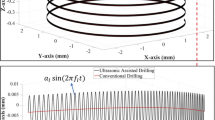
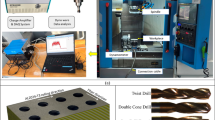
Abstract
In this research work, an ultrasonic assisted drilling system is employed to apply both rotation and vibration to drill bits. The transducer horn transfers power very efficiently and changes tools effortlessly. The setup used to conduct drilling tests is Inconel 738LC with depth-to-diameter ratios from 2 to 10 by conventional drilling (CD), ultrasonic assisted drilling (UAD), and electro discharge drilling (EDD). The effects of ultrasonic vibration amplitude, spindle speed, and number of steps to drill each hole on machining force and surface roughness in UAD are investigated. The results demonstrate not only a significant improvement in tool life (by applying ultrasonic vibration to the drilling process) but also a 40 % reduction in thrust force compared to CD. The UAD technique seems more appropriate than the EDD method due to the ability to reduce machining process time by up to 90 %, improve cylindricity by roughly 50 %, increase hole dimension accuracy by up to 80 %, and reduce surface roughness by 52 %.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takemaya H, Kato S (1991) Burrless drilling by means of ultrasonic assistance. Ann CIRP 40:83–86
Alam K, Mitrofanov AV, Silberschmidt VV (2009) Measurements of surface roughness in conventional and ultrasonically assisted bone drilling. Am J Biomed Sci 1:312–320
Alam K, Mitrofanov AV, Silberschmidt VV (2011) Experimental investigations of forces and torque in conventional and ultrasonically-assisted drilling of cortical bone. Med Eng Phys 33:234–239
Chang SSF, Bone GM (2005) Burr size reduction in drilling by ultrasonic assistance. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 21:442–450
Babitsky VI, Astashev VK, Meadows A (2007) Vibration excitation and energy transfer during ultrasonically assisted drilling. J Sound Vib 308:805–814
Chang SSF, Bone GM (2010) Burr height model for vibration assisted drilling of aluminum 6061-T6. Precis Eng 34:369–375
Aziz M, Ohnishi O, Onikura H (2012) Novel micro deep drilling using micro long flat drill with ultrasonic vibration. Precis Eng 36:168–174
Zhang DY, Feng XJ, Wang LJ, Chen DC (1994) Study on the drill skidding motion in ultrasonic vibration micro drilling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 34:847–857
Neugebauer R, Stoll A (2014) Ultrasonic application in drilling. J Mater Process Technol 149:633–639
Thomas PNH, Babitsky VI (2007) Experiments and simulations on ultrasonically assisted drilling. J Sound Vib 308:815–830
Lin TR, Shyu RF (2000) Improvement of tool life and exit burr using variable feeds when drilling stainless steel with coated drills. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 16:308–313
Xu X, Mo Y, Liu C, Zhao B (2009) Drilling force of SiC particle reinforced aluminum-matrix composites with ultrasonic vibration. Key Eng Mater 416:243–247
Laporte S, K’nevez J-Y, Cahuc O, Darnis P (2009) Phenomenological model for drilling operation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40:1–11
Pujanaet J, Rivero A, Celaya A, Lacalle LNLD (2009) Analysis of ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti6Al4V. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:500–508
Hsu I, Tsao C (2009) Study on the effect of frequency tracing in ultrasonic-assisted drilling of titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43:127–135
Azarhoushang B, Akbari J (2007) Ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Inconel 738-LC. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47:1027–1033
Liao YS, Chen YC, Lin HM (2007) Feasibility study of the ultrasonic vibration assisted drilling of Inconel superalloy. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47:1988–1996
Dvivedi A, Kumar P (2007) Surface quality evaluation in ultrasonic drilling through the Taguchi technique. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34:131–140
Onikura H, Ohnishi O, Feng JH, Kanda T, Morita T, Bopp U (1996) Effects of ultrasonic vibration on machining accuracy in micro drilling. Int J JSPE 30:210–216
Onikura H, Ohnishi O (1998) Drilling mechanisms in ultrasonic-vibration assisted micro drilling. J JSPE 64:1633–1637
Jin M, Murakawa M (2001) Development of a practical ultrasonic vibration cutting tool system. J Mater Process Technol 113:342–347
Takeyama H, Kato S (1991) Burrless drilling by means of ultrasonic vibration. Ann CIRP 40:83–86
Storck H, Littmann W, Wallaschek J, Mracek M (2002) The effect of friction reduction in presence of ultrasonic vibrations and its relevance to travelling wave ultrasonic motors. Ultrasonic 40:379–383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baghlani, V., Mehbudi, P., Akbari, J. et al. An optimization technique on ultrasonic and cutting parameters for drilling and deep drilling of nickel-based high-strength Inconel 738LC superalloy with deeper and higher hole quality. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82, 877–888 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7414-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7414-6