Abstract
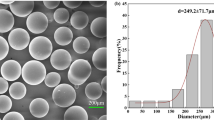
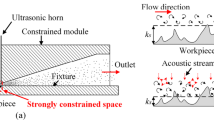
In the present study, the abrasive waterjet (AWJ) with the aid of ultrasonic vibration was used to improve the processing performance of hard-brittle materials. The method is termed as the ultrasonic-assisted abrasive waterjet polishing (UA-AWJP). Aluminum nitride was chosen as the workpiece material. Ultrasonic vibration perpendicular to the jet impact direction was applied on the workpiece by using a specially designed stage. A series of experiments were performed to evaluate the performance of the UA-AWJP. The processing performances and the polished surface topographies of the AWJP and UA-AWJP were compared to investigate the effects of ultrasonic vibration. The results show that UA-AWJP has a higher processing efficiency than AWJP. The surface roughness of the polished surface was modeled. The model shows a considerable agreement with the experimental results. The experimental results show that a lower pressure, finer abrasives, and a smaller impact angle are ideal to obtain a high surface quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paul S, Hoogstrate AM, van Luttervelt CA, Kals HJJ (1998) Analytical modelling of the total depth of cut in the abrasive water jet machining of polycrystalline brittle material. J Mater Process Technol 73:206–212. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00230-6
Wang J (2009) A new model for predicting the depth of cut in abrasive waterjet contouring of alumina ceramics. J Mater Process Technol 209:2314–2320. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.05.021
Deam R, Lemma E, Ahmed D (2004) Modelling of the abrasive water jet cutting process. Wear 257:877–891. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2004.04.002
Alberdi A, Rivero A, López de Lacalle LN, Etxeberria I, Suárez A (2010) Effect of process parameter on the kerf geometry in abrasive water jet milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:467–480. doi:10.1007/s00170-010-2662-y
El-Domiaty AA, Abdel-Rahman AA (1997) Fracture mechanics-based model of abrasive waterjet cutting for brittle materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 13:172–181. doi:10.1007/BF01305869
Zhu HT, Huang CZ, Wang J, Li QL, Che CL (2009) Experimental study on abrasive waterjet polishing for hard-brittle materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:569–578. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.02.005
Booij SM (2002) Nanometer deep shaping with fluid jet polishing. Opt Eng 41:1926. doi:10.1117/1.1489677
Nategh MJ, Razavi H, Abdullah A (2012) Analytical modeling and experimental investigation of ultrasonic-vibration assisted oblique turning, part I: kinematics analysis. Int J Mech Sci 63:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2012.04.007
Yanyan Y, Bo Z, Junli L (2008) Ultraprecision surface finishing of nano-ZrO2 ceramics using two-dimensional ultrasonic assisted grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43:462–467. doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1732-x
Uhlmann E, Spur G (1998) Surface formation in creep feed grinding of advanced ceramics with and without ultrasonic assistance. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 47:249–252. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62828-5
Peng Y, Wu YB, Liang ZQ, Guo YB, Lin X (2010) An experimental study of ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of polysilicon using two-dimensional vertical workpiece vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54:941–947. doi:10.1007/s00170-010-2991-x
Liu Y, Zhao H, Jing J, Wei S (2012) Investigation on the bonding strength patterns of ultrasonic vibration tools and influence on working performance during rotary ultrasonic grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65:533–541. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4192-2
Ding K, Fu Y, Su H, Gong X (2014) Wear of diamond grinding wheel in ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of silicon carbide. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71:1929–1938. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-5625-x
Tawakoli T, Azarhoushang B (2008) Influence of ultrasonic vibrations on dry grinding of soft steel. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1585–1591. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.05.010
Nik MG, Movahhedy MR, Akbari J (2012) Ultrasonic-assisted grinding of Ti6Al4V alloy. Procedia CIRP 1:353–358. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2012.04.063
Bhaduri D, Soo S, Aspinwall D, Novovic D, Harden P, Bohr S, Martin D (2012) A study on ultrasonic assisted creep feed grinding of nickel based superalloys. Procedia CIRP 1:359–364. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2012.04.064
Bifano TG, Dow TA, Scattergood RO (1991) Ductile-regime grinding: a new technology for machining brittle materials. J Eng Ind 113:184. doi:10.1115/1.2899676
Bo Z, Chuanshao L, Guofu G, Feng J (2002) Surface characteristics in the ultrasonic ductile honing of ZrO2 ceramics using coarse grits. J Mater Process Technol 123:54–60. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00041-9
Zhou M, Wang X, Ngoi BK, Gan JG (2002) Brittle–ductile transition in the diamond cutting of glasses with the aid of ultrasonic vibration. J Mater Process Technol 121:243–251. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01262-6
Mulik RS, Pandey PM (2010) Mechanism of surface finishing in ultrasonic-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Mater Manuf Process 25:1418–1427. doi:10.1080/10426914.2010.499580
Suzuki H, Moriwaki T, Okino T, Ando Y (2006) Development of ultrasonic vibration assisted polishing machine for micro aspheric die and mold. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 55:385–388. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60441-7
Suzuki H, Hamada S, Okino T, Kondo M, Yamagata Y, Higuchi T (2010) Ultraprecision finishing of micro-aspheric surface by ultrasonic two-axis vibration assisted polishing. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59:347–350. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.117
Kobayashi N, Wu Y, Nomura M, Sato T (2008) Precision treatment of silicon wafer edge utilizing ultrasonically assisted polishing technique. J Mater Process Technol 201:531–535. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.11.220
Finnie I, Mcfadden DH (1978) On the velocity dependence of the erosion of ductile metals by solid particles at low angles of incidence. Wear 48:181–190. doi:10.1016/0043-1648(78)90147-3
Momber A, Kovacevic R (1998) Principles of abrasive water jet machining. Springer, London
Hecker RL, Liang SY, Wu XJ, Xia P, Jin DGW (2006) Grinding force and power modeling based on chip thickness analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33:449–459. doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0473-y
Hecker RL, Liang SY (2003) Predictive modeling of surface roughness in grinding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:755–761. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00055-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Z., Huang, C., Zhu, H. et al. A research on ultrasonic-assisted abrasive waterjet polishing of hard-brittle materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78, 1361–1369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6528-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6528-6