knaapen AM, Albrecht C, Becker A, Höhr D, Winzer A, Haenen G, Borm PJA, Schins RPF (2002) DNA damage in lung epithelial cells isolated from rats exposed to quartz: role of surface reactivity and neutrophilic inflammation. Carcinogenisis 23(7):1111–1120
Kobzik L (1995) Lung macrophage uptake of unopsonised environmental particulates. role of scavenger type receptor. Am Assoc Immunol 155:367–376
Kobzik L, Godleski JJ, Brain JD (1990) Selective down-regulation of alveolar macrophages oxidative response to opsonine-independent phagocytosis. J Immunol 144(11):4312–4319
Kobzik L, Huang S, Paulauskis JD, Godleski JJ (1993) Particle opsonisation and lung macrophages cytokine response. In vitro and in vivo analysis. J Immunol 151(5):2753–2759
Kuempel ED, Attfield MD, Vallyathan V, Lapp NL, Hale JM, Smith RJ, Castranova V (2003) Pulmonary inflammation and crystalline silica in respirable coal mine dust: dose response. J Biosci 1:61–69
Kwitatkowska K, Sobota A (1999) Signaling pathways in phagocytosis. BioEssays 21:422–431
Mechnikoff E (1893) Lectures on the comparative pathology of inflammation. (Reprinted in 1968) Dover, New York
Nkamgueu EM, Adnet JJ, Bernard J, Zierold K, Kilian L, Jallot E, Benhayoune H, Bonhomme P (2000) In vitro effects of zirconia and alumina particles on human blood monocyte-derived macrophages: X-ray microanalysis and flow cytometric studies. J Biomed Mater Res 52(4):587–594
Palecanda A, Kobzik L (2000) Alveolar macrophage-environmental particle interaction: analysis by flow cytometry. Methods 21(3):241–247
Park JB (2003) Phagocytosis induces superoxide formation and apoptosis in macrophages. Exp Mol Med 35(5):325–335
Porter DW, Barger M, Robinson VA, Leonard SS, Landsittel D, Castranova V (2002) Comparison of low doses of aged and freshly fractured silica on pulmonary inflammation and damage in the rat. Toxicology 175:63–71
Porter DW, Hubbs AF, Mercer R, Robinson VA, Ramsey D, McLaurin J, Khan A, Battelli L, Brumbaugh K, Teass A, Castranova V (2004) progression of lung inflammation and damage in rats after cessation of silica inhalation. Toxicol Sci 79:370–380
Rao MK, Porter DW, Meigham T, Castranova V (2004) The source of inflammatory mediators in the lung after silica exposure. Environ Health Perspect 112(17):1679–1685
Richards RJ, Davies N, Atkins L, Oreffo VI (1987) Isolation, biochemical characterisation, and culture of lung typ II cells of the rat. Lung 165:143–158
Rimal B, Greenberg AK, Rom WN (2005) Basic pathogenetic mechanisms in silicosis: current understanding. Curr Opinion in Pul Med 11(1):169–173
Rosengart MR, Arbabi S, Bauer GJ, Garcia I, Jelacic S, Maier RV (2002) The actin cytoskeleton: an essential component for enhanced TNFα production by adherent monocytes. Shock 17(2):109–113
Rubins JB (2003) Alveolar macrophages: wielding the double-edged sword of inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167(2):103–104
Shi T, Knaapen AM, Begerow J, Birmili W, Borm PJ, Schins RP (2003) Temporal variation of hydroxyl radical generation and 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine formation by coarse and fine particulate matter. Occup Environ Med 60(5):315–321
Stringer B, Imrich A, Kobzik L (1995) Flow cytometric assay of lung macrophage uptake of environmental particulates. Cytometry 20(1):23–32
Stringer B, Imrich A, Kobzik L (1996) Lung epithelial cell (A549) interactions with unopsonized environmental particulates: quantification of particle-specific-binding and IL-8 production. Exp Lung Res 22:494–508
Thibodeau MS, Giardiani C, Knecht DA, Helble J, Hubbard AK (2004) Silica-induced apoptosis in mouse alveolar macrophages is initiated by lysosomal enzyme activity. Toxicol Sci 80:34–48
Tjelle ET, Løvdal T, Berg T (2000) Phagosome dynamics and function. BioEssays 22:255–263
Wakatsuki T, Schwab B, Thompson NC, Elson EL (2001) Effects of cytochalasin D and latrunculin B on mechanical properties of cells. J Cell Sci 114:1025–1036
Waterman-Storer C, Duey DY, Weber KL, Keech J, Cheney RE, Salmon ED, Bement WM (2000) Microtubules remodel actomyosin network in xenopus egg extracts via two mechanisms of F-Actin transport. J Cell Biol, 150(2):361–376
Wojciak-Stothhard B, Entwistle A, Garg R, Ridley AJ (1998) Regulation of TNF-alpha-induced reorganisation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell-cell junction by Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 176(1):150–165
Xiao GG, Wang M, Li N, Loo JA, Nel AE (2003) Use of proteomics to demonstrate a hierachical oxidative stress response to diesel exhaust particle chemicals in a macrophage cell line. J Biochem 278(50):50781–50790
Zetterberg G, Johansson A, Lundahl J, Lundborg M, Sköld CM, Tornling G, Camner P, Eklund A (1998) Differences between rat alveolar and interstitial macrophages 5 wk after quartz exposure. Am Physiol Soc 274(2 Pt 1):L226–L234
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the DFG International Graduate College “Molecular mechanisms of food toxicology” (IGK738). We thank Dr. S. Diabaté, Institut für Toxikologie und Genetik, Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Germany, for providing us with NR8383 cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haberzettl, P., Duffin, R., Krämer, U. et al. Actin plays a crucial role in the phagocytosis and biological response to respirable quartz particles in macrophages. Arch Toxicol 81, 459–470 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0178-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0178-5