Abstract
Purpose
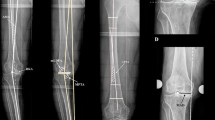
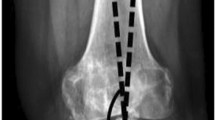
Approximately 10% of all patients that require a total knee arthroplasty present with valgus osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee. Valgus OA goes along with posterolateral bone loss and lateral soft tissue tightness. The role of malalignment on the development of OA is not fully understood. The current study investigates whether the femoral offset (FO), femoral mechanical–anatomical (FMA) angle, anatomical lateral distal femur angle (aLDFA), mechanical lateral distal femur angle (mLDFA), medial proximal femur angle (MPFA), medial proximal tibia angle (MPTA) or lateral distal tibia angle (LDTA) differ in patients with valgus OA of the knee.
Methods
FO, FMA angle, aLDFA, mLDFA, MPFA, MPTA and LDTA were assessed and compared between 100 consecutive knees with minimal valgus OA (50 male, 50 female) and 100 consecutive knees with minimal varus OA (50 male, 50 female).
Results
FO was significantly higher in males with valgus OA (p = 0.002) and females with varus OA (p = 0.01). The observed values for the FMA angle were significantly higher in males with valgus OA (p = 0.002) and females with varus OA (p = 0.041). The aLDFA and mLDFA were significantly smaller in all patients with valgus OA (p < 0.001). No differences between the varus and valgus groups were detected regarding MPFA (males: p = 0.052; females: p = 0.719). Tibial measurements showed significantly higher values for the MPTA (p < 0.001) in both valgus groups and no difference for LDTA (men: p = 0.139; women: p = 0.196).
Conclusion
Bony alterations in the femoral anatomy seem to be more important than in the tibial anatomy. While in male patients with valgus OA, the main anatomic variation is the hypoplasia of the lateral femoral condyle, in females both decreased femoral offset of the hip as well as hypoplasia of the lateral condyle are present.
Level of evidence
III.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriacchi TP (1994) Dynamics of knee malalignment. Orthop Clin North Am 25:395–403
Brouwer GM, van Tol AW, Bergink AP, Belo JN, Bernsen RM, Reijman M, Pols HA, Bierma-Zeinstra SM (2007) Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 56:1204–1211
Cicuttini F, Wluka A, Hankin J, Wang Y (2004) Longitudinal study of the relationship between knee angle and tibiofemoral cartilage volume in subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:321–324
Cooke TD, Scudamore RA, Bryant JT, Sorbie C, Siu D, Fisher B (1991) A quantitative approach to radiography of the lower limb. Principles and applications. J Bone Jt Surg Br 73:715–720
Davey JR (2003) Implant issues in using high offset femoral stems.In: Annual Meeting of the American Academy Orthopaedic Surgeons 70th Annual Meeting.
Deakin AH, Basanagoudar PL, Nunag P, Johnston AT, Sarungi M (2012) Natural distribution of the femoral mechanical-anatomical angle in an osteoarthritic population and its relevance to total knee arthroplasty. Knee 19:120–123
Eckstein F, Wirth W, Hudelmaier M, Stein V, Lengfelder V, Cahue S, Marshall M, Prasad P, Sharma L (2008) Patterns of femorotibial cartilage loss in knees with neutral, varus, and valgus alignment. Arthritis Rheum 59:1563–1570
Englund M (2010) The role of biomechanics in the initiation and progression of OA of the knee. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 24:39–46
Favero M, Ramonda R, Goldring MB, Goldring SR, Punzi L (2015) Early knee osteoarthritis. RMD Open 1:e000062
Felson DT, McLaughlin S, Goggins J, LaValley MP, Gale ME, Totterman S, Li W, Hill C, Gale D (2003) Bone marrow edema and its relation to progression of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med 139:330–336
Felson DT, Nevitt MC (2004) Epidemiologic studies for osteoarthritis: new versus conventional study design approaches. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 30(783–797):vii
Felson DT, Nevitt MC, Zhang Y, Aliabadi P, Baumer B, Gale D, Li W, Yu W, Xu L (2002) High prevalence of lateral knee osteoarthritis in Beijing Chinese compared with Framingham Caucasian subjects. Arthritis Rheum 46:1217–1222
Hess S, Moser LB, Amsler F, Behrend H, Hirschmann MT (2019) Highly variable coronal tibial and femoral alignment in osteoarthritic knees: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1368–1377
Hirschmann MT, Hess S, Behrend H, Amsler F, Leclercq V, Moser LB (2019) Phenotyping of hip-knee-ankle angle in young non-osteoarthritic knees provides better understanding of native alignment variability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1378–1384
Hirschmann MT, Moser LB, Amsler F, Behrend H, Leclercq V, Hess S (2019) Phenotyping the knee in young non-osteoarthritic knees shows a wide distribution of femoral and tibial coronal alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1385–1393
Hirschmann MT, Moser LB, Amsler F, Behrend H, Leclerq V, Hess S (2019) Functional knee phenotypes: a novel classification for phenotyping the coronal lower limb alignment based on the native alignment in young non-osteoarthritic patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1394–1402
Hoch MC, Weinhandl JT (2017) Effect of valgus knee alignment on gait biomechanics in healthy women. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 35:17–23
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY (1990) Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 255:215–227
Hunter DJ, Niu J, Felson DT, Harvey WF, Gross KD, McCree P, Aliabadi P, Sack B, Zhang Y (2007) Knee alignment does not predict incident osteoarthritis: the Framingham osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheum 56:1212–1218
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–502
Lampart M, Behrend H, Moser LB, Hirschmann MT (2019) Due to great variability fixed HKS angle for alignment of the distal cut leads to a significant error in coronal TKA orientation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1434–1441
Luyten FP, Denti M, Filardo G, Kon E, Engebretsen L (2012) Definition and classification of early osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:401–406
Madry H, Kon E, Condello V, Peretti GM, Steinwachs M, Seil R, Berruto M, Engebretsen L, Filardo G, Angele P (2016) Early osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:1753–1762
McAlindon TE, Snow S, Cooper C, Dieppe PA (1992) Radiographic patterns of osteoarthritis of the knee joint in the community: the importance of the patellofemoral joint. Ann Rheum Dis 51:844–849
Merle C, Waldstein W, Pegg E, Streit MR, Gotterbarm T, Aldinger PR, Murray DW, Gill HS (2012) Femoral offset is underestimated on anteroposterior radiographs of the pelvis but accurately assessed on anteroposterior radiographs of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br 94:477–482
Monazzam S, Bomar JD, Agashe M, Hosalkar HS (2013) Does femoral rotation influence anteroposterior alpha angle, lateral center-edge angle, and medial proximal femoral angle? A pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:1639–1645
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Jt Surg Am 69:745–749
Moser LB, Hess S, Amsler F, Behrend H, Hirschmann MT (2019) Native non-osteoarthritic knees have a highly variable coronal alignment: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1359–1367
Nam D, Vajapey S, Haynes JA, Barrack RL, Nunley RM (2016) Does use of a variable distal femur resection angle improve radiographic alignment in primary total knee arthroplasty? J Arthroplast 31:91–96
Paley D, Pfeil J (2000) Principles of deformity correction around the knee. Orthopade 29:18–38
Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S (2005) Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87(Suppl 1):271–284
Ranawat CS (1985) Total condylar knee arthroplasty: technique, results, and complications, 1st edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Rossi R, Rosso F, Cottino U, Dettoni F, Bonasia DE, Bruzzone M (2014) Total knee arthroplasty in the valgus knee. Int Orthop 38:273–283
Runhaar J, van Middelkoop M, Reijman M, Vroegindeweij D, Oei EH, Bierma-Zeinstra SM (2014) Malalignment: a possible target for prevention of incident knee osteoarthritis in overweight and obese women. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:1618–1624
Sharma L, Eckstein F, Song J, Guermazi A, Prasad P, Kapoor D, Cahue S, Marshall M, Hudelmaier M, Dunlop D (2008) Relationship of meniscal damage, meniscal extrusion, malalignment, and joint laxity to subsequent cartilage loss in osteoarthritic knees. Arthritis Rheum 58:1716–1726
Sharma L, Song J, Dunlop D, Felson D, Lewis CE, Segal N, Torner J, Cooke TD, Hietpas J, Lynch J, Nevitt M (2010) Varus and valgus alignment and incident and progressive knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1940–1945
Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD (2001) The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA 286:188–195
Tetsworth K, Paley D (1994) Malalignment and degenerative arthropathy. Orthop Clin North Am 25:367–377
Wise BL, Niu J, Yang M, Lane NE, Harvey W, Felson DT, Hietpas J, Nevitt M, Sharma L, Torner J, Lewis CE, Zhang Y, Multicenter Osteoarthritis G (2012) Patterns of compartment involvement in tibiofemoral osteoarthritis in men and women and in whites and African Americans. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64:847–852
Xie K, Han X, Jiang X, Ai S, Dai K, Yu Z, Wu H, Qu X, Yan M (2019) The effect of varus knee deformities on the ankle alignment in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res 14:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1191-0
Yang NH, Nayeb-Hashemi H, Canavan PK, Vaziri A (2010) Effect of frontal plane tibiofemoral angle on the stress and strain at the knee cartilage during the stance phase of gait. J Orthop Res 28:1539–1547
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Boettner has received royalties by Smith and Nephew and Orthodevelopment. Dr. Boettner has also received compensation by Smith and Nephew, Orthodevelopment and DePuy. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. Number of ethical approval: 2018-0697-CR1 IRB- contact person: castelc@hss.edu.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Springer, B., Bechler, U., Waldstein, W. et al. The influence of femoral and tibial bony anatomy on valgus OA of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28, 2998–3006 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05734-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05734-6