Abstract
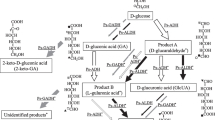
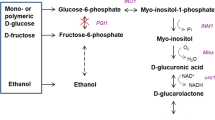
The bacterium Oenococcus oeni employs the heterolactic fermentation pathway (products lactate, ethanol, CO2) during growth on fructose as a substrate, and the mannitol pathway when using fructose as an electron acceptor. In this study, [U-13C]glucose, [U-13C]fructose, HPLC, NMR spectroscopy, and enzyme analysis were applied to elucidate the use of both pathways by the hexoses. In the presence of glucose or pyruvate, fructose was metabolized either by the mannitol or the phosphoketolase pathways, respectively. Phosphoglucose isomerase, which is required for channeling fructose into the phosphoketolase pathways, was inhibited by a mixed-type inhibition composed of competitive (K i=180 μM) and uncompetitive (K′i=350 μM) inhibition by 6-phosphogluconate. Erythrose 4-phosphate inhibited phosphoglucose isomerase competitively (K i=1.3 μM) with a low contribution of uncompetitive inhibition (K′i=13 μM). The cellular 6-phosphogluconate content during growth on fructose plus pyruvate (<75 μM) was significantly lower than during growth on fructose alone or fructose plus glucose (550 and 480 μM). We conclude that competitive inhibition of phosphoglucose isomerase by 6-phosphogluconate (and possibly erythrose 4-phosphate) is responsible for exclusion of fructose from the phosphoketolase pathway during growth on fructose plus glucose, but not during growth on fructose plus pyruvate.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Graaf AA, Mahle M, Möllney M, Wiechert W, Stahmann P, Sahm H (2000) Determination of full 13C isotopomer distributions for metabolic flux analysis using heteronuclear spin echo difference NMR spectroscopy. J Biotechnol 77:25–35
Dicks LM, Dellaglio F, Collins MD (1995) Proposal to reclassify Leuconostoc oenos as Oenococcus oeni [corrig.] gen. Nov., comb. Nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:395–397
Garvie EI (1967) The growth factor and amino acid requirements of species of the genus Leuconostoc, including Leuconostoc paramesenteroides (sp. nov.) and Leuconostoc oenos. J Gen Microbiol 48:439–447
Haid E (1974) D-Gluconat-6-phosphat. In Bergmeyer, HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, p. 1293
Hansen T, Oehlmann M, Schönheit P (2001) Novel type of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Bacteriol 183:3428–3435
Maicas S, Ferrer S, Pardo I. (2002) NAD(P)H regeneration is the key for heterolactic fermentation of hexoses in Oenococcus oeni. Microbiology 148:325–332
Nuraida L, Grigolava I, Owens JD, Campbell-Platt G (1992) Oxygen and pyruvate as external electron acceptors for Leuconostoc spp. J Appl Bacteriol 72:517–522
Petersen S, de Graaf AA, Eggeling L, Möllney M, Wiechert W, Sahm H (2000) In vivo quantitation of parallel and bidirectional fluxes in the anaplerosis of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biol Chem 175:35932–35–949
Pradhan PG, Nadkarni GB (1980) Functional multiplicty of phosphoglucose isomerase from Lactobacillus casei. Biochim Biophys Acta 615:465–473
Richter H, Vlad D, Unden G (2001) Significance of pantothenate for glucose fermentation by Oenoccoccus oeni and for suppression of the erythritol and acetate production. Arch Microbiol 175:26–31
Richter H, Hamann I, Unden G (2003) Use of the mannitol pathway in fructose fermentation of Oenococcus oeni due to limiting redox regeneration capacity of the ethanol pathway. Arch Microbiol 179:227–233
Ruijter GJG, Visser J (1999) Characterization of Aspergillus niger phosphoglucose isomerase. Use for quantitative determination of erythrose 4-phosphate. Biochimie 81:267–272
Salema M, Lolkema JS, San Romao MV, Loureiro Dias MC (1996) The proton motive force generated in Leuconostoc oenos by L-malate fermentation. J Bacteriol 178:3127–3132
Salou P, Loubiere P, Pareilleux A (1994) Growth and energetics of Leuconostoc oenos during cometabolism of glucose with citrate or fructose. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1459–1466
Szyperski T (1995) Biosynthetically directed fractional 13C-labeling of proteinogenic amino acids—an efficient analytical tool to investigate intermediary metabolism. Eur J Biochem 232:433–448
Takama M, Nosoh Y (1980) Purification and some properties of 6-phosphoglucose isomerase from Bacillus caldotenax. J Biochem 87:1821–1827
Veiga-Da-Cunha M, Firme P, San Romao MV, Santos H (1992) Application of [13C] nuclear magnetic resonance to elucidate the unexpected biosynthesis of erythritol by Leuconostoc oenos. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2271–2279
Veiga-Da-Cunha M, Santos H, van Schaftingen E (1993) Pathway and regulation of erythritol formation in Leuconostoc oenos. J Bacteriol 175:3941–3948
Voet D, Voet JG (1995) Biochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grants from Innovationsstiftung Rheinland-Pfalz and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie. We are grateful to Dr. Sprenger (Jülich) for helpful discussions, and to T. Zaunmüller for expert support with some of the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, H., De Graaf, A.A., Hamann, I. et al. Significance of phosphoglucose isomerase for the shift between heterolactic and mannitol fermentation of fructose by Oenococcus oeni . Arch Microbiol 180, 465–470 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-003-0617-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-003-0617-5