Abstract
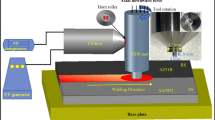
AA2219 aluminium alloy plates of large thickness ratios were successfully produced by refill friction stir spot welding (RFSSW) method. In addition to common defects, such as holes and hook, insufficient refill and weak bonding also appeared in the joints with large thickness ratios. Besides, the stir zone of the typical RFSSWed joint exhibited refined and equiaxed grains because of the dynamic recrystallization, while the elongated grains with a large proportion of the low angle grain boundaries were the main microstructure features in the thermomechanically affected zone due to insufficient heat input and deformation. Moreover, in all cases of large thickness ratio, the micro-hardness distribution of the joints presented an M-shaped profile. The maximum tensile-shear strength reached 7.2 kN, corresponding to the rotation speed of 2000 rpm, welding time of 3.6 s and plunge depth of 2.2 mm, which displayed a close correlation with the defect morphology, such as the weak bonding length and hook height. Also, two types of fracture modes were observed in the tensile-shear specimens, plug fracture mode and mixed fracture mode.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/ or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zhao S, Bi QZ, Wang YH, Shi J (2016) Empirical modelling for the effects of welding factors on tensile properties of bobbin tool friction stir-welded 2219-T87 aluminium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:1105–1118
Zhang J, Dong CL, Li G, Luan GH (2009) Application of friction stir spot welding in aviation industry. Aeronautical Manuf Technol 16:70–73
Shen ZK, Ding Y, Chen J, Fu L, Liu XC, Chen H (2019) Microstructure static and fatigue properties of refill friction stir spot welded 7075-T6 aluminium alloy using a modified tool. Sci Technol Weld Join 24:587–600
Ji SD, Wen Q, Li ZW (2020) A novel friction stir diffusion bonding process using convex-vortex pin tools. J Mater Sci Technol 48:23–30
Salih OS, Neate N, Ou H, Sun W (2020) Influence of process parameters on the microstructural evolution and mechanical characterisations of friction stir welded Al-Mg-Si alloy. J Mater Process Technol 275:116366
Mousavizade SM, Pouranvari M (2018) Projection friction stir spot welding: a pathway to produce strong keyhole-free welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 24:256–262
Prakash SJ, Muthukumaran S (2011) Refilling probe hole of friction spot joints by friction forming. Mater Manuf Process 26:1539–1545
Shen ZK, Ding Y, Gerlich AP (2020) Advances in friction stir spot welding. Crit Rev Solid State 45(6):457–534
Chu Q, Li WY, Hou HL, Yang XW, Vairis A, Wang C, Wang WB (2019) On the double-side probeless friction stir spot welding of AA2198 Al-Li alloy. J Mater Sci Technol 35:784–789
Xu ZW, Li ZW, Ji SD, Zhang L (2018) Refill friction stir spot welding of 5083-O aluminium alloy. J Mater Sci Technol 34:878–885
Li P, Chen S, Dong HG, Ji H, Li YB, Guo X, Yang GS, Zhao XS, Han XL (2020) Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar aluminium/ steel joint fabricated via refilled friction stir spot welding. J Manuf Process 49:85–396
Yue YM, Shi Y, Ji SD, Wang Y, Li ZW (2017) Effect of sleeve plunge depth on microstructure and mechanical properties of refill friction stir spot welding of 2198 aluminium alloy. J Mater Eng Perform 26:5064–5071
Chen Y, Chen J, Amirkhiz BS, Worswick MJ, Gerlich AP (2015) Microstructures and properties of Mg alloy/ DP600 steel dissimilar refill friction stir spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 20:494–501
Yoon SO, Kang MS, Kwon YJ, Hong ST, Park DH, Lee KH (2012) Influences of tool plunge speed and tool plunge depth on friction spot joining of AA5454-O aluminium alloy plates with different thicknesses. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 22:629–633
Zhang DK, Li Q, Zhao Y, Liu XL, Song JL, Wang GQ, Wu AP (2018) Microstructure and mechanical properties of three-layer TIG-welded 2219 aluminium alloys with dissimilar heat treatments. J Mater Eng Perform 27:2938–2948
Rosendo T, Parra B, Tier MAD, Silva AAMD, Santos JFD, Strohaecker TR (2011) Mechanical and microstructural investigation of friction spot welded AA6181-T4 aluminium alloy. Mater Des 32:1094–1100
Sato YS, Takauchi H, Park SHC, Kokawa H (2005) Characteristics of the kissing-bond in friction stir welded Al alloy 1050. Mater Sci Eng A 405:33–38
Rajesh S, Badheka VJ (2017) Process parameters/material location affecting hooking in friction stir lap welding: dissimilar aluminium alloys. Mater Manuf Process 33:323–332
Wu YN, Liao HC, Yang J, Zhou KX (2014) Effect of Si content on dynamic recrystallization of Al-Si-Mg alloys during hot extrusion. J Mater Sci Technol 30:1271–1277
Yang C, Wu CS, Shi L (2019) Phase-field modelling of dynamic recrystallization process during friction stir welding of aluminium alloys. Sci Technol Weld Join 25:345–358
Silva BH, Zepon G, Bolfarini C, dos Santos JF (2020) Refill friction stir spot welding of AA6082-T6 alloy: hook defect formation and its influence on the mechanical properties and fracture behavior. Mater Sci Eng A 773:138–724
Santana LM, Suhuddin UFH, Lscher MH, Strohaecker TR, dos Santos JF (2017) Process optimization and microstructure analysis in refill friction stir spot welding of 3-mm-thick Al-Mg-Si aluminium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:4213–4220
Zhou L, Luo LY, Zhang TP, He WX, Huang YX, Feng JC (2017) Effect of rotation speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of refill friction stir spot welded 6061-T6 aluminium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:3425–3433
Kubit A, Bucior M, Wydrzyński D, Trzepiecinski T, Pytel M (2017) Failure mechanisms of refill friction stir spot welded 7075-T6 aluminium alloy single-lap joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94:4479–4491
Funding
The authors receive financial support from the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing (NPU, China) (2019-QZ-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yangfan Zou: investigation, data curation, writing.
Wenya Li: reviewing, editing.
Qiang Chu: investigation, reviewing.
Zhikang Shen: technical guidance.
Feifan Wang: investigation, supervision.
Huawei Tang: reviewing and editing.
Achilles Vairis: grammar checking.
Liyuan Liu: investigation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Y., Li, W., Chu, Q. et al. The impact of macro/microstructure features on the mechanical properties of refill friction stir spot–welded joints of AA2219 alloy with a large thickness ratio. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 112, 3093–3103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06504-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06504-2