Abstract
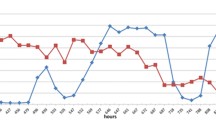
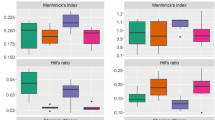
Fibrobacter succinogenes is one of the most pivotal fibrolytic bacterial species in the rumen. In a previous study, we confirmed enhancement of fiber digestion in a co-culture of F. succinogenes S85 with non-fibrolytic ruminal strains R-25 and/or Selenomonas ruminantium S137. In the present study, mRNA expression level of selected functional genes in the genome of F. succinogenes S85 was monitored by real-time RT-PCR. Growth profile of F. succinogenes S85 was similar in both the monoculture and co-cultures with non-fibrolytics. However, expression of 16S rRNA gene of F. succinogenes S85 in the co-culture was higher (P < 0.01) than that of the monoculture. This finding suggests that metabolic activity of F. succinogenes S85 was enhanced by coexistence with strains R-25 and/or S. ruminantium S137. The mRNA expression of fumarate reductase and glycoside hydrolase genes was up-regulated (P < 0.01) when F. succinogenes S85 was co-cultured with non-fibrolytics. These results indicate the enhancement of succinate production and fiber hydrolysis by F. succinogenes S85 in co-cultures of S. ruminantium and R-25 strains.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Béra-Maillet C, Broussolle V, Pristas P, Girardeau J-P, Gaudet G, Forano E (2000a) Characterisation of endoglucanases EGB and EGC from Fibrobacter succinogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1476:191–202
Béra-Maillet C, Gaudet G, Forano E (2000b) Endoglucanase activity and relative expression of glycoside hydrolase genes of Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 grown on different substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta 1543:77–85
Béra-Maillet C, Mosoni P, Kwasiborski A, Suau F, Ribot Y, Forano E (2009) Development of a RT-qPCR method for the quantification of Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 glycoside hydrolase transcripts in the rumen content of gnotobiotic and conventional sheep. J Microbiol Methods 77:8–16
Berg Miller ME, Antonopoulos DA, Rincon MT et al (2009) Diversity and strain specificity of plant cell wall degrading enzymes revealed by the draft genome of Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1. PLoS ONE 4:e6650
Brulc JM, Antonopoulos DA, Berg Miller ME et al (2009) Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1948–1953
Bryant MP, Burkey LA (1953) Cultural methods and characterization of some of the more numerous groups of bacteria in the bovine rumen. J Dairy Sci 36:205–217
Cavicchioli R, Watson K (1991) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of endoglucanase genes from Fibrobacter succinogenes AR1. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:359–365
Cotta MA (1988) Amylolytic activity of selected species of ruminal bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:772–776
Dehority BA, Scott HW (1967) Extent of cellulose and hemicellulose digestion in various forages by pure culture of the rumen bacteria. J Dairy Sci 50:1136–1141
Flint HJ (1997) The rumen microbial ecosystem -some recent developments. Trends Microbiol 5:483–488
Fondevila M, Dehority BA (1996) Interactions between Fibrobacter succinogenes, Prevotella ruminicola, and Ruminococcus flavefaciens in the digestion of cellulose from forages. J Anim Sci 74:678–684
Fukuma N, Koike S, Kobayashi Y (2012) Involvement of recently cultured group U2 bacterium in ruminal fiber digestion revealed by coculture with Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. FEMS Microbiol Lett 336:17–25
Huang L, Forsberg CW (1987) Isolation of a cellodextrinase from Bacteroides succinogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1034–1041
Jun HS, Ha JK, Malburg LM, Verrinder GAM, Forsberg CW (2003) Characteristics of a cluster of xylanase genes in Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. Can J Microbiol 49:171–180
Kobayashi Y, Shinkai T, Koike S (2008) Ecological and physiological characterization shows that Fibrobacter succinogenes is important in rumen fiber digestion—review. Folia Microbiol 53:195–200
Koike S, Kobayashi Y (2009) Fibrolytic rumen bacteria: their ecology and functions. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 22:131–138
Koike S, Yoshitani S, Kobayashi Y, Tanaka K (2003) Phylogenetic analysis of fiber-associated rumen bacterial community and PCR detection of uncultured bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 229:23–30
Koike S, Yabuki H, Kobayashi Y (2007) Validation and application of real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for representative rumen bacteria. Anim Sci J 78:135–141
Koike S, Handa Y, Goto H, Sakai K, Miyagawa E, Matsui H, Ito S, Kobayashi Y (2010) Molecular monitoring and isolation of previously uncultured bacterial strains from the sheep rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1887–1894
Koike S, Yabuki H, Kobayashi Y (2014) Interaction of rumen bacteria as assumed by colonization patterns on untreated and alkali-treated rice straw. Anim Sci J 85:524–531
Krause DO, Denman SE, Mackie RI, Morrison M, Rae AL, Attwood GT, McSweeney CS (2003) Opportunities to improve fiber degradation in the rumen: microbiology, ecology, and genomics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:663–693
Kudo H, Cheng KJ, Costerton JW (1987) Interaction between Treponema bryantii and cellulolytic bacteria in the in vitro degradation of straw cellulose. Can J Microbiol 33:244–248
Latham MJ, Wolin MJ (1977) Fermentation of cellulose by Ruminococcus flavefaciens in the presence and absence of Methanobacterium ruminantium. Appl Environ Microbiol 34:297–301
Lettat A, Nozière P, Silberberg M, Morgavi DP, Berger C, Martin C (2012) Rumen microbial and fermentation characteristics are affected differently by bacterial probiotic supplementation during induced lactic and subacute acidosis in sheep. BMC Microbiol 12:142
Malburg SR, Malburg LM, Liu T, Iyo AH, Forsberg CW (1997) Catalytic properties of the cellulose-binding endoglucanase F from Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2449–2453
McGavin MJ, Forsberg CW, Crosby B, Bell AW, Dignard D, Thomas DY (1989) Structure of the cel-3 gene from Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 and characteristics of the encoded gene product, endoglucanase 3. J Bacteriol 171:5587–5595
McGavin M, Lam J, Forsberg CW (1990) Regulation and distribution of Fibrobacter succinogenes subsp. succinogenes S85 endoglucanases. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1235–1244
Mosoni P, Martin C, Forano E, Morgavi DP (2011) Long-term defaunation increases the abundance of cellulolytic ruminococci and methanogens but does not affect the bacterial and methanogen diversity in the rumen of sheep. J Anim Sci 89:783–791
Muttray A, Mohn W (1999) Quantitation of the population size and metabolic activity of a resin acid degrading bacterium in activated sludge using slot-blot hybridization to measure the rRNA:rDNA ratio. Microb Ecol 38:348–357
Muttray AF, Yu Z, Mohn WW (2001) Population dynamics and metabolic activity of Pseudomonas abietaniphila BKME-9 within pulp mill wastewater microbial communities assayed by competitive PCR and RT-PCR. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:21–31
Paradis FW, Zhu H, Krell PJ, Phillips JP, Forsberg CW (1993) The xynC gene from Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 codes for a xylanase with two similar catalytic domains. J Bacteriol 175:7666–7672
Pérez-Osorio AC, Williamson KS, Franklin MJ (2010) Heterogeneous rpoS and rhlR mRNA levels and 16S rRNA/rDNA (rRNA gene) ratios within Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms, sampled by laser capture microdissection. J Bacteriol 192:2991–3000
Rychlik JL, May T (2000) The effect of methanogen, Methanobrevibacter smithii, on the growth rate, organic acid production, and specific ATP activity of three predominant ruminal cellulolytic bacteria. Curr Microbiol 40:176–180
Saro C, Ranilla MJ, Carro MD (2012) Postprandial changes of fiber-degrading microbes in the rumen of sheep fed diets varying in type of forage as monitored by real-time PCR and automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis. J Anim Sci 90:4487–4494
Sawanon S, Koike S, Kobayashi Y (2011) Evidence for the possible involvement of Selenomonas ruminantium in rumen fiber digestion. FEMS Microbiol Lett 325:170–179
Shinkai T, Ohji R, Matsumoto N, Kobayashi Y (2009) Fibrolytic capabilities of ruminal bacterium Fibrobacter succinogenes in relation to its phylogenetic grouping. FEMS Microbiol Lett 294:183–190
Shinkai T, Ueki T, Koike S, Kobayashi Y (2014) Determination of bacteria constituting ruminal fibrolytic consortia developed on orchard grass hay stem. Anim Sci J 85:254–261
Suen G, Stevenson DM, Bruce DC et al (2011a) Complete genome of the cellulolytic ruminal bacterium Ruminococcus albus 7. J Bacteriol 193:5574–5575
Suen G, Weimer PJ, Stevenson DM et al (2011b) The complete genome sequence of Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 reveals a cellulolytic and metabolic specialist. PLoS ONE 6:e18814
Tajima K, Aminov RI, Nagamine T, Matsui H, Nakamura M, Benno Y (2001) Diet-dependent shifts in the bacterial population of the rumen revealed with real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2766–2774
Williams AG, Withers SE, Joblin KN (1994) The effect of cocultivation with hydrogen-consuming bacteria on xylanolysis by Ruminococcus flavefaciens. Curr Microbiol 29:133–138
Yu Z, Morrison M (2004) Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 36:808–812
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (No. 22780238 to S. K. and No. 17380157 to Y. K.) from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Shuang-Jiang Liu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuma, N.M., Koike, S. & Kobayashi, Y. Monitoring of gene expression in Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 under the co-culture with non-fibrolytic ruminal bacteria. Arch Microbiol 197, 269–276 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-1049-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-1049-0