Abstract
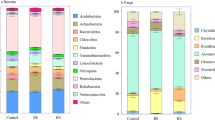
Soil microorganisms play a vital role in biogeochemical processes and nutrient turnover in agricultural ecosystems. However, the information on how the structure and co-occurrence patterns of microbial communities response to the change of planting methods is still limited. In this study, a total of 34 soil samples were collected from 17 different fields of 2 planting types (wheat and orchards) along the Taige Canal in Yangtze River Delta. The structure of bacterial and fungal communities in soil were determined by 16S rRNA gene and ITS gene, respectively. The dominated bacteria were Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, Chloroflexi, Bacteroidota, and Firmicutes. The relative abundances of Actinobacteriota and Firmicutes were higher in the orchards, while Chloroflexi and Nitrospirota were more abundant in wheat fields. Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, and Basidiomycota were the predominant fungus in both soil types. Diversity of bacterial and fungal communities were greater in the wheat fields than in orchards. Statistical analyses showed that pH was the main factor shaping the community structure, and parameters of water content (WC), total organic carbon (TOC) and total nitrogen (TN) had great influences on community structure. Moreover, high co-occurrence patterns of bacterial and fungal were confirmed in both wheat fields and orchards. Network analyses showed that both wheat fields and orchards occurred modular structure, including nodes of Acidobacteriota, Chloroflexi, Gemmatimonadota, Nitrospirota and Ascomycota. In summary, our work showed the co-occurrence network and the convergence/divergence of microbial community structure in wheat fields and orchards, giving a comprehensive understanding of the microbe–microbe interaction during planting methods’ changes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Nucleotide sequence data of this study are deposited in NODE (The National Omics Data Encyclopedia) public available database for full access under the accession number OEP002256.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bahram M, Hildebrand F, Forslund SK, Anderson JL, Soudzilovskaia NA, Bodegom PM, Bengtsson-Palme J, Anslan S, Coelho LP, Harend H, Huerta-Cepas J, Medema MH, Maltz MR, Mundra S, Olsson PA, Pent M, Põlme S, Sunagawa S, Ryberg M, Tedersoo L, Bork P (2018) Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 560(7717):233–237
Barberán A, Bates S, Casamayor E et al (2012) Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME 6:343–351
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. ICWSM 8:361–362
Bokulich NA, Kaehler BD, Rideout JR, Dillon M, Bolyen E, Knight R, Huttley GA, Caporaso JG (2018) Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6(1):90
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon M, Bokulich N, Abnet C, Al-Ghalith G, Alexander H, Alm E, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz J, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn C, Brown CT, Callahan B, Caraballo Rodríguez A, Chase J. (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nature Biotech 37:852–857
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583
Chao A (1984) Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Statist 11(4):265–270
Christian Q, Elmar P, Pelin Y, Jan G, Timmy S, Pablo Y, Jörg P, Frank Oliver G (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(1):590–596
D’Acunto L, Andrade JF, Poggio SL, Semmartin M (2018) Diversifying crop rotation increased metabolic soil diversity and activity of the microbial community. Agr Ecosyst Environ 257:159–164
de Boer W, Folman LB, Summerbell RC, Boddy L (2005) Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29:795–811
de Vries FT, Griffiths RI, Bailey M, Craig H, Girlanda M, Gweon HS, Hallin S, Kaisermann A, Keith AM, Kretzschmar M, Lemanceau P, Lumini E, Mason KE, Oliver A, Ostle N, Prosser JI, Thion C, Thomson B, Bardgett RD (2018) Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nat Commun 9(1):3033
Deng L, Peng C, Huang C, Wang K, Liu Q, Liu Y, Hai X, Shangguan Z (2019) Drivers of soil microbial metabolic limitation changes along a vegetation restoration gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 353:188–200
Fierer N (2017) Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 15(10):579–590
Fisher MC, Henk DA, Briggs CJ, Brownstein JS, Madoff LC, McCraw SL, Gurr SJ (2012) Emerging fungal threats to animal, plant and ecosystem health. Nature 484(7393):186–194
Gabriele B, Daria R, Martin G, Martina K (2016) The plant microbiome explored: implications for experimental botany. J Exp Bot 67(4):995–1002
Gabriele B, Martina K, Daria R, Henry M, Rita G, Kornelia S. (2017) Plant microbial diversity is suggested as the key to future biocontrol and health trends. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93(5): fix050
Gao W, Huang Z, Huang Y, Huang S, Ye G (2020) Effects of forest types and environmental factors on soil microbial biomass in a coastal sand dune of subtropical China. J Res Ecol 11(5):454–465
Grau O, Geml J, Pérez-Haase A, Ninot J, Semenova T, Penuelas J (2017) Abrupt changes in the composition and function of fungal communities along an environmental gradient in the High Arctic. Mol Ecol 26(18):4798–4810
Guo Y, Liu X, Tsolmon B, Chen J, Wei W, Lei S, Yang J, Bao Y (2020) The influence of transplanted trees on soil microbial diversity in coal mine subsidence areas in the Loess Plateau of China. Global Ecol Conserv 21:877
Hortal S, Bastida F, Moreno JL, Armas C, García C, Pugnaire FI (2015) Benefactor and allelopathic shrub species have different effects on the soil microbial community along an environmental severity gradient. Soil Biol Biochem 88:48–57
Huber K, Geppert A, Wanner G, Foesel B, Kaul P, Overmann J (2016) Vicinamibacter silvestris—the first representative of the globally widespread subdivision 6 acidobacteria isolated from subtropical savannah soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(8):2971–2979
Jangid K, Williams MA, Franzluebbers AJ, Schmidt TM, Coleman DC, Whitman WB (2011) Land-use history has a stronger impact on soil microbial community composition than aboveground vegetation and soil properties. Soil Biol Biochem 43(10):2184–2193
Ji HJ, Zhang RL, Wu SX, Zhang HZ, Zhang WL (2008) Analysis of fertilizer input and nutrient balance of farmland in Taihu watershed. Soils Fertil Sci China 5:70–75
Jiang R, Wang M, Chen W, Li X, Balseiro-Romero M (2020) Changes in the integrated functional stability of microbial community under chemical stresses and the impacting factors in field soils. Ecol Ind 110:105919
Jiao C, Zhao D, Zeng J, Guo L, Yu Z (2020) Disentangling the seasonal co-occurrence patterns and ecological stochasticity of planktonic and benthic bacterial communities within multiple lakes. Sci Total Environ 740:140010
Ju F, Xia Y, Guo F et al (2014) Taxonomic relatedness shapes bacterial assembly in activated sludge of globally distributed wastewater treatment plants. Environ Microbiol 16(8):2421–2432
Kong CH, Wang P, Zhao H, Xu XH, Zhu YD (2008) Impact of allelochemical exuded from allelopathic rice on soil microbial community. Soil Biol Biochem 40(7):1862–1869
Konietzny U, Greiner R (2002) Molecular and catalytic properties of phytate-degrading enzymes (phytases). Int J Food Sci Technol 37(7):791–812
Lemanceau P, Bailey M, Faber JH, Griffiths B, Maron PA, Martin F, Mougel C, Philippot L, Pascual U, Pélé N. (2016) Connecting soil biodiversity to functions and ecosystem services: presentation of case studies and of the EU FP7 project EcoFINDERS. International Congress Eurosoil 2012-Soil Science for the Benefit of Mankind and Environment, Jul 2012, Bari, Italy
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8228–8235
Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Kelley ST, Knight R (2007) Quantitative and qualitative beta diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(5):1576–1585
Luisa WH, Hugo AW, Sverker L, Hedvig EJ, Mathilda L, Sandra R, Lars E, Anders FA (2014) DegePrime, a program for degenerate primer design for broad-taxonomic-range PCR in microbial ecology studies. Appl Env Microbiol 80(16):5116–5123
Mandic-Mulec I, Prosser JI (2011) Diversity of endospore-forming bacteria in soil: characterization and driving mechanisms. In: Logan NA, De Vos P (eds) Endospore-forming soil bacteria, soil biology 27. Springer, Berlin, pp 31–59
Meng H, Wu R, Wang Y, Gu J (2017) A comparison of denitrifying bacterial community structures and abundance in acidic soils between natural forest and re-vegetated forest of Nanling Nature Reserve in southern China. J Environ Manage 198:41–49
Min J, Ji R, Wang X, Chen K, Xu J, Pan Y, Lu Z, Lu G, Wang Yuan SW (2020) Changes in planting structure and nitrogen and phosphorus loss loads of farmland in Taihu Lake region. Chin J Eco-Agric 28(8):1230–1238
Miransari M (2011) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(4):917–930
Nelson M, Sadowsky M (2015) Secretion systems and signal exchange between nitrogen-fixing rhizobia and legumes. Front Plant Sci 6:491
Newman M (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(23):8577–8582
Nilsson RH, Larsson K, Taylor AFS, Bengtsson-Palme J, Jeppesen TS, Schigel D, Kennedy P, Picard K, Glöckner FO, Tedersoo L, Saar I, Kõljalg U, Abarenkov K (2019) The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res 47(1):259–264
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PO, Hara RB, Simpson G, Solymos P, Others. (2015) Vegan: community ecology package (CRAN)
Pascault N, Ranjard L, Kaisermann A, Bachar D, Christen R, Terrat S, Mathieu O, Lévêque J, Mougel C, Henault C, Lemanceau P, Péan M, Boiry S, Fontaine S, Maron P (2013) Stimulation of different functional groups of bacteria by various plant residues as a driver of soil priming effect. Ecosystems 16(5):810–822
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J Theor Biol 13:131–144
Proulx SR, Promislow DE, Phillips PC (2005) Network thinking in ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology Evolution 20:345–353
Revelle W. (2013) Psych: procedures for psychological, psychometric, and personality research. R Package Version 1.0–95. Evanston, Illinois
Shanmugam SG, Kingery WL (2018) Changes in soil microbial community structure in relation to plant succession and soil properties during 4000 years of pedogenesis. Eur J Soil Biol 88:80–88
Shannon C, Weaver W (1962) The mathematic theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, p 31
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature 163(4148):688
Sinha S, Masto RE, Ram LC, Selvi VA, Srivastava NK, Tripathi RC, George J (2009) Rhizosphere soil microbial index of tree species in a coal mining ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 41(9):1824–1832
Suleiman AKA, Manoeli L, Boldo JT, Pereira MG, Roesch LFW (2013) Shifts in soil bacterial community after eight years of land-use change. Syst Appl Microbiol 36(2):137–144
Taylor DL, Walters W, Lennon N, Bochicchio J, Andrews L, Caporaso J, Pennanen T (2016) Accurate estimation of fungal diversity and abundance through improved lineage-specific primers optimized for Illumina amplicon sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:2516–2576
Team D. (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing team RDCVienna
Thomson BC, Tisserant E, Plassart P, Uroz S, Griffiths RI, Hannula SE, Buée M, Mougel C, Ranjard L, Van Veen JA, Martin F, Bailey MJ, Lemanceau P (2015) Soil conditions and land use intensification effects on soil microbial communities across a range of European field sites. Soil Biol Biochem 88:403–413
USDA, U. D. O. A. (2020). Soil survey manual-chapter three | NRCS soils retrieved 2020/11/17 from http://soils.usda.gov/technical/manual/contents/chapter3.html. Accessed 17 Nov 2020
Wagner M, Kahmen A, Schlumprecht H, Audorff V, Volker PJ, Buchmann N, Weisser W (2007) Prediction of herbage yield in grassland: how well do Ellenberg N-values perform? Appl Vegetation Sci 10(1):15–24
Wallace DL (1959) Simplified beta-approximations to the Kruskal-Wallis H Test. J Am Stat Assoc 54(285):225–230
Wang L, Tong J, Li Y et al (2020) Bacterial and fungal assemblages and functions associated with biofilms differ between diverse types of plastic debris in a freshwater system. Env Res 196:110371
Wang Q, Li Z, Li X, Ping Q, Feng Z (2021) Interactive effects of ozone exposure and nitrogen addition on the rhizosphere bacterial community of poplar saplings. Sci Total Environ 754:142134
Xiao R, Guo Y, Zhang M, Pan W, Wang JJ (2020) Stronger network connectivity with lower diversity of soil fungal community was presented in coastal marshes after sixteen years of freshwater restoration. Sci Total Environ 744:140623
Xu Z, Li T, Bi J, Wang C (2018) Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of antibiotic pollution and ecological risk assessment in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci Total Environ 643:12–20
Ying Y, Ding W, Zhou Y, Li Y (2012) Influence of panax ginseng continuous cropping on metabolic function of soil microbial communities. Chin Herbal Med 4(4):329–334
Zhang Q, Liu X, Ma X, Fang J, Fan T, Wu F, An L, Feng H (2014) Microcalorimetric study of the effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial activity in a wheat field on the Loess Plateau. Ecotoxicology 23(10):2035–2040
Zhang C, Liu G, Xue S, Wang G (2016a) Soil bacterial community dynamics reflect changes in plant community and soil properties during the secondary succession of abandoned farmland in the Loess Plateau. Soil Biol Biochem 97:40–49
Zhang T, Wang N, Liu H, Zhang Y, Yu L (2016b) Soil pH is a key determinant of soil fungal community composition in the Ny-Ålesund region, Svalbard (High Arctic). Front Microbiol 7:227
Zhang T, Wang N, Yu L (2020a) Soil fungal community composition differs significantly among the Antarctic, Arctic, and Tibetan Plateau. Extremophiles 24(6):821–829
Zhang X, Li S, Cheng W, Zhao Y, Cui H, Xie X, Wu J, Wei Z, Liu Y (2020b) Oxytetracycline stress reconstruct the core microbial community related to nitrogen transformation during composting. Bioresour Technol 319:124142
Zhao Y, Xu X, Darilek JL, Huang B, Sun W, Shi X (2009) Spatial variability assessment of soil nutrients in an intense agricultural area, a case study of Rugao County in Yangtze River Delta Region. China Environ Geol 57(5):1089–1102
Zheng W, Zhao Z, Lv F, Yin Y, Wang Z, Zhao Z, Li Z, Zhai B (2021) Fungal alpha diversity influences stochasticity of bacterial and fungal community assemblies in soil aggregates in an apple orchard. Appl Soil Ecol 162:103878
Zhou Y, Si Y, Zhao X, Wang Q, Xu H, Wang S, Xing G (2012) Situation, problems and countermeasures in nitrogen fertilization in rice/wheat rotation paddy field of Taihu Lake Watershed. China Soils 44(3):510–514
Funding
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of China (No. 41907202, 91951112, 41877336), National Water Pollution Control and Governance of Science and Technology Major Special (No. 2017ZX07202-004), Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M651877), Natural Science Found of Jiangsu Province (No. SBK2019043965), High-level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talents Introduction Program of Jiangsu Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XC sampling, methodology, data analysis, writing–original draft. HH Data analysis, supervision, writing–review and editing. FZ supervision, review and editing. XL writing and review. YM sampling, methodology. HM conceptualization, supervision, methodology, investigation, writing–review and editing. LZ supervision, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication and participation
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., He, H., Zhu, F. et al. Community structure and co-occurrence network analysis of bacteria and fungi in wheat fields vs fruit orchards. Arch Microbiol 204, 453 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03074-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03074-7