Abstract
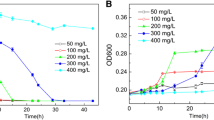
Aerobic enrichment cultures with taurocholate or alkanesulfonates as sole sources of carbon and energy for growth were successful and yielded nine bacterial isolates, all of which utilized taurocholate. Growth was complex and involved not only many, usually transient, excretion products but also sorption of taurocholate and cholate to cells. Three metabolic strategies to dissimilate taurocholate were elucidated, all of which involved bile salt hydrolase cleaving taurocholate to cholate and taurine. Comamonas testosteroni KF-1 utilized both the taurine and the cholate moieties for growth. Pseudomonas spp., e.g. strain TAC-K3 and Rhodococcus equi TAC-A1 grew with the cholate moiety and released taurine quantitatively. Delftia acidovorans SPH-1 utilized the taurine moiety and released cholate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Berg AM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L (2007) Biochemistry, 6th edn. Freeman, New York
Brüggemann C, Denger K, Cook AM, Ruff J (2004) Enzymes and genes of taurine and isethionate dissimilation in Paracoccus denitrificans. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 150:805–816
Buggy BP, Hawkins CC, Fekety R (1985) Effect of adding sodium taurocholate to selective media on the recovery of Clostridium difficile from environmental surfaces. J Clin Microbiol 21:636–637
Cook AM (1987) Biodegradation of s-triazine xenobiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 46:93–116
Cook AM, Denger K (2002) Dissimilation of the C2 sulfonates. Arch Microbiol 179:1–6
Cook AM, Denger K (2006) Metabolism of taurine in microorganisms: a primer in molecular diversity? Adv Exp Med Biol 583:3–13
Cook AM, Hütter R (1981) s-Triazines as nitrogen sources for bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 29:1135–1143
Cook AM, Smits THM, Denger K (2007) Sulfonates and organotrophic sulfite metabolism. In: Dahl C, Friedrich CG (eds) Microbial sulfur metabolism. Springer, Berlin, pp 170–181
Dejonghe W, Berteloot E, Goris J, Boon N, Crul K, Maertens S, Hofte M, De Vos P, Verstraete W, Top EM (2003) Synergistic degradation of linuron by a bacterial consortium and isolation of a single linuron-degrading variovorax strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1532–1541
Delpino MV, Marchesini MI, Estein SM, Comerci DJ, Cassataro J, Fossati CA, Baldi PC (2007) A bile salt hydrolase of Brucella abortus contributes to the establishment of a successful infection through the oral route in mice. Infect Immun 75:299–305
Denger K, Weinitschke S, Hollemeyer K, Cook AM (2004) Sulfoacetate generated by Rhodopseudomonas palustris from taurine. Arch Microbiol 182:254–258
Denger K, Smits THM, Cook AM (2006) Genome-enabled analysis of the utilization of taurine as sole source of carbon or nitrogen by Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 152:3167–3174
Denger K, Weinitschke S, Smits THM, Schleheck D, Cook AM (2008) Bacterial sulfite dehydrogenases in organotrophic metabolism: separation and identification in Cupriavidus necator H16 and in Delftia acidovorans SPH-1. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 154:256–263
Eichhorn E, van der Ploeg JR, Leisinger T (2000) Deletion analysis of the Escherichia coli taurine and alkanesulfonate transport systems. J Bacteriol 182:2687–2795
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC
Gorzynska AK, Denger K, Cook AM, Smits THM (2006) Inducible transcription of genes involved in taurine uptake and dissimilation by Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3T. Arch Microbiol 185:402–406
Hylemon PB, Harder J (1998) Biotransformation of monoterpenes, bile acids, and other isoprenoids in anaerobic ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:475–488
Kertesz MA, Kölbener P, Stockinger H, Beil S, Cook AM (1994) Desulfonation of linear alkylbenzenesulfonate surfactants and related compounds by bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2296–2303
Kumar RS, Brannigan JA, Prabhune AA, Pundle AV, Dodson GG, Dodson EJ, Suresh CG (2006) Structural and functional analysis of a conjugated bile salt hydrolase from Bifidobacterium longum reveals an evolutionary relationship with penicillin V acylase. J Biol Chem 281:32516–32525
Laue H, Denger K, Cook AM (1997) Taurine reduction in anaerobic respiration of Bilophila wadsworthia RZATAU. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2016–2021
Lührmann A, Mauder N, Sydor T, Fernandez-Mora E, Schulze-Luehrmann J, Takai S, Haas A (2004) Necrotic death of Rhodococcus equi-infected macrophages is regulated by virulence-associated plasmids. Infect Immun 72:853–862
MacConkey AT (1900) Note on a new medium for the growth and differentiation of the Bacillus coli communis and the Bacillus typhi abdominalis. Lancet 2:20
Mayer J, Denger K, Smits THM, Hollemeyer K, Groth U, Cook AM (2006) N-Acetyltaurine dissimilated via taurine by Delftia acidovorans NAT. Arch Microbiol 186:61–67
McAuliffe O, Cano RJ, Klaenhammer TR (2005) Genetic analysis of two bile salt hydrolase activities in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4925–4929
Metzler DE (2003) Biochemistry: the chemical reactions of living cells, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Amsterdam
Moser SA, Savage DC (2001) Bile salt hydrolase activity and resistance to toxicity of conjugated bile salts are unrelated properties in lactobacilli. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3476–3480
Muscatello G, Anderson GA, Gilkerson JR, Browning GF (2006) Associations between the ecology of virulent Rhodococcus equi and the epidemiology of R. equi pneumonia on Australian thoroughbred farms. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6152–6160
Nishimori E, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Wakabayashi H (2000) Pseudomonas plecoglossicida sp. nov., the causative agent of bacterial haemorrhagic ascites of ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:83–89
Philipp B, Erdbrink H, Suter MJ, Schink B (2006) Degradation of and sensitivity to cholate in Pseudomonas sp. strain Chol1. Arch Microbiol 185:192–201
Schleheck D, Cook AM (2005) ω-Oxygenation of the alkyl sidechain of linear alkylbenzenesulfonate (LAS) surfactant in Parvibaculum lavamentivorans T. Arch Microbiol 183:369–377
Schleheck D, Knepper TP, Fischer K, Cook AM (2004) Mineralization of individual congeners of linear alkylbenzenesulfonate (LAS) by defined pairs of heterotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4053–4063
Schumacher UK, Lutz F, Werner H (1996) Taurine and taurine conjugated bile acids enhance growth of Bilophila wadsworthia. In: 21st international congress on microbial ecology and disease, Paris
Sörbo B (1987) Sulfate: turbidimetric and nephelometric methods. Methods Enzymol 143:3–6
Sue D, Boor KJ, Wiedmann M (2003) σB-dependent expression patterns of compatible solute transporter genes opuCA and lmo1421 and the conjugated bile salt hydrolase gene bsh in Listeria monocytogenes. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 149:3247–3256
Tanaka H, Hashiba H, Kok J, Mierau I (2000) Bile salt hydrolase of Bifidobacterium longum—biochemical and genetic characterization. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2502–2512
Thurnheer T, Köhler T, Cook AM, Leisinger T (1986) Orthanilic acid and analogues as carbon sources for bacteria: growth physiology and enzymic desulphonation. J Gen Microbiol 132:1215–1220
Wiethaus J, Schubert B, Pfander Y, Narberhaus F, Masepohl B (2008) The GntR-like regulator TauR activates expression of taurine utilization genes in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol 190:487–493
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to A. Haas (University of Bonn), who kindly made available PCR-primers for the vapA gene, plasmid DNA with the vapA gene, and for advice on R. equi. We thank K. Hollemeyer (University of the Saarland) for MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of taurocholate. Janosch Klebensberger (University of Konstanz) kindly discussed the effects of biofilm formation on growth kinetics. The US DOE Joint Genome Institute sequenced the genomes of C. testosteroni KF-1 and D. acidovorans SPH-1 for S. Kjelleberg and DS in its programme “DOE 2006 Microbes”. The project in Konstanz was supported by funds from the University of Konstanz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Walter Reinecke.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rösch, V., Denger, K., Schleheck, D. et al. Different bacterial strategies to degrade taurocholate. Arch Microbiol 190, 11–18 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0357-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0357-7