Abstract.
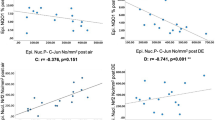
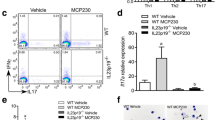
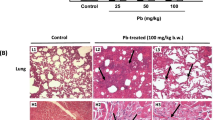
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) derived from diesel exhaust particles (DEP) are implicated in the pathophysiology of respiratory diseases. Cytochrome P450 (Cyp) 1A1 can be induced by several kinds of PAH and produce ROS. We determined whether acute inhalation exposure to DEP induced the expression of Cyp 1A1 in murine lung. Intratracheal instillation of DEP dose-dependently increased the lung expression of Cyp 1A1 at the levels of both mRNA and protein, whereas DEP decreased expression in the lung of aryl hydrocarbon receptors in a dose-dependent manner. In contrast, charcoal particles as the control did not affect the expression of these molecules. These results suggest that the lung expression of Cyp 1A1 can be a biomarker of acute inhalation exposure to DEP and may be implicated in an accelerated production of ROS and the subsequent aggravation of lung injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takano, H., Yanagisawa, R., Ichinose, T. et al. Lung expression of cytochrome P450 1A1 as a possible biomarker of exposure to diesel exhaust particles. Arch Toxicol 76, 146–151 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-002-0323-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-002-0323-0