Abstract
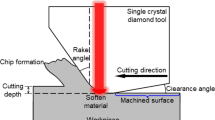
A method for fabricating a diamond tool with controllable edge radius was proposed. Using diamond tools with different edge radii at a low speed, nano-cutting tests were performed on single crystal silicon using a special instrument with SEM online observation. The chip morphology and deformation coefficient were analyzed to study the size effect of tool edge in the ductile-cut region. Electron back-scattered diffraction and laser micro-Raman spectroscopy were employed to detect subsurface damage in the machined silicon. The results indicated that the cutting-induced amorphous layer thickness is strongly dependent on the depth of cut and tool edge radius. In the beginning, the amorphous damage layer thickness decreases rapidly with the depth of cut, and then it increases gradually with the further increase in the depth of cut. The minimum amorphous damage can be obtained when the depth of cut is comparable to the tool edge radius.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi DH, Lee JR, Kang NR, Je TJ, Kim JY, Jeon EC (2017) Study on ductile mode machining of single-crystal silicon by mechanical machining. Int J Mach Tool Manu 113:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.10.006
Liang Z, Wu Y, Wang X, Zhao W (2010) A new two-dimensional ultrasonic assisted grinding (2d-uag) method and its fundamental performance in monocrystal silicon machining. Int J Mach Tool Manu 50(8):728–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.04.005
Fang C, Zhao Z, Lu L, Lin Y (2017) Influence of fixed abrasive configuration on the polishing process of silicon wafers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8808-9
Fang F, Xu F, Lai M (2015) Size effect in material removal by cutting at nano scale. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80(1–4):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7032-3
Fang F, Liu B, Xu Z (2015) Nanometric cutting in a scanning electron microscope. Precis Eng 41:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.01.009
Auzelyte V, Gallinet B, Flauraud V, Santschi C, Dutta-Gupta S, Martin OJF, Brugger J (2013) Large-area gold/parylene plasmonic nanostructures fabricated by direct nanocutting. Adv Opt Mater 1(1):50–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201200017
Zhang Z, Guo D, Kang R, Gao H, Jin Z, Meng Y (2010) Subsurface crystal lattice deformation machined by ultraprecision grinding of soft-brittle CdZnTe crystals. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(9–12):1065–1081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2253-y
Xu F, Fang F, Zhang X (2018) Effects of recovery and side flow on surface generation in nano-cutting of single crystal silicon. Comput Mater Sci 143:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2017.11.002
Zhang P, Zhao H, Zhang L, Shi C, Huang H (2014) A study on material removal caused by phase transformation of monocrystalline silicon during nanocutting process via molecular dynamics simulation. J Comput Theor Nanosci 11(1):291–296. https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2014.3350
Zhao CW, Xing YM (2008) Nanoscale experimental study of a micro-crack in silicon. Physica B 403(23–24):4202–4204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.09.004
Dahlman P, Gunnberg F, Jacobson M (2004) The influence of rake angle, cutting feed and cutting depth on residual stresses in hard turning. J Mater Process Technol 147(2):181–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.12.014
Yan J, Asami T, Harada H, Kuriyagawa T (2009) Fundamental investigation of subsurface damage in single crystalline silicon caused by diamond machining. Precis Eng 33(4):378–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2008.10.008
Agarwal S, Rao PV (2008) Experimental investigation of surface/subsurface damage formation and material removal mechanisms in SiC grinding. Int J Mach Tool Manu 48(6):698–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2007.10.013
Azimi M, Mirjavadi SS, Hamouda AMS, Makki H (2017) Heterogeneities in polymer structural and dynamic properties in graphene and graphene oxide nanocomposites: molecular dynamics simulations. Macromol Theory Simul 26(2):1600086. https://doi.org/10.1002/mats.201600086
Dai H, Chen G, Fang Q, Yin J (2016) The effect of tool geometry on subsurface damage and material removal in nanometric cutting single-crystal silicon by a molecular dynamics simulation. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 122(9):804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0319-x
Wang Z, Chen J, Wang G, Bai Q, Liang Y (2017) Anisotropy of single-crystal silicon in nanometric cutting. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):300. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-2046-4
Zhao H, Shi C, Zhang P, Zhang L, Huang H, Yan J (2012) Research on the effects of machining-induced subsurface damages on mono-crystalline silicon via molecular dynamics simulation. Appl Surf Sci 259(41):66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.06.087
Liu K, Li XP, Rahman M, Neo KS, Liu XD (2007) A study of the effect of tool cutting edge radius on ductile cutting of silicon wafers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(7–8):631–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-0364-7
Zhu Y, Xiang Z, Xie LL, Zhang YC, Zhao XC (2015) Study of the effects of cutting parameters on poly-silicon nano machining. Appl Mech Mater 697:369–372. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.697.369
Uddin MS, Seah KHW, Li XP, Rahman M, Liu K (2004) Effect of crystallographic orientation on wear of diamond tools for nano-scale ductile cutting of silicon. Wear 257(7–8):751–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2004.03.012
Xu ZW, Fang FZ, Zhang SJ, Zhang XD, Hu XT, Fu YQ, Li L (2010) Fabrication of micro DOE using micro tools shaped with focused ion beam. Opt Express 18(8):8025–8032. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.008025
Mallock A (1881) The action of cutting tools. Proc R Soc Lond 33(2751):118–120. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspl.1881.0079
Liu B, Xu Z, Fang F, Zhao B (2015) Experimental study on in-situ nanometric cutting based on SEM. J Tianjin Univ Sci Technol (11):1035–1040. https://doi.org/10.11784/tdxbz201501067
Crawford THR, Yamanaka J, Botton GA, Hangen HK (2008) High-resolution observations of an amorphous layer and subsurface damage formed by femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J Appl Phys 103(5):215–453. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2885111
Gogotsi Y, Baek C, Kirscht F (1999) Raman microspectroscopy study of processing-induced phase transformations and residual stress in silicon. Semicond Sci Technol 14(10):936–944. https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/14/10/310
Mirjavadi SS, Alipour M, Hamouda AMS, Matin A, Kord S, Afshari BM, Koppad PG (2017) Effect of multi-pass friction stir processing on the microstructure, mechanical and wear properties of AA5083/ZrO 2 nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd 726:1262–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.084
Mirjavadi SS, Alipour M, Emamian S, Kord S, Hamouda AMS, Koppad PG, Keshavamurthy R (2017) Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles incorporation to friction stir welded 5083 aluminum alloy on the microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance. J Alloys Compd 712:795–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.04.114
Fang FZ, Wu H, Zhou W, Hu XT (2007) A study on mechanism of nano-cutting single crystal silicon. J MATER PROCESS TECH 184(1):407–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.12.007
Yan J, Asami T, Harada H, Kuriyagawa T (2012) Crystallographic effect on subsurface damage formation in silicon microcutting. CIRP ANN-MANUF TECHN 61(1):131–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2012.03.070
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the MNMT Lab for the support with the experimental instruments.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (Grant No. 17JCZDJC38200) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51575389).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(MPG 18418 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Fang, F., Li, R. et al. Experimental study on size effect of tool edge and subsurface damage of single crystal silicon in nano-cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98, 1093–1101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2310-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2310-5