Abstract
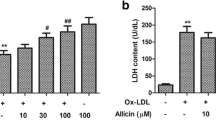
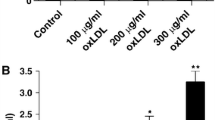
Magnolol, a compound extracted from the Chinese medicinal herb Magnolia officinalis, has several biological effects. However, its protective effects against endothelial injury remain unclear. In this study, we examined whether magnolol prevents oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL)-induced vascular endothelial apoptosis. Incubation of oxLDL with magnolol (2.5–20 μM) inhibited copper-induced oxidative modification via diene formation, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) assay and electrophoretic mobility assay. Apoptotic cell death as characterized by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) stain. We measured the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by using the fluorescent probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein acetoxymethyl ester (DCF-AM), and observed the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Furthermore, several apoptotic signaling pathways which showed NF-κB activation, increased cytosolic calcium, alteration of mitochondrial membrane potential, cytochrome c release and activation of caspase 3 were also investigated. We demonstrated that magnolol prevented the copper-induced oxidative modification of LDL. Magnolol attenuated the oxLDL-induced ROS generation and subsequent NF-κB activation. Furthermore, intracellular calcium accumulation and subsequent mitochondrial membrane potential collapse, cytochome c release and activation of caspase 3 caused by oxLDL were also inhibited by magnolol. Our results suggest that magnolol may have clinical implications in the prevention of atherosclerotic vascular disease through decreasing the oxLDL-induced ROS production.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikawa Y, Yamamoto M, Yamamoto T, Morimoto K, Tanaka K (2002) An anti-rheumatic agent T-614 inhibits NF-kappaB activation in LPS- and TNF-alpha-stimulated THP-1 cells without interfering with IkappaBalpha degradation. Inflamm Res 51:188–194
Bedner E, Li X, Gorczyca W, Melamed MR, Darzynkiewicz Z (1999) Analysis of apoptosis by laser scanning cytometry. Cytometry 35:181–195
Berliner JA, Navab M, Fogelman AM, Frank JS, Demer LL, Edwards PA, Watson AD, Lusis AJ (1995) Atherosclerosis: basic mechanisms : oxidation, inflammation, and genetics. Circulation 91:2488–2496
Bian ZX, Zhang G.S, Wong KL, Hu XG, Liu L, Yang Z, Li M (2006) Inhibitory effects of magnolol on distal colon of guinea pig in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull 29:790–795
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brand K, Page S, Rogler G, Bartsch A, Brandl R, Knuechel R, Page M, Kaltschmidt C, Baeuerle PA, Neumeier D (1996) Activated transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B is present in the atherosclerotic lesion. J Clin Invest 97:1715–1722
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Calara F, Dimayuga P, Niemann A, Thyberg J, Diczfalusy U, Witztum JL, Palinski W, Shah PK, Cercek B, Nilsson J, Regnstrom J (1998) An animal model to study local oxidation of LDL and its biological effects in the arterial wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:884–893
Chang CP, Hsu YC, Lin MT (2003) Magnolol protects against cerebral ischaemic injury of rat heatstroke. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:387–392
Chen FE, Huang DB, Chen YQ, Ghosh G. (1998) Crystal structure of p50/p65 heterodimer of transcription factor NF-[kappa]B bound to DNA. Nature 391:410–413
Chen SC, Chang YL, Wang DL, Cheng JJ (2006) Herbal remedy magnolol suppresses IL-6-induced STAT3 activation and gene expression in endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 148:226–232
Collins T, Palmer HJ, Whitley MZ, Neish AS, Williams AJ (1993) A common theme in endothelial activation: insights from the structural analysis of the genes for E-selectin and VCAM-1. Trends Cardiovasc Med 3:92–97
Cominacini L, Pasini AF, Garbin U, Davoli A, Tosetti ML, Campagnola M, Rigoni A, Pastorino AM, Lo Cascio V, Sawamura T (2000) Oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) binding to ox-LDL Receptor-1 in endothelial cells induces the activation of NF-kappa B through an increased production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem 275:12633–12638
Cristofori P, Lanzoni A, Gaviraghi G, Turton J, Sbarbati A (2000) Anti-atherosclerotic activity of the calcium antagonist lacidipine in cholesterol-fed hamsters. Biomed Pharmacother 54:93–99
Cushing SD, Berliner JA, Valente AJ, Territo MC, Navab M, Parhami F, Gerrity R, Schwartz CJ, Fogelman AM (1990) Minimally modified low density lipoprotein induces monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5134–5138
Denizot F, Lang R (1986) Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89:271–277
Ding Y, Vaziri ND (2000) Nifedipine and Diltiazem but Not Verapamil up-regulate endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:606–609
Escargueil-Blanc I, Andrieu-Abadie N, Caspar-Bauguil S, Brossmer R, Levade T, Negre-Salvayre A, Salvayre R (1998) Apoptosis and activation of the sphingomyelin-ceramide pathway induced by oxidized low density lipoproteins are not causally related in ECV-304 endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 273:27389–27395
Esterbauer H, Striegl G, Puhl H, Rotheneder M (1989) Continuous monitoring of in vitro oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. Free Radic Res Commun 6:67–75
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Harada-Shiba M, Kinoshita M, Kamido H, Shimokado K (1998) Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces Apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells by common and unique mechanisms. J Biol Chem 273:9681–9687
Haraguchi H, Ishikawa H, Shirataki N, Fukuda A (1997) Antiperoxidative activity of neolignans from Magnolia obovata. J Pharm Pharmacol 49:209–212
Havel RJ, Eder HA, Bragdon JH (1955) The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest 34:1345–1353
Heermeier K, Schneider R, Heinloth A, Wanner C, Dimmeler S, Galle J (1999) Oxidative stress mediates apoptosis induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein and oxidized lipoprotein(a). Kidney Int 56:1310–1312
Hsieh CC, Yen MH, Yen CH, Lau YT (2001) Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces apoptosis via generation of reactive oxygen species in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 49:135–145
Ikarashi Y, Yuzurihara M, Sakakibara I, Nakai Y, Hattori N, Maruyama Y (2001) Effects of the extract of the bark of Magnolia obovata and its biphenolic constituents magnolol and honokiol on histamine release from peritoneal mast cells in rats. Planta Med 67:709–713
Ikeda K, Nagase H (2002) Magnolol has the ability to induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Biol Pharm Bull 25:1546–1549
Indrajit C, Binu T, Ganapathy KB (2006) Current concepts in apoptosis: the physiological suicide program revisited. Cell Mol Biol Lett V11:506–525
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52:2745–2756
Ko CH, Chen HH, Lin YR, Chan MH (2003) Inhibition of smooth muscle contraction by magnolol and honokiol in porcine trachea. Planta Med 69:532–536
Lee J, Jung E, Park J, Jung K, Lee S, Hong S, Park J, Park E, Kim J, Park S, Park D (2005) Anti-inflammatory effects of magnolol and honokiol are mediated through inhibition of the downstream pathway of MEKK-1 in NF-kappaB activation signaling. Planta Med 71:338–343
Lee YM, Hsiao G, Chen HR, Chen YC, Sheu JR, Yen MH (2001) Magnolol reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via neutrophil inhibition in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 422:159–167
Lindner V (1998). The NF-kappaB and IkappaB system in injured arteries. Pathobiology 66:311–320
Liou KT, Shen YC, Chen CF, Tsao CM, Tsai SK (2003a) The anti-inflammatory effect of honokiol on neutrophils: mechanisms in the inhibition of reactive oxygen species production. Eur J Pharmacol 475:19–27
Liou KT, Shen YC, Chen CF, Tsao CM, Tsai SK (2003b) Honokiol protects rat brain from focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting neutrophil infiltration and reactive oxygen species production. Brain Res 992:159–166
Littlewood TD, Bennett MR (2003) Apoptotic cell death in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol 14:469–475
Lo YC, Teng CM, Chen CF, Chen CC, Hong CY (1994) Magnolol and honokiol isolated from Magnolia officinalis protect rat heart mitochondria against lipid peroxidation. Biochem Pharmacol 47:549–553
Lu YC, Chen HH, Ko CH, Lin YR, Chan MH (2003) The mechanism of honokiol-induced and magnolol-induced inhibition on muscle contraction and Ca2+ mobilization in rat uterus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 368:262–269
Napoli C (2003) Oxidation of LDL, atherogenesis, and apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:698–709
Neish AS, Williams AJ, Palmer HJ, Whitley MZ, Collins T (1992) Functional analysis of the human vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promoter. J Exp Med 176:1583–1593
Park J, Lee J, Jung E, Park Y, Kim K, Park B, Jung K, Park E, Kim J, Park D (2004) In vitro antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of honokiol and magnolol against Propionibacterium sp. Eur J Pharmacol 496:189–195
Sata M, Walsh K (1998) Oxidized LDL activates Fas-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. J Clin Invest 102:1682–1689
Schreck R, Albermann K, Baeuerle PA (1992) Nuclear factor kappa B: an oxidative stress–responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun 17:221–237
Selzman CH, Shames BD, Reznikov LL, Miller SA, Meng X, Barton HA, Werman A, Harken AH, Dinarello CA, Banerjee A (1999) Liposomal delivery of purified inhibitory-{kappa}B{alpha} inhibits tumor necrosis factor-{alpha}induced human vascular smooth muscle proliferation. Circ Res 84:867–875
Sugano M, Tsuchida K, Makino N (2002) Nifedipine prevents apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by oxidized low-density lipoproteins. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 40:146–152
Telford WG, Komoriya A, Packard BZ (2002) Detection of localized caspase activity in early apoptotic cells by laser scanning cytometry. Cytometry 47:81–88
Terpstra AH, Woodward CJ, Sanchez-Muniz FJ (1981) Improved techniques for the separation of serum lipoproteins by density gradient ultracentrifugation: visualization by prestaining and rapid separation of serum lipoproteins from small volumes of serum. Anal Biochem 111:149–157
Tohda Y, Haraguchi R, Kubo H, Muraki M, Fukuoka M, Nakajima S (1999) Effects of saiboku-to on dual-phase bronchoconstriction in asthmatic guinea pigs. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 21:449–452
Vindis C, Elbaz M, Escargueil-Blanc I, Auge N, Heniquez A, Thiers JC, Negre-Salvayre A, Salvayre R (2005) Two distinct calcium-dependent mitochondrial pathways are involved in oxidized LDL-Induced apoptosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:639–645
Wilson T, March H, Ban WJ, Hou Y, Adler S, Meyers CY, Winters TA, Maher MA (2002) Antioxidant effects of phyto-and synthetic-estrogens on cupric ion-induced oxidation of human low-density lipoproteins in vitro. Life Sci 70:2287–2297
Yang SE, Hsieh MT, Tsai TH, Hsu SL (2003) Effector mechanism of magnolol-induced apoptosis in human lung squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Br J Pharmacol 138:193–201
Zhai H, Nakade K, Mitsumoto Y, Fukuyama Y (2003) Honokiol and magnolol induce Ca2+ mobilization in rat cortical neurons and human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Eur J Pharmacol 474:199–204
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Science Council (NSC 94-2314-B-075A-012) and Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH-953505C, TCVGH-TTMHH958502), Taiwan, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, HC., Chou, FP., Sheu, W.HH. et al. Protective effects of magnolol against oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells. Arch Toxicol 81, 421–432 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0172-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0172-3