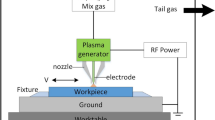
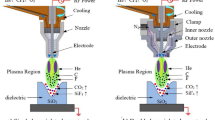
Abstract
Continuous phase plate (CPP) with complex surface structures is used to smooth the focal spot of laser beam. Great demand for CPP in laser fusion system requires mass production technology with low cost. Therefore, the rapid fabrication method for CPP using atmospheric pressure plasma processing (APPP) is presented in this paper. Firstly, the fundamental characteristics of APPP were studied to obtain the optimal processing parameters. Considering the influence on etching rate from surface temperature, trench machining experiments were conducted to establish the exponential model of influence function. Based on this model, the iterative calculation method for dwell time was developed to minimize the thermal effect on machining error, and the sinusoidal surface experiments prove its effectiveness. At last, a 320 mm × 320 mm × 2 mm CPP of BOROFLOAT33 (B33) with 2.78 μm PV was fabricated within 16 h using APPP, and the RMS of form error is 96 nm. The far field focal spot of the machined CPP was calculated. The result shows that the machined CPP has an acceptable beam-shaping function, which demonstrates the potential for fabricating CPP using APPP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wegner PJ, Auerbach JM, Biesiada TA, Dixit SN, Lawson JK, Menapace JA, Parham TG, Swift DW, Whitman PK, Williams WH (2004) NIF final optics system: frequency conversion and beam conditioning. In: Optical Engineering at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory II: The National Ignition Facility. International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 180–190
Xu M, Dai Y, Xie X, Zhou L, Peng W (2017) Fabrication of continuous phase plates with small structures based on recursive frequency filtered ion beam figuring. Opt Express 25(10):10765–10778
Tricard M, Dumas P, Menapace J (2008) Continuous phase plate polishing using magnetorheological finishing. In: Laser Beam Shaping IX. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 70620V
Mori Y, Yamamura K, Yamauchi K, Yoshii K, Kataoka T, Endo K, Inagaki K, Kakiuchi H (1993) Plasma CVM (chemical vaporization machining): an ultra precision machining technique using high-pressure reactive plasma. Nanotechnology 4(4):225–229
Mori Y, Yamamura K, Sano Y (1993) Plasma-CVM (Chemical Vaporization Machining). Crystal Growth Technol 1993:587–606
Arnold T, Boehm G, Eichentopf IM, Janietz M, Meister J, Schindler A (2010) Plasma jet machining. Vakuum in Forschung und Praxis 22(4):10–16
Arnold T, Böhm G, Paetzelt H (2016) Nonconventional ultra-precision manufacturing of ULE mirror surfaces using atmospheric reactive plasma jets. In: Advances in Optical and Mechanical Technologies for Telescopes and Instrumentation II. International Society for Optics and Photonics p 99123N
Castelli M, Jourdain R, Morantz P, Shore P (2012) Rapid optical surface figuring using reactive atom plasma. Precis Eng 36(3):467–476
Takino H, Yamamura K, Sano Y, Mori Y (2010) Removal characteristics of plasma chemical vaporization machining with a pipe electrode for optical fabrication. Appl Opt 49(23):4434–4440
Takino H, Shibata N, Itoh H, Kobayashi T, Yamamura K, Sano Y, Mori Y (2002) Fabrication of optics by use of plasma chemical vaporization machining with a pipe electrode. Appl Opt 41(19):3971–3977
Takino H, Shibata N, Itoh H, Kobayashi T, Tanaka H, Ebi M, Yamamura K, Sano Y, Mori Y (1998) Computer numerically controlled plasma chemical vaporization machining with a pipe electrode for optical fabrication. Appl Opt 37(22):5198–5210
Meister J, Böhm G, Eichentopf IM, Arnold T (2009) Simulation of the substrate temperature field for plasma assisted chemical etching. Plasma Process Polym 6(S1):S209–S213
Meister J, Arnold T (2011) New process simulation procedure for high-rate plasma jet machining. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 31(1):91–107
Arnold T, Meister J, Böhm G (2008) Atmospheric plasma jet machining: simulation of Spatio-temporal substrate surface temperature distributions. In: Optical Fabrication and Testing
Castelli M, Jourdain R, Mcmeeking G, Morantz P, Shore P, Proscia D, Subrahmanyan P (2010) Initial strategies for 3D RAP processing of optical surfaces based on a temperature adaptation approach. Springer London
Jourdain R, Castelli M, Yu N, Gourma M, Shore P (2016) Estimation of the power absorbed by the surface of optical components processed by an inductively coupled plasma torch. Appl Therm Eng 108:1372–1382
Qiang X, Peng Z, Na L, Bo W (2016) Research on the Electron temperature and emission spectroscopy of the atmospheric inductively coupled with plasma processing. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 36(6):1872–1876
Lieberman MA, Lichtenberg AJ (2005) Principles of plasma discharges and materials processing. John Wiley & Sons,
Yao Y, Wang B, Wang J, Jin H, Zhang Y, Dong S (2010) Chemical machining of Zerodur material with atmospheric pressure plasma jet. CIRP Ann 59(1):337–340
SCHOTT BOROFLOAT® 33. https://wwwschottcom/borofloat/english/production/indexhtml
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51175123) and the National Science and Technology Major Project (2013ZX04006011-205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, X., Zhang, P., Liu, K. et al. Fabrication of continuous phase plate using atmospheric pressure plasma processing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105, 4559–4570 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03406-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03406-w