Abstract
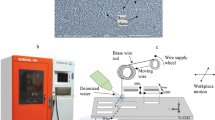
The development of cladded materials to augment the industrial requirements is grown because of having combination of properties in end use applications. However, the real challenge regarding the application of these materials is its machining with reasonable surface finish and accuracy owing to the heterogeneous nature. Therefore, oftenly, thermal cutting process like gas cutting and plasma arc cutting are used, but these processes not only offer poor surface quality but also necessitate additional finishing operations. Wire electric discharge machining (WEDM) process is a viable alternate but the roughness generated on the two surfaces is different as the said process is thermoelectric in nature and both layers of material have different thermoelectric properties. In the current research the cutting performance of WEDM of stainless clad steel has been evaluated with a focus not only to reduce the surface roughness of individual layer but also to minimize the difference as well. The influence of uncommon parameters, such as layer thickness of specific layer, workpiece orientation, pressure ratio, and wire diameter are primarily investigated. Wire diameter and workpiece orientation have proved to be the significant control factors affecting the surface roughness of both the layers, whereas pressure ratio affects the surface roughness of one layer (mild steel). Optimal settings of control factors have been developed using grey relational analysis. The results of confirmatory experiment validates the model as not only the surface roughness of both layers have been decreased, but also the difference comes to be minimal of only about 0.02 μm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao RV, Kalyankar VD (2014) Optimization of modern machining processes using advanced optimization techniques: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73:1159–1188
Kumar A, Kumar V, Kumar J (2016) Surface crack density and recast layer thickness analysis in WEDM process through response surface methodology. Mach Sci Technol 20(2):201–230
B. Azhiri, R. Teimouri, M. Ghasemi Baboly, and Z. Leseman (2014) Application of Taguchi, ANFIS and grey relational analysis for studying, modeling and optimization of wire EDM process while using gaseous media, Int J Adv Manuf Technol
A. Varun and N. Venkaiah (2014) Simultaneous optimization of WEDM responses using grey relational analysis coupled with genetic algorithm while machining EN 353, Int J Adv Manuf Technol
I. Maher, A. A. D. Sarhan, and M. Hamdi (2014) Review of improvements in wire electrode properties for longer working time and utilization in wire EDM machining, Int J Adv Manuf Technol
Pragadish N, Pradeep Kumar M (2016) Optimization of dry EDM process parameters using grey relational analysis. Arab J Sci Eng 41(11):4383–4390
Altug M, Erdem M, Ozay C (2015) Experimental investigation of kerf of Ti6Al4V exposed to different heat treatment processes in WEDM and optimization of parameters using genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78:1573–1583
K. Kanlayasiri and S. Boonmung (2007) Effects of wire-EDM machining variables on surface roughness of newly developed DC 53 die steel: design of experiments and regression model, J Mater Process Technol
Li L, Li ZY, Wei XT, Cheng X (2015) Machining characteristics of Inconel 718 by sinking-EDM and wire-EDM. Mater Manuf Process 30(8):968–973
Raju P, Sarcar MMM, Satyanarayana B (2014) Optimization of wire electric discharge machining parameters for surface roughness on 316 L stainless steel using full factorial experimental design. Procedia Mater Sci 5:1670–1676
C. Zhang (2014) Effect of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) parameters on surface integrity of nanocomposite ceramics, Ceram Int, vol. 40, no. 7 PART A, pp. 9657–9662
Gopal PM, Prakash KS, Jayaraj S (2017) WEDM of mg/CRT/BN composites: effect of materials and machining parameters. Mater Manuf Process:1–8
Materials Hand Book by Georges, Brady, Henry R.Clauser, John A. Vaccari, 15th edition, ISBN No. 0–07-136076-X, McGraw-Hill
www.asminternational.org/documents/.../152a4ca7-ca11-4a48-ad7d-4c2b2c39bd16. Accessed on 10/5/2017, 4: 40pm
corrosiondoctors.org/MetalCoatings/Cladding.htm. Accessed on 15/5/2017, 3:10pm
http://www.steel-intelligence.com/product reports/articles/the-market-for-clad-plate.html. Accessed on 1/6/2017, 2:30pm
Nieslony P, Cichosz P, Krolczyk GM, Legutko S, Smyczek D, Kolodziej M (2016) Experimental studies of the cutting force and surface morphology of explosively clad Ti-steel plates. Meas J Int Meas Confed 78:129–137
http://www.jfesteel.co.jp/en/products/plate/catalog/c1e-009.pdf. Accessed on 9/6/2017, 9:30am
Tosun N, Cogun C, Inan A (2003) The effect of cutting parameters on workpiece surface roughness in wire EDM. Mach Sci Technol 7(2):209–219
Lopez JG, Verleysen P, Degrieck J (2012) Effect of fatigue damage on static and dynamic tensile behaviour of electro-discharge machined Ti-6Al-4 V. Int J Fatigue Frac Eng Mater Struct 35(12):1120–1132
Ghodsiyeh D, Golshan A, Izman S (2014) Multi-objective process optimization of wire electrical discharge machining based on response surface methodology. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 36(2):301–313
Bobbili R, Madhu V, Gogia AK (2013) Effect of wire-EDM machining parameters on surface roughness and material removal rate of high strength armor steel. Mater Manuf Process 28(4):364–368
Khan NZ, Khan ZA, Siddiquee AN, Chanda AK (2014) Investigations on the effect of wire EDM process parameters on surface integrity of HSLA: a multi-performance characteristics optimization. Prod Manuf Res 2(1):501–518
Mandal A, Dixit AR, Das AK, Mandal N (2016) Modeling and optimization of machining nimonic C-263 superalloy using multicut strategy in WEDM. Mater Manuf Process 31(7):860–868
Yang RT, Tzeng CJ, Yang YK, Hsieh MH (2012) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters for cutting tungsten. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60(1–4):135–147
Kumar K, Agarwal S (2012) Multi-objective parametric optimization on machining with wire electric discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(5–8):617–633
Sharma P, Chakradhar D, Narendranath S (2016) Effect of wire diameter on surface integrity of wire electrical discharge machined Inconel 706 for gas turbine application. J Manuf Process 24:170–178
Singh V, Bhandari R, Yadav VK (2016) An experimental investigation on machining parameters of AISI D2 steel using WEDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol:1–12
Durairaj M, Sudharsun D, Swamynathan N (2013) Analysis of process parameters in wire EDM with stainless steel using single objective Taguchi method and multi objective grey relational grade. Procedia Engineering 64:868–877
K. Rajmohan and A. S. Kumar (2016) Experimental investigation and prediction of optimum process parameters of micro-wire-cut EDM of 2205 DSS, Int J Adv Manuf Technol, pp. 1–15
http://www.azom.com/properties.aspx?ArticleID=863. Accessed on 12/4/2017 at 12:20pm
http://www.matweb.com/search/datasheet. aspx?matguid=9ccee2d0841a404ca504620085056e14 accessed on 12/4/2017 at 12:40pm
K. Ishfaq, R. Naveed, S. A. Khan, A. Hussain, and F. Noor (2016) Taguchi’s based optimization of machining parameters to control surface roughness using TiAlN-coated tungsten carbide milling cutter, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 19–28
J. Morán, E. Granada, J. L. Míguez, and J. Porteiro (2006) Use of grey relational analysis to assess and optimize small biomass boilers, in Fuel Processing Technology, vol. 87, no. 2, pp. 123–127
Kuo Y, Yang T, Huang GW (2008) The use of grey relational analysis in solving multiple attribute decision-making problems. Comput Ind Eng 55(1):80–93
Pramanik A, Littlefair G (2016) Wire EDM mechanism of MMCs with the variation of reinforced particle size. Mater Manuf Process 31(13):1700–1708
S. Rajendran, M. Sakthivel, and S. Dharamalingam (2014) Investigation on effect of surface integrity and layer thickness using T90Mn2W50Cr45 tool steel, Mater Manuf Process, vol. 6914, no. August 2014, p.140808143743007
A. A. Khan, M. H. F. A. Hazza, M. R. H. C. Daud, and N. S. B. M. Kamal (2016) Optimization of surface quality of mild steel machined by wire EDM using simulated annealing algorithm, in Proceedings - 2015 4th international conference on advanced computer science applications and technologies, ACSAT 2015
Miller SF, Shih AJ, Qu J (2004) Investigation of the spark cycle on material removal rate in wire electrical discharge machining of advanced materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(4):391–400
Habib S (2017) Optimization of machining parameters and wire vibration in wire electrical discharge machining process. Mech Adv Mater Mod Process 3(1):3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishfaq, K., Mufti, N.A., Ahmed, N. et al. An investigation of surface roughness and parametric optimization during wire electric discharge machining of cladded material. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97, 4065–4079 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2240-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2240-2