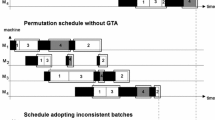
Abstract
A batch processing machine can process several jobs simultaneously. In this research, we consider the problem of a two-stage flow shop with two batch processing machines to minimize the makespan. We assume that the processing time of a batch is the longest processing time among all the jobs in that batch and the sizes of the jobs are nonidentical. There is a limitation on batch sizes and the sum of job sizes in a batch must be less than or equal to the machine capacity. Since this problem is strongly nondeterministic polynomial time hard, we propose two heuristic algorithms. The first one is knowledge-based and the other is based on the batch first fit heuristic proposed previously. To further enhance the solution quality, two different simulated annealing (SA) algorithms based on the two constructive heuristics is also developed. Since heuristic methods for this problem has not been proposed previously, a lower bound is developed for evaluating the performance of the proposed methods. Several test problems have been solved by SAs and lower bound method and the results are compared. Computational studies show that both algorithms provide good results but the first SA (ARSA) algorithm considerably outperforms the second one (FLSA). In addition, the results of ARSA algorithm, optimal solutions, and lower bounds are compared for several small problems. The comparisons show that except for one instance, the ARSA could find the optimal solutions and the proposed lower bound provides small gaps comparing with the optimal solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts EHL, Korst J (1989) Simulated annealing and Boltzmann machines: a stochastic approach to combinatorial optimization and neural computing. Wiley, Chichester, England
Ahmadi JH, Ahmadi RH, Dasu S, Tang CS (1992) Batching and scheduling jobs on batch and discrete processors. Oper Res 4:750–763. doi:10.1287/opre.40.4.750
Baker KR (1974) Introduction to sequencing and scheduling. Wiley, New York
Chang P-C, Wang H-M (2004) A heuristic for a batch processing machine scheduled to minimise total completion time with non-identical job sizes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 24:615–620. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1740-9
Cheng TCE, Wang G (1998) Batching and scheduling to minimize the makespan in the two-machine flowshop. IIE Trans 30:447–453. doi:10.1080/07408179808966485
Chou F-D (2007) A joint GA+ DP approach for single burn-in oven scheduling problems with makespan criterion. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 35:587–595. doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0738-5
Coffman EG, Garey M, Johnson DS (1984) Approximation algorithm for bin-packing problem an updated survey. In: Ausiello Y, Licertini M, Serafini P (eds) Algorithm design for computer system design. Springer, New York, NY, pp 49–106
Damodaran P, Srihari K (2004) Mixed integer formulation to minimize makespan in a flow-shop with batch processing machines. Math Comput Model 40:1465–1472. doi:10.1016/j.mcm.2005.01.005
Danneberg D, Tautenhahn T, Werner F (1999) A comparison of heuristic algorithms for flow shop scheduling problems with setup times and limited batch size. Math Comput Model 29:101–126. doi:10.1016/S0895-7177(99) 00085-0
Dobson G, Karmarkar US, Rummel JL (1989) Batching to minimize flow times on parallel heterogeneous machines. Manage Sci 35(5):607–613. doi:10.1287/mnsc.35.5.607
Glass CA, Potts CN, Strusevich VA (2001) Scheduling batches with sequential job processing for two-machine flow and open shops. INFORMS J Comput 13(2):120–137. doi:10.1287/ijoc.13.2.120.10521
Kashani AH, Karimi B, Jolai F (2006) Effective hybrid genetic algorithm for minimizing makespan on a single-batch-processing machine with non-identical job sizes. Int J Prod Res 12:2337–2360. doi:10.1080/00207540500525254
Lee C-Y, Uzsoy R, Martin-Vega LA (1992) Efficient algorithms for scheduling semiconductor burn-in operations. Oper Res 40(4):764–775. doi:10.1287/opre.40.4.764
Lin BMT, Cheng TCE (2001) Batch scheduling in the no-wait two-machine flow shop to minimize the makespan. Comput Oper Res 28:613–624. doi:10.1016/S0305-0548(99) 00138-0
Lin BMT, Cheng TCE (2005) Two-machine flowshop batching and scheduling. Ann Oper Res 133:149–161. doi:10.1007/s10479-004-5029-7
Mathirajan M, Sivakumar AI (2006) A literature review, classification and simple meta-analysis on scheduling of batch processors in semiconductor. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29:990–1001. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-2585-1
Melouk S, Damodaran P, Chang PY (2004) Minimizing makespan for single machine batch processing with non-identical job sizes using simulated annealing. Int J Prod Econ 87:141–147. doi:10.1016/S0925-5273(03) 00092-6
Nawaz M, Enscore EE, Ham I (1983) A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow shop sequencing problem. Omega 11:91–95. doi:10.1016/0305-0483(83) 90088-9
Oulamara A (2007) Makespan minimization in a no-wait flow shop problem with two batching machines. Comput Oper Res 34:1033–1050. doi:10.1016/j.cor.2005.05.028
Su L (2003) A hybrid two-stage flow shop with limited waiting time constraints. Comput Ind Eng 44:409–424. doi:10.1016/S0360-8352(02) 00216-4
Sung CS, Kim YH (2002) Minimizing makespan in a two-machine flow shop with dynamic arrivals allowed. Comput Oper Res 29:275–294. doi:10.1016/S0305-0548(00) 00071-X
Sung CS, Kim YH (2003) Minimizing due date related performance measures on two batch processing machines. Eur J Oper Res 147:644–656. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(02) 00352-1
Sung CS, Kim YH, Yoon SH (2000) A problem reduction and decomposition approach for scheduling for a flow shop of batch processing machines. Eur J Oper Res 121:179–192. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(99) 00031-4
Sung CS, Min JI (2001) Scheduling in a two-machine flowshop with batch processing machine(s) for earliness/tardiness measure under a common due date. Eur J Oper Res 131:95–106. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(99) 00447-6
Uzsoy R (1994) Scheduling a single batch processing machine with non-identical job sizes. Int J Prod Res 32(7):1615–1635. doi:10.1080/00207549408957026
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirsanei, H.S., Karimi, B. & Jolai, F. Flow shop scheduling with two batch processing machines and nonidentical job sizes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45, 553–572 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-1986-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-1986-y