Abstract
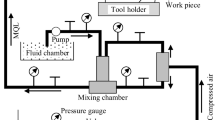
Micro end milling has an outstanding capability in machining micro-scale structures of various materials. Prediction of cutting forces is significant on controlling quality and safety of machining process. This paper proposes a mechanic model to predict cutting forces in micro end milling process, which includes a novel algorithm of instant uncut chip thickness. This algorithm takes into account the geometric errors of machining system and trochoidal trajectory of cutting edge, which redefines cutting radii with consideration of the tool runout. A feasible technique to reduce the influence of tool runout is put forward by analyzing the redefined cutting radii. Since the existing method for cutting force coefficient identification is generally conducted using finite element simulation, it is difficult for some composite materials due to lack of the material properties. To overcome the above shortcomings, an experimental-based cutting force coefficient identification technique has been developed by groove milling. A number of experimental testing have been conducted to validate the developed cutting force model. Experimental results are in good agreement with theoretical predictions, which demonstrates the validity of proposed cutting force modeling.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Uhlmann E, Piltz S, Doll U (2005) Machining of micro/miniature dies and moulds by electrical discharge machining - recent development. J Mater Process Technol 167(2-3):488–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.06.013
Boswell B, Islam MN, Davies IJ (2018) A review of micro-mechanical cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(1-4):789–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0912-y
Camara MA, Campos Rubio JC, Abrao AM et al (2012) State of the art on micromilling of materials, a review. J Mater Sci Technol 28(8):673–685
Liang C, Wang F, Huo Z et al (2019) A 2-DOF monolithic compliant rotation platform driven by piezoelectric actuators. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(8):6963–6974
Miao JC, Chen GL, Lai XM, Li HT, Li CF (2007) Review of dynamic issues in micro-end-milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31(9):897–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-0276-6
Altintas Y, Jin X (2011) Mechanics of micro-milling with round edge tools. CIRP Ann 60(1):77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.084
Zhang XW, Ehmann KF, Yu TB et al (2016) Cutting forces in micro-end-milling processes. Int J Mach Tool Manu 107:21–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.04.012
Tansel I, Rodriguez O, Trujillo M, Paz E, Li W (1998) Micro-end-milling - I. Wear and breakage. Int J Mach Tool Manu 38(12):1419–1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0890-6955(98)00015-7
Bao WY, Tansel IN (2000) Modeling micro-end-milling operations. Part I: analytical cutting force model. Int J Mach Tool Manu 40(15):2155–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0890-6955(00)00054-7
Bao WY, Tansel IN (2000) Modeling micro-end-milling operations. Part II: tool run-out. Int J Mach Tool Manu 40(15):2175–2192. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0890-6955(00)00055-9
Li HZ, Liu K, Li XP (2001) A new method for determining the undeformed chip thickness in milling. J Mater Process Technol 113(1-3):378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-0136(01)00586-6
Dow TA, Miller EL, Garrard K (2004) Tool force and deflection compensation for small milling tools. Precision Eng J Int Soc Prec Eng Nanotechnol 28(1):31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-6359(03)00072-2
Vogler MP, Kapoo SG, Devor RE (2004) On the modeling and analysis of machining performance in micro-endmilling, Part II: Cutting force prediction. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans Asme 126(4):695–705. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1813471
Bissacco G, Hansen HN, Slunsky J (2008) Modelling the cutting edge radius size effect for force prediction in micro milling. Cirp Annals-Manuf Technol 57(1):113–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.085
Lai X, Li H, Li C, Lin Z, Ni J (2008) Modelling and analysis of micro scale milling considering size effect, micro cutter edge radius and minimum chip thickness. Int J Mach Tool Manu 48(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2007.08.011
Malekian M, Park SS, Jun MBC (2009) Modeling of dynamic micro-milling cutting forces. Int J Mach Tool Manu 49(7-8):586–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.02.006
Jin X, Altintas Y (2012) Prediction of micro-milling forces with finite element method. J Mater Process Technol 212(3):542–552
Jing X, Li H, Wang J, Tian Y (2014) Modelling the cutting forces in micro-end-milling using a hybrid approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(9-12):1647–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5953-x
De Oliveira FB, Rodrigues AR, Coelho RT et al (2015) Size effect and minimum chip thickness in micromilling. Int J Mach Tool Manu 89:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2014.11.001
Grossi N, Sallese L, Scippa A, Campatelli G (2015) Speed-varying cutting force coefficient identification in milling. Precision Eng J Int Soc Prec Eng Nanotechnol 42:321–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.04.006
Mamedov A, Layegh KSE, Lazoglu I (2015) Instantaneous tool deflection model for micro milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(5-8):769–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6877-9
Thepsonthi T, Ozel T (2015) 3-D finite element process simulation of micro-end milling Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy: experimental validations on chip flow and tool wear. J Mater Process Technol 221:128–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.02.019
Zhang X, Yu T, Wang W (2017) Instantaneous uncut chip thickness modeling for micro-end milling process. Mach Sci Technol 21(4):582–602. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2017.1336181
Yuan Y, Jing X, Ehmann KF, Cao J, Li H, Zhang D (2018) Modeling of cutting forces in micro end-milling. J Manuf Process 31:844–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.01.012
Jing X, Li H, Wang J, Tian Y (2014) Modelling the cutting forces in micro-end-milling using a hybrid approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(9-12):1647–1656
Zhou Y, Tian Y, Jing X, Ehmann KF (2017) A novel instantaneous uncut chip thickness model for mechanistic cutting force model in micro-end-milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(5-8):2305–2319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0638-x
Zhang X, Yu T, Wang W (2019) Cutting forces modeling for micro flat end milling by considering tool run-out and bottom edge cutting effect. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 233(2):470–485. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405417726811
Armarego E (1998) A generic mechanics of cutting approach to predictive technological performance modeling of the wide spectrum of machining operations. Mach Sci Technol 2(2):191–211
Jing X, Tian Y, Yuan Y, Wang F (2017) A runout measuring method using modeling and simulation cutting force in micro end-milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(9):4191–4201
Mittal RK, Kulkarni SS, Singh RK (2017) Effect of lubrication on machining response and dynamic instability in high-speed micromilling of Ti-6Al-4V. J Manuf Process 28:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.04.007
Wojciechowski S, Matuszak M, Powalka B et al (2019) Prediction of cutting forces during micro end milling considering chip thickness accumulation. Int J Mach Tool Manu 147:103466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.103466
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the supports of the Laboratory of Precision Manufacturing Technology (CAEP. NO. ZM18007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weijie Wang: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and writing. Weiwei Zhang: Resources and supervision. Dingchuan Huang: Data curation and original draft. Wei Wang: Validation and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhang, W., Huang, D. et al. Cutting force modeling and experimental validation for micro end milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117, 933–947 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07815-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07815-8