Abstract
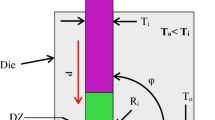
Equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) is one of the most prominent severe plastic deformation (SPD) processes to achieve ultra-fine grained (UFG) structures. Using bimetallic specimens has been recently considered in this process. In the present study, the effects of casing with lower strength, compared to the billet, and the casing thickness on mechanical properties of ECAPed billet are investigated experimentally and by simulation. Bimetallic specimens of pure Cu and Al-7075 alloy with different dimensions are ECAPed in one pass at room temperature. The effect of casing and its thickness on the required forming load, the average amount of equivalent plastic strain and Vickers micro-hardness, and their distributions in cross section of billet, strain homogeneity, compression strength of billets, and stress distribution in the deformation zone are investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwahashi Y, Wang J, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1996) Principle of equal-channel angular pressing for the processing of ultra-fine grained materials. Scr Mater 35(2):143–146
Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (2006) Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog Mater Sci 51(7):881–981
Xu C, Langdon TG (2003) Influence of a round corner die on flow homogeneity in ECA pressing. Scr Mater 48(1):1–4
Xu C, Langdon TG (2007) The development of hardness homogeneity in aluminum and an aluminum alloy processed by ECAP. J Mater Sci 42(5):1542–1550
Nakashima K, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (2000) Development of a multi-pass facility for equal-channel angular pressing to high total strains. Mater Sci Eng A 281(1):82–87
Zhao X, Yang X, Liu X, Wang X, Langdon TG (2010) The processing of pure titanium through multiple passes of ECAP at room temperature. Mater Sci Eng A 527(23):6335–6339
Zhang Y, Figueiredo RB, Alhajeri SN, Wang JT, Gao N, Langdon TG (2011) Structure and mechanical properties of commercial purity titanium processed by ECAP at room temperature. Mater Sci Eng A 528(25):7708–7714
Zhao X, Yang X, Liu X, Wang CT, Huang Y, Langdon TG (2014) Processing of commercial purity titanium by ECAP using a 90 degrees die at room temperature. Mater Sci Eng A 607:482–489
Cornwall LR, Hartwig KT, Goforth RE, Semiatin SL (1996) The equal channel angular extrusion process for materials processing. Mater Charact 37(5):295–300
Valiev RZ, Islamgaliev RK, Alexandrov IV (2000) Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation. Prog Mater Sci 45(2):103–189
Eivani AR, Taheri AK (2007) A new method for producing bimetallic rods. Mater Lett 61(19):4110–4113
Zebardast M, Taheri AK (2011) The cold welding of copper to aluminum using equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) process. J Mater Process Technol 211(6):1034–1043
Djavanroodi F, Daneshtalab M, Ebrahimi M (2012) A novel technique to increase strain distribution homogeneity for ECAPed materials. Mater Sci Eng A 535:115–121
Shaeri MH, Djavanroodi F, Sedighi M, Ahmadi S, Salehi MT, Seyyedein SH (2013) Effect of copper tube casing on strain distribution and mechanical properties of Al-7075 alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. The Journal of Strain Analysis for Engineering Design 48(8):512–521
Djavanroodi F, Zolfaghari AA, Ebrahimi M, Nikbin KM (2013) Equal channel angular pressing of tubular samples. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters) 26(5):574–580
Li Y, Ng HP, Jung HD, Kim HE, Estrin Y (2014) Enhancement of mechanical properties of grade 4 titanium by equal channel angular pressing with billet encapsulation. Mater Lett 114:144–147
Djavanroodi F, Zolfaghari AA, Ebrahimi M, Nikbin K (2014) Route effect on equal channel angular pressing of copper tube. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters) 27(1):95–100
Djavanroodi F, Zolfaghari AA, Ebrahimi M (2015) Experimental investigation of three different tube equal channel angular pressing techniques. Kovove Materialy 53:27–34
Yapici GG, Karaman I, Luo ZP, Rack H (2003) Microstructure and mechanical properties of severely deformed powder processed Ti–6Al–4V using equal channel angular extrusion. Scr Mater 49(10):1021–1027
Pham Q, Jeong YG, Hong SH, Kim HS (2006) Equal channel angular pressing of carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Key Eng Mater 326-328:325–328
Segal VM (1977) The method of material preparation for subsequent working. Patent of the USSR 575892
Segal VM, Reznikov VI, Drobyshevskii AE, Kopylov VI (1981) Plastic working of metals by simple shear. Russ Metall 1:99–105
Djavanroodi F, Ebrahimi M (2010) Effect of die channel angle, friction and back pressure in the equal channel angular pressing using 3D finite element simulation. Mater Sci Eng A 527(4):1230–1235
Djavanroodi F, Ahmadian H, Koohkan K, Naseri R (2013) Ultrasonic assisted-ECAP. Ultrasonics 53(6):1089–1096
Djavanroodi F, Ahmadian H, Naseri R, Koohkan K, Ebrahimi M (2016) Experimental investigation of ultrasonic assisted equal channel angular pressing process. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering 16(3):249–255
Zhao X, Yang X, Jia J, Qi B (2014) The evolution of hardness homogeneity in commercially pure Ti processed by ECAP. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Materials Science Edition 29(3):578–584
Prell M, Xu C, Langdon TG (2008) The evolution of homogeneity on longitudinal sections during processing by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A 480(1):449–455
Alhajeri SN, Gao N, Langdon TG (2011) Hardness homogeneity on longitudinal and transverse sections of an aluminum alloy processed by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A 528(10):3833–3840
Stolyarov VV, Zhu YT, Alexandrov IV, Lowe TC, Valiev RZ (2001) Influence of ECAP routes on the microstructure and properties of pure Ti. Mater Sci Eng A 299(1):59–67
Yu X, Li Y, Wei Q, Guo Y, Suo T, Zhao F (2015) Microstructure and mechanical behavior of ECAP processed AZ31B over a wide range of loading rates under compression and tension. Mech Mater 86:55–70
Djavanroodi F, Ebrahimi M (2010) Effect of die parameters and material properties in ECAP with parallel channels. Mater Sci Eng A 527(29):7593–7599
Ahmadabadi MN, Shirazi H, Ghasemi-Nanesa H, Nedjad SH, Poorganji B, Furuhara T (2011) Role of severe plastic deformation on the formation of nanograins and nano-sized precipitates in Fe–Ni–Mn steel. Mater Des 32(6):3526–3531
Semiatin SL, Delo DP, Shell EB (2000) The effect of material properties and tooling design on deformation and fracture during equal channel angular extrusion. Acta Mater 48(8):1841–1851
Prangnell PB, Harris C, Roberts SM (1997) Finite element modelling of equal channel angular extrusion. Scr Mater 37(7):983–989
Shan A, Moon IG, Ko HS, Park JW (1999) Direct observation of shear deformation during equal channel angular pressing of pure aluminum. Scr Mater 41(4):353–357
Yoon SC, Kim HS (2008) Finite element analysis of the effect of the inner corner angle in equal channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A 490(1):438–444
Figueiredo RB, Aguilar MTP, Cetlin PR (2006) Finite element modelling of plastic instability during ECAP processing of flow-softening materials. Mater Sci Eng A 430(1):179–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseri, R., Kadkhodayan, M. & Shariati, M. An experimental investigation of casing effect on mechanical properties of billet in ECAP process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90, 3203–3216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9658-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9658-1