Abstract
Purpose
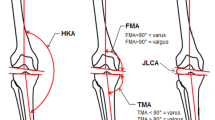
Coronal alignment of the knee is defined by the hip–knee–ankle angle (HKA), the femoral mechanical angle (FMA), the tibial mechanical angle (TMA), and the joint line convergence angle (JLCA). To date, there is still a lack of knowledge about the variability of native coronal knee alignment. The purpose of this paper is to present a systematic review of the current literature about the variability of coronal knee alignment (HKA, FMA, TMA, and JLCA) in non-osteoarthritic knees.
Methods
The electronic databases MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Google Scholar were searched from database inception to search date (November 1, 2018) and screened for relevant studies. The PRISMA guidelines were followed. Inclusion criteria were studies that reported the coronal alignment of the native, non-osteoarthritic knee.
Results
A total of 15 studies met the inclusion criteria. Thirteen studies performed the measurements on weight-bearing long-leg standing radiographs (LLR), one study used MRI, and one study used the EOS imaging system. The mean HKA ranged from 176.7° ± 2.8° (male) to 180.7° (female). The mean FMA ranged from 92.08° ± 1.78° (female) to 97.2° ± 2.7° (female). The mean TMA ranged from 84.6° ± 2.5° (female) to 89.6° (female). The mean JLCA ranged from − 0.47° ± 0.98° (male) to − 1.9° ± 1.4° (female).
Conclusion
This systematic review provides a detailed overview about the variability of the coronal knee alignment in non-osteoarthritic knees. The broad variability of all coronal alignment parameters highlights the necessity for a more anatomic and individualized approach in knee arthroplasty. It also offers the fundament to understand the changes in osteoarthritic knees.
Level of clinical evidence
Systematic review, Level IV.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HKA:
-
Hip–knee–ankle angle
- FMA:
-
Femoral mechanical angle
- TMA:
-
Tibial mechanical angle
- JLCA:
-
Joint line convergence angle
- LLR:
-
Long-leg radiographs
- MRI:
-
Magnet resonance imaging
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
References
Altman RD, Fries JF, Bloch DA, Carstens J, Cooke TD, Genant H et al (1987) Radiographic assessment of progression in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 30:1214–1225
Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J (2012) The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:45–53
Cooke D, Scudamore A, Li J, Wyss U, Bryant T, Costigan P (1997) Axial lower-limb alignment: comparison of knee geometry in normal volunteers and osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 5:39–47
Cooke TD, Li J, Scudamore RA (1994) Radiographic assessment of bony contributions to knee deformity. Orthop Clin North Am 25:387–393
Deep K (2014) Collateral ligament laxity in knees: what is normal? Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:3426–3431
Hirschmann MT, Behrend H (2018) Functional knee phenotypes: a call for a more personalised and individualised approach to total knee arthroplasty? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-4973-8
Hirschmann MT, Konala P, Amsler F, Iranpour F, Friederich NF, Cobb JP (2011) The position and orientation of total knee replacement components: a comparison of conventional radiographs, transverse 2D-CT slices and 3D-CT reconstruction. J Bone Jt Surg Br 93:629–633
Hovinga KR, Lerner AL (2009) Anatomic variations between Japanese and Caucasian populations in the healthy young adult knee joint. J Orthop Res 27:1191–1196
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY (1990) Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 255:215–227
Hungerford DS, Krackow KA (1985) Total joint arthroplasty of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 192:23–33
Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, Mestriner LA (1985) Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 192:13–22
Jabalameli M, Moghimi J, Yeganeh A, Nojomi M (2015) Parameters of lower extremities alignment view in Iranian adult population. Acta Med Iran 53:293–296
Khattak MJ, Umer M, Davis ET, Habib M, Ahmed M (2010) Lower-limb alignment and posterior tibial slope in Pakistanis: a radiographic study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 18:22–25
Lampart M, Behrend H, Moser LB, Hirschmann MT (2018) Due to great variability fixed HKS angle for alignment of the distal cut leads to a significant error in coronal TKA orientation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5041-0
Luyckx T, Zambianchi F, Catani F, Bellemans J, Victor J (2013) Coronal alignment is a predictor of the rotational geometry of the distal femur in the osteo-arthritic knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2331–2337
Maini L, Singh S, Kushwaha NS, Saini A, Rohilla S, Sharma H et al (2015) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity in Indian adult males. J Arthrosc Jt Surg 2:128–131
Markolf KL, Mensch JS, Amstutz HC (1976) Stiffness and laxity of the knee–the contributions of the supporting structures. A quantitative in vitro study. J Bone Jt Surg Am 58:583–594
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:745–749
Mullaji AB, Marawar SV, Mittal V (2009) A comparison of coronal plane axial femoral relationships in Asian patients with varus osteoarthritic knees and healthy knees. J Arthroplasty 24:861–867
Nakano N, Matsumoto T, Hashimura M, Takayama K, Ishida K, Araki D et al (2016) Coronal lower limb alignment in normal knees–a radiographic analysis of 797 normal knee subjects. Knee 23:209–213
Nam D, Shah RR, Nunley RM, Barrack RL (2014) Evaluation of the 3-dimensional, weight-bearing orientation of the normal adult knee. J Arthroplasty 29:906–911
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Shetty GM, Mullaji A, Bhayde S, Nha KW, Oh HK (2014) Factors contributing to inherent varus alignment of lower limb in normal Asian adults: role of tibial plateau inclination. Knee 21:544–548
Slevin O, Hirschmann A, Schiapparelli FF, Amsler F, Huegli RW, Hirschmann MT (2018) Neutral alignment leads to higher knee society scores after total knee arthroplasty in preoperatively non-varus patients: a prospective clinical study using 3D-CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:1602–1609
Slevin O, Schmid FA, Schiapparelli FF, Rasch H, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT (2017) Coronal femoral TKA position significantly influences in vivo patellar loading in unresurfaced patellae after primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:3605–3610
Song MH, Yoo SH, Kang SW, Kim YJ, Park GT, Pyeun YS (2015) Coronal alignment of the lower limb and the incidence of constitutional varus knee in korean females. Knee Surg Relat Res 27:49–55
Tanaka T, Takayama K, Hashimoto S, Kanzaki N, Hayashi S, Kuroda R et al (2017) Radiographic analysis of the lower limbs using the hip-calcaneus line in healthy individuals and in patients with varus knee osteoarthritis. Knee 24:1146–1152
Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY (2000) Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Jt Surg Am 82-A:1603–1608
Than P, Szuper K, Somoskeoy S, Warta V, Illes T (2012) Geometrical values of the normal and arthritic hip and knee detected with the EOS imaging system. Int Orthop 36:1291–1297
Thienpont E, Schwab PE, Cornu O, Bellemans J, Victor J (2017) Bone morphotypes of the varus and valgus knee. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137:393–400
Thienpont E, Schwab PE, Paternostre F, Koch P (2014) Rotational alignment of the distal femur: anthropometric measurements with CT-based patient-specific instruments planning show high variability of the posterior condylar angle. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:2995–3002
Funding
There was no financial conflict of interest with regards to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LBM participated in study design, literature review, data collection, figures and tables, and manuscript writing. SH participated in literature review, data collection, and manuscript editing. FA participated in study design and manuscript editing. HB participated in study design and manuscript editing. MTH participated in study design and manuscript editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as this is a pure review of the literature not involving humans nor animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moser, L.B., Hess, S., Amsler, F. et al. Native non-osteoarthritic knees have a highly variable coronal alignment: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27, 1359–1367 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05417-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05417-2