Abstract
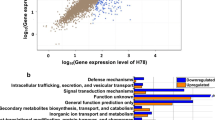
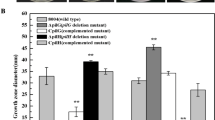
The phytopathogen Xylella fastidiosa produces long type IV pili and short type I pili involved in motility and adhesion. In this work, we have investigated the role of sigma factor σ54 (RpoN) in the regulation of fimbrial biogenesis in X. fastidiosa. An rpoN null mutant was constructed from the non-pathogenic citrus strain J1a12, and microarray analyses of global gene expression comparing the wild type and rpoN mutant strains showed few genes exhibiting differential expression. In particular, gene pilA1 (XF2542), which encodes the structural pilin protein of type IV pili, showed decreased expression in the rpoN mutant, whereas two-fold higher expression of an operon encoding proteins of type I pili was detected, as confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis. The transcriptional start site of pilA1 was determined by primer extension, downstream of a σ54-dependent promoter. Microarray and qRT-PCR data demonstrated that expression of only one of the five pilA paralogues, pilA1, was significantly reduced in the rpoN mutant. The rpoN mutant made more biofilm than the wild type strain and presented a cell-cell aggregative phenotype. These results indicate that σ54 differentially regulates genes involved in type IV and type I fimbrial biogenesis, and is involved in biofilm formation in X. fastidiosa.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alm RA, Mattick JS (1995) Identification of a gene, pilV, required for type 4 fimbrial biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, whose product possesses a pre-pilin-like leader sequence. Mol Microbiol 16:485–496
Ball CA, Brazma A, Causton H, Chervitz S, Edgar R, Hingamp P, Matese JC, Parkinson H, Quackenbush J, Ringwald M, Sansone SA, Sherlock G, Spellman P, Stoeckert C, Tateno Y, Taylor R, White J, Winegarden N (2004) Submission of microarray data to public repositories. PLoS Biol 2:E317
Barrios H, Valderrama B, Morett E (1999) Compilation and analysis of sigma (54)-dependent promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27:4305–4313
Bhaya D, Bianco NR, Bryant D, Grossman A (2000) Type IV pilus biogenesis and motility in the Cyanobacterium synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Mol Microbiol 37:941–951
Buck M, Gallegos MT, Studholme DJ, Guo Y, Gralla JD (2000) The bacterial enhancer-dependent sigma (54) (sigma (N)) transcription factor. J Bacteriol 182:4129–4136
Burgess RR, Knuth MW (1996) Purification of a recombinant protein overproduced in Escherichia coli. In: Marshak DR, Kadonaga JT, Burgess RR, Knuth M, Brennan WA, Lin SH (eds) Strategies for protein purification and characterization: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 205–274
Campoy S, Mazón G, Fernández de Henestrosa AR, Llagostera M, Monteiro PB, Barbé J (2002) A new regulatory DNA motif of the gamma subclass Proteobacteria: identification of the LexA protein binding site of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Microbiology 148:3583–3597
Craig L, Pique ME, Tainer JA (2004) Type IV pilus structure and bacterial pathogenicity. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:363–378
da Silva Neto JF, Koide T, Gomes SL, Marques MV (2002) Site-directed gene disruption in Xylella fastidiosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 210:105–110
da Silva Neto JF, Koide T, Gomes SL, Marques MV (2007) The single extracytoplasmic-function sigma factor of Xylella fastidiosa is involved in the heat shock response and presents an unusual regulatory mechanism. J Bacteriol 189:551–560
Davis MJ, French WJ, Schaad NW (1981) Axenic culture of the bacteria associated with phony peach disease of peach and plum leaf scald. Curr Microbiol 6:309–314
De La Fuente L, Montanes E, Meng Y, Li Y, Burr TJ, Hoch HC, Wu M (2007) Assessing adhesion forces of type I and type IV pili of Xylella fastidiosa bacteria by use of a microfluidic flow chamber. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2690–2696
de Souza AA, Takita MA, Coletta-Filho HD, Caldana C, Goldman GH, Yanai GM, Muto NH, de Oliveira RC, Nunes LR, Machado MA (2003) Analysis of gene expression in two growth states of Xylella fastidiosa and its relationship with pathogenicity. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:867–875
Feil H, Feil WS, Detter JC, Purcell AH, Lindow SE (2003) Site-directed disruption of the fimA and fimF fimbrial genes of Xylella fastidiosa. Phytopathology 93:675–682
Gaurivaud P, Souza LC, Virgilio AC, Mariano AG, Palma RR, Monteiro PB (2002) Gene disruption by homologous recombination in the Xylella fastidiosa citrus variegated chlorosis strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4658–4665
Gil H, Benach JL, Thanassi DG (2004) Presence of pili on the surface of Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun 72:3042–3047
Graupner S, Wackernagel W (2001) Pseudomonas stutzeri has two closely related pilA genes (type IV pilus structural protein) with opposite influences on natural genetic transformation. J Bacteriol 183:2359–2366
Grigorova IL, Phleger NJ, Mutalik VK, Gross CA (2006) Insights into transcriptional regulation and sigma competition from an equilibrium model of RNA polymerase binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5332–5337
Gruber TM, Gross CA (2003) Multiple sigma subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:441–466
Guilhabert MR, Kirkpatrick BC (2005) Identification of Xylella fastidiosa antivirulence genes: hemagglutinin adhesins contribute to X. fastidiosa biofilm maturation and colonization and attenuate virulence. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:856–868
Ishimoto KS, Lory S (1989) Formation of pilin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires the alternative sigma factor (RpoN) of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:1954–1957
Ishimoto KS, Lory S (1992) Identification of pilR, which encodes a transcriptional activator of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin gene. J Bacteriol 174:3514–3521
Kang Y, Liu H, Genin S, Schell MA, Denny TP (2002) Ralstonia solanacearum requires type 4 pili to adhere to multiple surfaces and for natural transformation and virulence. Mol Microbiol 46:427–437
Koide T, Zaini PA, Moreira LM, Vêncio RZ, Matsukuma AY, Durham AM, Teixeira DC, El-Dorry H, Monteiro PB, da Silva AC, Verjovski-Almeida S, da Silva AM, Gomes SL (2004) DNA microarray-based genome comparison of a pathogenic and a nonpathogenic strain of Xylella fastidiosa delineates genes important for bacterial virulence. J Bacteriol 186:5442–5449
Koide T, Vencio RZN, Gomes SL (2006) Global gene expression analysis of the heat shock response in the phytopathogen Xylella fastidiosa. J Bacteriol 188:5821–5830
Lang EA, Marques MV (2004) Identification and transcriptional control of Caulobacter crescentus genes encoding proteins containing a cold shock domain. J Bacteriol 186:5603–5613
Li Y, Hao G, Galvani CD, Meng Y, De La Fuente L, Hoch HC, Burr TJ (2007) Type I and type IV pili of Xylella fastidiosa affect twitching motility, biofilm formation and cell-cell aggregation. Microbiology 153:719–726
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods 25:402–408
Mattick JS (2002) Type IV pili and twitching motility. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:289–314
Meng Y, Li Y, Galvani CD, Hao G, Turner JN, Burr TJ, Hoch HC (2005) Upstream migration of Xylella fastidiosa via pilus-driven twitching motility. J Bacteriol 187:5560–5567
Merrick MJ (1993) In a class of its own—the RNA polymerase sigma factor sigma 54 (sigma N). Mol Microbiol 10:903–909
Merrick MJ, Coppard JR (1989) Mutations in genes downstream of the rpoN gene (encoding sigma 54) of Klebsiella pneumoniae affect expression from sigma 54-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol 3:1765–1775
Monteiro PB, Teixeira DC, Palma RR, Garnier M, Bové JM, Renaudin J (2001) Stable transformation of the Xylella fastidiosa citrus variegated chlorosis strain with oriC plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2263–2269
Moreira LM, de Souza RF, Almeida Jr NF, Setubal JC, Oliveira JCF, Furlan LR, Ferro JA, da Silva ACR (2004) Comparative genomics analysis of citrus-associated bacteria. Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:163–1184
Newman KL, Almeida RP, Purcell AH, Lindow SE (2004) Cell-cell signaling controls Xylella fastidiosa interactions with both insects and plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1737–1742
Parker D, Kennan RM, Myers GS, Paulsen IT, Songer JG, Rood JI (2006) Regulation of type IV fimbrial biogenesis in Dichelobacter nodosus. J Bacteriol 188:4801–4811
Pizarro-Cerdá J, Cossart P (2006) Bacterial adhesion and entry into host cells. Cell 124:715–727
Purcell AH, Hopkins DL (1996) Fastidious xylem-limited bacterial plant pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:131–151
Rakotoarivonina H, Larson MA, Morrison M, Girardeau JP, Gaillard-Martinie B, Forano E, Mosoni P (2005) The Ruminococcus albus pilA1-pilA2 locus: expression and putative role of two adjacent pil genes in pilus formation and bacterial adhesion to cellulose. Microbiology 151:1291–1299
Reitzer L, Schneider BL (2001) Metabolic context and possible physiological themes of sigma (54)-dependent genes in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:422–444
Simpson AJ, Reinach FC, Arruda P, Abreu FA, Acencio M, Alvarenga R, Alves LM, Araya JE, Baia GS, Baptista CS, Barros MH, Bonaccorsi ED, Bordin S, Bove JM, Briones MR, Bueno MR, Camargo AA, Camargo LE, Carraro DM, Carrer H, Colauto NB, Colombo C, Costa FF, Costa MC, Costa-Neto CM, Coutinho LL, Cristofani M, Dias-Neto E, Docena C, El-Dorry H, Facincani AP, Ferreira AJ, Ferreira VC, Ferro JA, Fraga JS, Franca SC, Franco MC, Frohme M, Furlan LR, Garnier M, Goldman GH, Goldman MH, Gomes SL, Gruber A, Ho PL, Hoheisel JD, Junqueira ML, Kemper EL, Kitajima JP, Krieger JE, Kuramae EE, Laigret F, Lambais MR, Leite LC, Lemos EG, Lemos MV, Lopes SA, Lopes CR, Machado JA, Machado MA, Madeira AM, Madeira HM, Marino CL, Marques MV, Martins EA, Martins EM, Matsukuma AY, Menck CF, Miracca EC, Miyaki CY, Monteriro-Vitorello CB, Moon DH, Nagai MA, Nascimento AL, Netto LE, Nhani A Jr, Nobrega FG, Nunes LR, Oliveira MA, de Oliveira MC, de Oliveira RC, Palmieri DA, Paris A, Peixoto BR, Pereira GA, Pereira HA Jr, Pesquero JB, Quaggio RB, Roberto PG, Rodrigues V, de M Rosa AJ, de Rosa VE Jr, de Sa RG, Santelli RV, Sawasaki HE, da Silva AC, da Silva AM, da Silva FR, da Silva WA Jr, da Silveira JF, Silvestri ML, Siqueira WJ, de Souza AA, de Souza AP, Terenzi MF, Truffi D, Tsai SM, Tsuhako MH, Vallada H, Van Sluys MA, Verjovski-Almeida S, Vettore AL, Zago MA, Zatz M, Meidanis J, Setubal JC (2000) The genome sequence of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Nature 406:151–157
Smolka MB, Martins D, Winck FV, Santoro CE, Castellari RR, Ferrari F, Brum IJ, Galembeck E, Della Coletta Filho H, Machado MA, Marangoni S, Novello JC (2003) Proteome analysis of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa reveals major cellular and extracellular proteins and a peculiar codon bias distribution. Proteomics 3:224–237
Souza LC, Wulff NA, Gaurivaud P, Mariano AG, Virgilio AC, Azevedo JL, Monteiro PB (2006) Disruption of Xylella fastidiosa CVC gumB and gumF genes affects biofilm formation without a detectable influence on exopolysaccharide production. FEMS Microbiol Lett 257:236–242
Studholme DJ, Dixon R (2003) Domain architectures of sigma 54-dependent transcriptional activators. J Bacteriol 185:1757–1767
Studholme DJ, Buck M, Nixon BT (2000) Identification of potential σN-dependent promoters in bacterial genomes. Microbiology 146:3021–3023
Totten PA, Lara JC, Lory S (1990) The rpoN gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for expression of diverse genes, including the flagellin gene. J Bacteriol 172:389–396
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Van Sluys MA, de Oliveira MC, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Miyaki CY, Furlan LR, Camargo LE, da Silva AC, Moon DH, Takita MA, Lemos EG, Machado MA, Ferro MI, da Silva FR, Goldman MH, Goldman GH, Lemos MV, El-Dorry H, Tsai SM, Carrer H, Carraro DM, de Oliveira RC, Nunes LR, Siqueira WJ, Coutinho LL, Kimura ET, Ferro ES, Harakava R, Kuramae EE, Marino CL, Giglioti E, Abreu IL, Alves LM, do Amaral AM, Baia GS, Blanco SR, Brito MS, Cannavan FS, Celestino AV, da Cunha AF, Fenille RC, Ferro JA, Formighieri EF, Kishi LT, Leoni SG, Oliveira AR, Rosa VE Jr, Sassaki FT, Sena JA, de Souza AA, Truffi D, Tsukumo F, Yanai GM, Zaros LG, Civerolo EL, Simpson AJ, Almeida NF Jr, Setubal JC, Kitajima JP (2003) Comparative analyses of the complete genome sequences of Pierce`s disease and citrus variegated chlorosis strains of Xylella fastidiosa. J Bacteriol 185:1018–1026
Vencio RZN, Koide T (2005) HTself: self-self based statistical test for low replication microarray studies. DNA Res 12:211–214
Villar MT, Hirschberg RL, Schaefer MR (2001) Role of the Eikenella corrodens pilA locus in pilus function and phase variation. J Bacteriol 183:55–62
Wells JM, Raju BC, Hung HY, Weisburg WG, Mandelco-Paul L, Brenner DJ (1987) Xylella fastidiosa gen. nov., sp. nov.: gram-negative, xylem-limited, fastidious plant bacteria related to Xanthomonas spp. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:136–143
Wolfgang M, van Putten JP, Hayes SF, Koomey M (1999) The comP locus of Neisseria gonorrhoeae encodes a type IV prepilin that is dispensable for pilus biogenesis but essential for natural transformation. Mol Microbiol 31:1345–1357
Wosten MMSM (1998) Eubacterial sigma-factors. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:127–150
Wu SS, Kaiser D (1997) Regulation of expression of the pilA gene in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol 179:7748–7758
Yang YH, Dudoit S, Luu P, Lin DM, Peng V, Ngai J, Speed TP (2002) Normalization for cDNA microarray data: a robust composite method addressing single and multiple slide systematic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e15
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). During the course of this work, J. F. S. N. and T. K. were supported by predoctoral fellowships from FAPESP. M. V. M. and S. L. G. are partly supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jack Meeks.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva Neto, J.F., Koide, T., Abe, C.M. et al. Role of σ54 in the regulation of genes involved in type I and type IV pili biogenesis in Xylella fastidiosa . Arch Microbiol 189, 249–261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0314-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0314-x