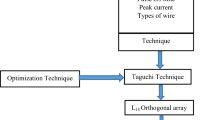
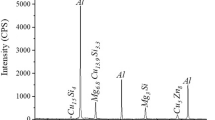
Abstract
Determining the optimal cutting parameters has always been a critical matter to achieve high performance in different types of machining. In this study the behavior of four major control parameters includes pulse on time (T on), pulse off time (T off), peak current (IP), and servo voltage base on design of experiment method during wire electrical discharge machining of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4 V) experimentally studied. A zinc-coated brass wire of 0.25 mm diameter was used as a tool electrode to cut the specimen. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) technique was used to find out the parameters affecting the surface roughness, sparking gap, wire lag, wire wear ratio, and white layer thickness. Assumptions of ANOVA were discussed and carefully examined. This work has been established as a second-order mathematical model based on the response surface methodology. The residual analysis and confirmation runs indicate that the proposed model could adequately describe the performance of the factors those are being investigated. The results are particularly useful for scientists and engineers to determine which subset of the process variable has the maximum influence on the process performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Datta S, Mahapatra SS (2010) Modeling, simulation and parametric optimization of wire-EDM process using response surface methodology coupled with grey-Taguchi technique. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2:162–183
Boyer HE, Gall TL (1985) Metals handbook. American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, pp 9.1–9.12
Donachie Jr, Matthew J (2000) Titanium-A technical guide, 2nd edn, ASM Int., pp 318–323
Lopez JG, Verleysen P, Degrieck J (2012) Effect of fatigue damage on static and dynamic tensile behaviour of electro-discharge machined Ti-6Al-4 V. Int J Fatigue Frac Eng Mater Struct 35(12):1120–1132
Parashar V, Rehman A, Bhagoria JL, Puri YM (2010) Kerfs width analysis for wire cut electro discharge machining of SS 304L using design of experiments. Indian J Sci Technol 3(4):369–373
Ghodsiyeh D, Golshan A, Shirvanehdeh JA (2013) Review on current research trends in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). Indian J Sci Technol 6(2):154–168
Tosun N, Cogun C, Inan A (2003) The effect of cutting parameters on workpiece surface roughness in wire EDM. Mach Sci Technol Int J 7(2):209–219
Tosun N, Cogun C (2003) An investigation on wire wear in WEDM. J Mater Process Technol 134(3):273–278
Tosun N, Cogun C, Tosun G (2004) A study on kerf and material removal rate in wire electrical discharge machining based on Taguchi method. J Mater Process Technol 152:316–322
Huang JT, Liao YS, Hsue WJ (1999) Determination of finish cutting operation number and machining parameters setting in wire electrical discharge machining. J Mater Process Technol 87:69–81
Puri AB, Bhattacharyya B (2003) An analysis and optimisation of the geometrical inaccuracy due to wire lag phenomenon in WEDM. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:151–159
Mahapatra SS, Patnaik Amar (2006) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(9–10):911–925
Mahapatra SS, Patnaik Amar (2006) Parametric optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process using Taguchi method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 28(4):422–429
Kanlayasiri K, Boonmung S (2007) Effects of wire-EDM machining variables on surface roughness of newly developed DC 53 die steel: design of experiments and regression model. J Mater Process Technol 192–193:459–464
Vamsi KP, Surendra BB, Madar VP, Swapna M (2010) Optimizing surface finish in WEDM using the Taguchi parameter design method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 22(2):107–113
Newton TR, Melkote SN, Watkins TR, Trejo RM, Reister L (2009) Investigation of the effect of process parameters on the formation and characteristics of recast layer in wire-EDM of Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A 513–514:208–215
Kuruvila N, Ravindra HV (2011) Parametric influence and optimization of wire EDM of hot die steel. Mach Sci Technol Int J 15(1):47–75
Montgomery DC (2009) Design and analysis of experiments, 7th edn. John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pvt Ltd, Singapore, pp 207–264
Scott D, Boyina S, Rajurkar KP (1991) Analysis and optimization of parameter combination in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Prod Res 29(11):2189–2207
Noordin MY, Venkatesh VC, Sharif S, Elting S, Abdullah A (2004) Application of response surface methodology in describing the performance of coated carbide tools when turning AISI 1045 steel. J Mater Process Technol 145:46–58
Routara B, Bandyopadhyay A, Sahoo P (2009) Roughness modeling and optimization in CNC end milling using response surface method: effect of workpiece material variation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40:1166–1180
Sarkar S, Mitra S, Bhattacharyya B (2005) Parametric analysis and optimization of wire electrical discharge machining of γ-titanium aluminide alloy. J Mater Process Technol 159:286–294
Kanlayasiri K, Boonmung S (2007) An investigation on effects of wire-EDM machining parameters on surface roughness of newly developed DC53 die steel. J Mater Process Technol 187–188:26–29
Shah A, Mufti AN, Rakwal D, Bamberg E (2011) Material removal rate kerf and surface roughness of tungsten carbide machined with wire electrical discharge MACHINING. J Mater Eng Perform 20:71–76
Bobbili R, Madhu V, Gogia AK (2013) Effect of wire-EDM machining parameters on surface roughness and material removal rate of high strength armor steel. Mater Manuf Process 28(4):364–368
Swain AK, Ray S, Mandal NK (2012) Study on Kerf width in wire-EDM based on Taguchi method. Appl Mech Mater 110–116:1808–1816
Po-Huai Y, Hsiang-Kuo L, Yang-Xin L, Shi-Jie Q, Biing-Hwa Y, Fuang-Yuan H (2011) Machining characteristics of polycrystalline silicon by wire electrical discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 26(12):1443–1450
Ramakrishnan R, Karunamoorthy L (2006) Multi response optimization of wire EDM operations using robust design of experiments. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29:105–112
Puri AB, Bhattacharyya B (2005) Modeling and analysis of white layer depth in a wire-cut EDM process through response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:301–307
Myers RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-Cook CM (2009) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New Jersy, pp 244–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Alexandre Mendes Abrao.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghodsiyeh, D., Golshan, A. & Izman, S. Multi-objective process optimization of wire electrical discharge machining based on response surface methodology. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 36, 301–313 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-013-0079-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-013-0079-x