Abstract
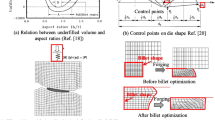
The present study aims to determine the optimum blank shape design for deep drawing of arbitrary shaped cups with a uniform trim allowance at the flange, i.e., cups without ears. The earing, or non-uniform flange, is caused by non-uniform material flow and planar anisotropy in the sheet. In this research, a new method for optimum blank shape design using finite element analysis is proposed. The deformation process is first divided into multiple steps. A shape error metric is defined to measure the amount of earing and to compare the deformed shape and target shape set for each stage of the analysis. This error metric is then used to decide whether the blank needs to be modified. The blank geometry change is based on material flow. The cycle is repeated until the converged results are achieved. This iterative design process leads to optimal blank shape. To test the proposed method, three examples of cup drawing are presented. In every case converged results are achieved after a few iterations. The proposed systematic method for optimal blank design is found to be very effective in the deep drawing process and can be further applied to other sheet metal forming applications such as stamping processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung K, Richmond O (1993) Ideal forming I. Homogeneous deformation with minimum plastic work. Int J Mech Sci 34(7):575–591
Chung K, Richmond O (1992) Ideal forming II. Sheet forming with optimum deformation. Int J Mech Sci 34(8):617–633
Park SH, Yoon JW, Yang DY, Kim YH (1999) Optimum blank design in sheet metal forming by deformation path iteration method. Int J Mech Sci 41:1217–1232
Chung K, Barlat F, Brem JC (1997) Blank shape design for a planar anisotropy sheet based on ideal forming design theory and FEM analysis. Int J Mech Sci 39:617–633
Sowerby R, Duncan JL, Chu E (1986) The modeling of sheet metal stampings. Int J Mech Sci 28(7):415–430
Blount GN, Fischer BV (1995) Computerized blank shape prediction for sheet metal components having doubly-curved surfaces. Int J Prod Res 33(4):993–1005
Gerdeen JC, Chen P (1989) Geometric mapping method off computer modeling of sheet metal forming. NUMIFORM’89 Thompson et al (eds), Balkema, Rotterdam, ISBN 9061918979
Parsa MH, Pournia P (2007) Optimization of initial blank shape predicted based on inverse finite element method. Finite Elem Anal Des 43(3):218–233
Tang BT, Zhao Z, Lu XY, Wang ZQ, Zhao XW, Chen SY (2007) Fast thickness prediction and blank design in sheet metal forming based on an enhanced inverse analysis method. Int J Mech Sci 49(9):1018–1028
Toshihiko M, Kawai N, Marumo Y, Senga M (1987) Square shell deep drawability of commercially pure aluminum sheets. Nippon kikai Gakkai Ronbunshu 53(487):771–779
Gloeckl H, Lange K (1983) Computer aided design of blanks for deep drawing irregular shaped components. Manuf Eng Trans 11:243–251
Duncan JL, Sowerby R (1981) Computer aids in sheet metal forming. Ann CIRP 30(2):541–546
Chen X, Sowerby R (1996) Blank development and the prediction of earing in cup drawing. Int J Mech Sci 8(5):509–516
Liu F, Sowerby R (1991) The determination of optimal blank shapes when deep drawing prismatic cups. J Mater Shap Technol 9(3):153–159
Lo SW, Lee JY (1998) Optimum blank shapes for prismatic cup drawing-consideration of friction and material anisotropy. J Manuf Sci Eng 120:306–315
Agrawal A, Reddy NV, Dixit PM (2008) Optimal blank shape prediction considering sheet thickness variation: An upper bound approach. J Mater Proc Tech 196:249–258
Kim N, Kobayashi S (1986) Blank design in rectangular cup drawing by an approximate method. Int J Machine Tool Des Res 26(2):125–135
Chung K, Shah K (1992) Finite element simulation of sheet metal forming for planar anisotropic metals. Int J Plasticity 8:453–476
Barlet O, Batoz JL, Guo YQ, Mercier F, Naceur H, Knopf-Lenoir C (1996) Optimum design of blank contour using the inverse approach and a mathematical programming technique. NUMISHEET’96 178–85
Hu P, Liu YQ, Wang JC (2000) Numerical study of the flange earing of deep drawing sheets with stronger anisotropy. Int J Mech Sci 43:279–296
Gea HC, Ramamurthy R (1998) Blank design optimization on deep drawing of square shells. Trans IIE 30(10):913–921
Ohata T, Nakamura Y, Katayama T, Nakamachi E, Nakano K (1996) Development of optimum process design system by numerical simulation. J Mater Process Technol 60:543–548
Cai Z-Y, Li M-Z, Zhang H-M (2007) A simplified algorithm for planar development of 3D surface and its application in the blank design of sheet metal forming. Finite Elem Anal Des 43(4):301–310
Sattari H, Sedaghati R, Ganesan R (2007) Analysis and design optimization of deep drawing process: Part II: Optimization. J Mater Process Technol 184(1–3):84–92
Yeh F–H, Wu M–T, Li C–L (2007) Accurate optimization of blank design in stretch flange based on a forward-inverse prediction scheme. Int J Machine Tools and Manufacture 47(12–13):1854–1863
Iseki H, Murota T (1986) On the determination of the optimum blank shape of non-axisymmetric drawn cup by finite element method. Bulletin of JSME 29(249):249–254
Mamalis AG, Manolakosand DE, Baldoukas AK (1996) On the finite-element modelling of the deep drawing of square sections of coated steels. J Mater Process Technol 58:153–159
Mamalis AG, Manolakosand DE, Baldoukas AK (1997) Simulation of sheet metal forming using explicit finite-element techniques: effect of material and forming characteristics. Part 1. Deep drawing of cylindrical cups. J Mater Process Technol 72:48–60
Mamalis AG, Manolakos DE, Baldoukas AK (1997) Simulation of sheet metal forming using explicit finite-element techniques: effect of material and forming characteristics. Part 2. Deep drawing of square cups. J Mater Process Technol 72:110–116
Shim HB, Son KC, Kim KH (1999) Optimum blank shape design by sensitivity analysis. Proceedings of the Numisheet’99, Besancon, France 1:523–528
Shim HB, Son KC (2000) Optimal blank design for the drawings of arbitrary shapes by the sensitivity method. Proc ASME 2000, Manufacturing in Engineering Division, Orlando, FL, MED-11:487–493
Shim HB, Son KC, Kim KH (2000) Optimal blank shape design by sensitivity method. J Mater Process Technol 104:191–199
Son K, Shim H (2003) Optimal blank shape design using the initial velocity of boundary nodes. J Mater Process Technol 134:92–98
Iseki H, Sowerby R (1995) Determination of the optimal blank shape when deep drawing non-axisymmetric cups using a finite element method. JSME Int A 38(4):473–479
Lee CH, Huh H (1997) Blank design and strain prediction of automobile stamping parts by an inverse finite element approach. J Mater Process Technol 63:645–650
Kim SD, Park MH, Kim SJ, Seo DG (1998) Blank design and formability for non-circular deep drawing processes by the finite element method. J Mater Process Technol 75:94–99
Kim DH, Lee JM, Park SH, Yang DY, Kim YH (1997) Blank design system for sheet forming. J Korean Soc Tech Plast 6(5):400–407
Xueshan L, Bingwen L (1986) Modeling of flange deformation of irregular drawn cups using a fluid analogy. Int J Mech Sci 28(8):491–497
Zhaotao Z, Bingwen L (1986) Determination of blank shapes for drawing irregular cups using an electrical analogue method. Int J Mech Sci 28(8):499–503
Toh CH, Kobayashi S (1985) Deformation analysis and blank design in square cup drawing. Int J Mech Sci 25(1):15–32
Guo YQ, Batoz JL, Detraux JM, Duroux P (1990) Finite element procedures for strain estimations of sheet metal forming parts. Int J Num Meth Eng 30:1385–1401
Pegada V, Chun Y, Santhanam S (2002) An algorithm for determining the optimal blank shape for the deep drawing of aluminum cups. J Mater Process Technol 125–126:743–750
Kishor N, Kumar DR (2002) Optimization of initial blank shape to minimize earing in deep drawing using finite element method. J Mater Process Technol 130–131:20–30
Lan F, Lin J, Chen J (2006) An integrated numerical technique in determining blank shape for netshape sheet metal forming. J Mater Process Technol 177(1–3):72–75
Park CS, Ku TW, Kang BS, Hwang SM (2004) Process design and blank modification in the multistage rectangular deep drawing of an extreme aspect ratio. J Mater Process Technol 153–154:778–784
Gantar G, Peplnjak T, Kuzman K (2002) Optimization of sheet metal forming processes by use of numerical simulations. J Mater Process Technol 130–131:54–59
Fourment L et al (1995) NUMIFORM’ 95:557–562
Zaky AM, Nassr AB, El-Sebaie MG (1998) Optimal blank shape of cylindrical cups in deep drawing of anisotropic sheet metals. J Mater Process Technol 76:203–211
Wilson FW, Harvey PD, Gump Jr CB (1965) Die design handbook. SME, McGraw Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Goel, A., Yang, F. et al. Blank optimization for sheet metal forming using multi-step finite element simulations. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40, 709–720 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1383-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1383-y