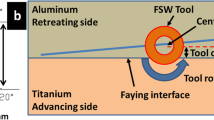
Abstract
This investigation highlights the influence of tool offset on the microstructural evolution, phase formation, and hardness distribution during friction stir welding (FSW) of commercially pure aluminum (Al) to commercially pure titanium (Ti) with a copper (Cu) interlayer (200-μm thick). It was observed that tool offset position controls the mechanical mixing of materials in the weld nugget. The mechanical mixing also depends on the deformation, fragmentation, and distribution of each material in the weld nugget. The fragmentation of materials leads to the development of comparatively fine particles with variation in size and morphology. Insufficient mixing at higher tool offsets promotes the formation of root defects and produces inferior welds. On the other hand, when the tool offset is less than the optimum value, severe deformation and mechanical mixing lead to the formation of wormhole defects and evolution of intermetallic compounds in the weld. The spatial distribution of particles and intermetallics in the weld nugget leads to a large scatter in hardness values. Since mechanical mixing affects the morphology, phase evolution, and mechanical properties of the weld, tool offset is considered to be a very important parameter to be optimized for monitoring mechanical mixing and further development of the dissimilar weld with interlayer material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sujata M, Bhargava S, Sangal S (1997) On the formation of TiAl3 during reaction between solid Ti and liquid Al. J Mater Sci Lett 16(13):1175–1178. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1018509026596
Shouzheng W, Yajiang L, Juan W, Kun L, Pengfei Z (2014) Microstructure and joining mechanism of Ti/Al dissimilar joint by pulsed gas metal arc welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(5):1137–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5290-5
Chen Y, Chen S, Li L (2008) Effects of heat input on microstructure and mechanical property of Al/Ti joints by rectangular spot laser welding-brazing method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(3):265–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1837-2
Shouzheng W, Yajiang L, Juan W, Kun L (2014) Improving of interfacial microstructure of Ti/Al joint during GTA welding by adopting pulsed current. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(9):1307–1312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5929-x
Chen YC, Nakata K (2009) Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties in friction stir welding of aluminum and titanium dissimilar alloys. Mater Des 30(3):469–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.06.008
Kreimeyer M, Wagner F, Vollertsen F (2005) Laser processing of aluminum–titanium-tailored blanks. Opt Lasers Eng 43(9):1021–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2004.07.005
Majumdar B, Galun R, Weisheit A, Mordike BL (1997) Formation of a crack-free joint between Ti alloy and Al alloy by using a high-power CO2 laser. J Mater Sci 32(23):6191–6200. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1018620723793
Dressler U, Biallas G, Alfaro Mercado U (2009) Friction stir welding of titanium alloy TiAl6V4 to aluminium alloy AA2024-T3. Mater Sci Eng A 526(1–2):113–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.07.006
Watanabe T, Takayama H, Yanagisawa A (2006) Joining of aluminum alloy to steel by friction stir welding. J Mater Process Technol 178(1):342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.04.117
Fuji A (2002) In situ observation of interlayer growth during heat treatment of friction weld joint between pure titanium and pure aluminium. Sci Technol Weld Join 7(6):413–416. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217102225006903
Kim YC, Fuji A (2002) Factors dominating joint characteristics in Ti – Al friction welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 7(3):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217102225004185
Fuji A, Ikeuchi K, Sato YS, Kokawa H (2004) Interlayer growth at interfaces of Ti/Al–1%Mn, Ti/Al–4·6%Mg and Ti/pure Al friction weld joints by post-weld heat treatment. Sci Technol Weld Join 9(6):507–512. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217104225021797
Wilden J, Bergmann JP (2004) Manufacturing of titanium/aluminium and titanium/steel joints by means of diffusion welding. Weld Cut 56(5):285–290
Çam G, Koçak M, Dobi D, Heikinheimo L, Siren M (1997) Fracture behaviour of diffusion bonded bimaterial Ti–Al joints. Sci Technol Weld Join 2(3):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1179/stw.1997.2.3.95
Kar A, Suwas S, Kailas SV (2018) Two-pass friction stir welding of aluminum alloy to titanium alloy: a simultaneous improvement in mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng A 733:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.057
Kar A, Devinder Y, Suwas S, Kailas SV (2016) A study of deformation and microstructural evolution in friction stir welding of aluminum and titanium. Trends Weld Res S39-1:728–731
Çam G, İpekoğlu G (2017) Recent developments in joining of aluminum alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(5):1851–1866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9861-0
Çam G, Mistikoglu S (2014) Recent developments in friction stir welding of Al-alloys. J Mater Eng Perform 23(6):1936–1953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0968-x
Bozkurt Y, Salman S, Çam G (2013) Effect of welding parameters on lap shear tensile properties of dissimilar friction stir spot welded AA 5754-H22/2024-T3 joints. Sci Technol Weld Join 18(4):337–345. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813y.0000000111
Zhang HJ, Wang M, Qi RL, Zhu Z, Zhang X, Yu T, Wu ZQ (2017) Effect of rotation speed on nugget structure and property of high rotation speed friction stir welded Al-Mn aluminum alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(5–8):2401–2410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0295-0
İpekoğlu G, Erim S, Çam G (2014) Effects of temper condition and post weld heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir butt-welded AA7075 Al alloy plates. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(1):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5255-8
Mao Y, Ke L, Chen Y, Liu F, Xing L (2017) Improving local and global mechanical properties of friction stir welded thick AA7075-T6 joints by optimizing pin-tip profile. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88(5–8):1863–1875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8886-8
Çam G (2011) Friction stir welded structural materials: beyond Al-alloys. Int Mater Rev 56(1):1–48. https://doi.org/10.1179/095066010x12777205875750
Mironov S, Onuma T, Sato YS, Yoneyama S, Kokawa H (2017) Tensile behavior of friction-stir welded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 679:272–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.10.036
Buffa G, Campanella D, Forcellese A, Fratini L, La Commare U, Simoncini M (2018) In-process control strategies for friction stir welding of AZ31 sheets with non-uniform thickness. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(1–4):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1223-z
Dorbane A, Ayoub G, Mansoor B, Hamade RF, Kridli G, Shabadi R, Imad A (2016) Microstructural observations and tensile fracture behavior of FSW twin roll cast AZ31 Mg sheets. Mater Sci Eng A 649:190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.09.097
Küçükömeroğlu T, Şentürk E, Kara L, İpekoğlu G, Çam G (2016) Microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welded nickel-aluminum bronze (NAB) alloy. J Mater Eng Perform 25(1):320–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1838-x
Çam G, Serindağ HT, Çakan A, Mistikoglu S, Yavuz H (2008) The effect of weld parameters on friction stir welding of brass plates. Mater Werkst 39(6):394–399. https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.200800314
Gao Y, Morisada Y, Fujii H, Liao J (2018) Dissimilar friction stir lap welding of magnesium to aluminum using plasma electrolytic oxidation interlayer. Mater Sci Eng A 711:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.11.034
Günen A, Kanca E, Demir M, Çavdar F, Mistikoğlu S, Çam G (2018) Microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welded pure lead. Indian J Eng Mat Sci 25(1):26–32
Chen Y-h, Ni Q, Ke L-m (2012) Interface characteristic of friction stir welding lap joints of Ti/Al dissimilar alloys. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 22(2):299–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61174-6
Aonuma M, Nakata K (2011) Dissimilar metal joining of 2024 and 7075 aluminium alloys to titanium alloys by friction stir welding. Mater Trans 52(5):948–952. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.L-MZ201102
Bang H, Bang H, Song H, Joo S (2013) Joint properties of dissimilar Al6061-T6 aluminum alloy/Ti–6%Al–4%V titanium alloy by gas tungsten arc welding assisted hybrid friction stir welding. Mater Des 51:544–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.04.057
Aonuma M, Nakata K (2010) Effect of calcium on intermetallic compound layer at interface of calcium added magnesium–aluminum alloy and titanium joint by friction stir welding. Mater Sci Eng B 173(1–3):135–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2009.12.015
Wei Y, Li J, Xiong J, Huang F, Zhang F, Raza SH (2012) Joining aluminum to titanium alloy by friction stir lap welding with cutting pin. Mater Charact 71:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2012.05.013
Cole EG, Fehrenbacher A, Duffie NA, Zinn MR, Pfefferkorn FE, Ferrier NJ (2014) Weld temperature effects during friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys 6061-t6 and 7075-t6. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(1):643–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5485-9
Rajakumar S, Muralidharan C, Balasubramanian V (2011) Statistical analysis to predict grain size and hardness of the weld nugget of friction-stir-welded AA6061-T6 aluminium alloy joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 57(1):151–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3279-5
Dixit S, MH C, Kailas SV, Chattopadhyay K (2017) Role of insert material on process loads during FSW. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(9):3427–3435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9974-5
Kar A, Suwas S, Kailas SV (2017) An investigation on friction stir welding of aluminum to titanium using a nickel interlayer. Conference proceedings: Indian Institute of Welding-International Congress C051: 261–266
Abdollah-Zadeh A, Saeid T, Sazgari B (2008) Microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welded aluminum/copper lap joints. J Alloys Compd 460(1):535–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.06.009
Barekatain H, Kazeminezhad M, Kokabi AH (2014) Microstructure and mechanical properties in dissimilar butt friction stir welding of severely plastic deformed aluminum AA 1050 and commercially pure copper sheets. J Mat Sci Technol 30(8):826–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.11.007
Kim S-Y, Jung S-B, Shur C-C, Yeon Y-M, Kim D-U (2003) Mechanical properties of copper to titanium joined by friction welding. J Mater Sci 38(6):1281–1287. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022890611264
Xue P, Xiao BL, Ni DR, Ma ZY (2010) Enhanced mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar Al–Cu joint by intermetallic compounds. Mater Sci Eng A 527(21–22):5723–5727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.05.061
Ouyang JH, Kovacevic R (2002) Material flow and microstructure in the friction stir butt welds of the same and dissimilar aluminum alloys. J Mater Eng Perform 11(1):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-002-0008-0
Song Z, Nakata K, Wu A, Liao J, Zhou L (2014) Influence of probe offset distance on interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir butt welded joint of Ti6Al4V and A6061 dissimilar alloys. Mater Des 57:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.12.040
Çam G, İpekoğlu G, Tarık Serindağ H (2014) Effects of use of higher strength interlayer and external cooling on properties of friction stir welded AA6061-T6 joints. Sci Technol Weld Join 19(8):715–720. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171814y.0000000247
Xu RZ, Ni DR, Yang Q, Liu CZ, Ma ZY (2015) Influence of Zn interlayer addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ31 Mg alloy. J Mater Sci 50(12):4160–4173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8841-3
Nadammal N, Kailas SV, Suwas S (2015) A bottom-up approach for optimization of friction stir processing parameters; a study on aluminium 2024-T3 alloy. Mat Des (1980–2015) 65:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.09.005
Chen S, Yang D, Li M, Zhang Y, Huang J, Yang J, Zhao X (2016) Laser penetration welding of an overlap titanium-on-aluminum configuration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(9):3069–3079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8732-z
Gao X-L, Liu J, Zhang L-J (2018) Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of pulsed laser welded joints in Ti6Al4V/Nb dissimilar alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(9):3937–3947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1134-z
Rajakumar S, Balasubramanian V (2016) Diffusion bonding of titanium and AA 7075 aluminum alloy dissimilar joints—process modeling and optimization using desirability approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(1):1095–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-8223-7
Zhu Z, Lee KY, Wang X (2012) Ultrasonic welding of dissimilar metals, AA6061 and Ti6Al4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59(5):569–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3534-9
Zhou L, Min J, He WX, Huang YX, Song XG (2018) Effect of welding time on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Ti ultrasonic spot welds. J Manuf Process 33:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.04.013
Plaine AH, Suhuddin UFH, Alcântara NG, dos Santos JF (2017) Microstructure and mechanical behavior of friction spot welded AA6181-T4/Ti6Al4V dissimilar joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(9):3703–3714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0439-2
Wei Y, Li J, Xiong J, Zhang F (2016) Investigation of interdiffusion and intermetallic compounds in Al–Cu joint produced by continuous drive friction welding. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19(1):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2015.05.009
Kattner UR, Lin J-C, Chang YA (1992) Thermodynamic assessment and calculation of the Ti-Al system. Metall Trans A 23(8):2081–2090. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02646001
Wei Y, Aiping W, Guisheng Z, Jialie R (2008) Formation process of the bonding joint in Ti/Al diffusion bonding. Mater Sci Eng A 480(1–2):456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.07.027
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Institute X-ray facility and Advanced Facility for Microscopy and Microanalysis (AFMM) at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore, for providing the facilities.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), Department of Science and Technology (DST), and Ministry of Human Resources Development (MHRD), India, for the support and research funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, A., Suwas, S. & Kailas, S.V. Significance of tool offset and copper interlayer during friction stir welding of aluminum to titanium. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100, 435–443 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2682-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2682-6