Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to determine whether the learning curve of arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) could be verified by analyzing the complication rate of this procedure. Additionally, it was investigated whether supervision by an experienced surgeon leads to a steeper learning curve (lower number of complications) when starting to perform arthroscopic FAI treatment.
Methods
The complications occurring in 317 consecutive patients treated with the sole diagnosis of FAI were analyzed. 256 patients (collective A) were treated by surgeon A between June 2005 and January 2010. Sixty-one patients (collective B) were treated by surgeon B between August 2008 and December 2009. From January to June 2008, surgeon B performed many hip arthroscopies under supervision of surgeon A. Complications were recorded in a central complication register. Statistic analysis of the complication rates was performed using Fischer’s exact T test.
Results
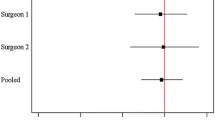
Subdividing collective A chronologically into thirds a significant decline of complications (p = 0.0044) was found with growing experience of the surgeon. Comparing the first 61 patients of both surgeons a significantly lower complication rate was discovered in the patients of surgeon B (p = 0.0375). In total there were 21 complications (6.6 %; CI 4.4–9.9 %). The observed complication rate was 7.0 % in collective A and 4.9 % in collective B.
Conclusion
The learning curve can be comprehended by the distribution of complications in collective A. Having spent 6 months performing under supervision of surgeon A, surgeon B has a lower complication rate than surgeon A when comparing the first 61 patients each surgeon operated on. This implies that surgeon B benefits from the experience of surgeon A. According to this analysis, beginners in arthroscopic FAI treatment should be taught at a specialized centre to reduce the number of complications.
Level of evidence
III.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R (2005) Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(7):1012–1018
Bedi A, Kelly BT, Khanduja V (2013) Arthroscopic hip preservation surgery: current concepts and perspective. Bone Joint J 95-B(1):10–19
Botser IB, Smith TW Jr, Nasser R, Domb BG (2011) Open surgical dislocation versus arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: a comparison of clinical outcomes. Arthroscopy 27(2):270–278
Bredella MA, Ulbrich EJ, Stoller DW, Anderson SE (2013) Femoroacetabular impingement. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 21(1):45–64
Buchler L, Neumann M, Schwab JM, Iselin L, Tannast M, Beck M (2013) Arthroscopic versus open cam resection in the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy 29(4):653–660
Byrd T (2001) Hip arthroscopy. The supine position. Clin Sports Med 20(4):703–731
Byrd T (2006) Hip arthroscopy: surgical indications. Arthroscopy 22(12):1260–1262
Byrd T, Jones KS (2009) Arthroscopic femoroplasty in the management of cam-type femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(3):739–746
Byrd T, Jones KS (2009) Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement. Instr Course Lect 58:231–239
Clarke MT, Arora A, Villar RN (2003) Hip arthroscopy: complications in 1,054 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 406:84–88
Clohisy JC, St John LC, Schutz AL (2010) Surgical treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(2):555–564
Colvin AC, Harrast J, Harner C (2012) Trends in hip arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(4):e23
Espinosa N, Beck M, Rothenfluh DA, Ganz R, Leunig M (2007) Treatment of femoro-acetabular impingement: preliminary results of labral refixation. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(Suppl 2 Pt.1):36–53
Fayad TE, Khan MA, Haddad FS (2013) Femoroacetabular impingement: an arthroscopic solution. Bone Joint J 95-B(11 Suppl A):26–30
Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Notzli H, Siebenrock KA (2003) Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 417:112–120
Harris JD, McCormick FM, Abrams GD, Gupta AK, Ellis TJ, Bach BR Jr, Bush-Joseph CA, Nho SJ (2013) Complications and reoperations during and after hip arthroscopy: a systematic review of 92 studies and more than 6,000 patients. Arthroscopy 29(3):589–595
Ilizaliturri VM Jr (2009) Complications of arthroscopic femoroacetabular impingement treatment: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(3):760–768
Ito K, Minka MA 2nd, Leunig M, Werlen S, Ganz R (2001) Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect. A MRI-based quantitative anatomical study of the femoral head-neck offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83(2):171–176
Konan S, Rhee SJ, Haddad FS (2011) Hip arthroscopy: analysis of a single surgeon’s learning experience. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93(Suppl 2):52–56
Kowalczuk M, Bhandari M, Farrokhyar F, Wong I, Chahal M, Neely S, Gandhi R, Ayeni OR (2012) Complications following hip arthroscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(7):1669–1675
Larson CM, Giveans MR, Taylor M (2011) Does arthroscopic FAI correction improve function with radiographic arthritis? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(6):1667–1676
Lee YK, Ha YC, Hwang DS, Koo KH (2012) Learning curve of basic hip arthroscopy technique: CUSUM analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(8):1940–1944
Leunig M, Beaule PE, Ganz R (2009) The concept of femoroacetabular impingement: current status and future perspectives. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(3):616–622
Mohtadi NG, Griffin DR, Pedersen ME, Chan D, Safran MR, Parsons N, Sekiya JK, Kelly BT, Werle JR, Leunig M, McCarthy JC, Martin HD, Byrd JW, Philippon MJ, Martin RL, Guanche CA, Clohisy JC, Sampson TG, Kocher MS, Larson CM, Multicenter Arthroscopy of the Hip Outcomes Research N (2012) The Development and validation of a self-administered quality-of-life outcome measure for young, active patients with symptomatic hip disease: the International Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT-33). Arthroscopy 28(5):595–605
Ng VY, Arora N, Best TM, Pan X, Ellis TJ (2010) Efficacy of surgery for femoroacetabular impingement: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med 38(11):2337–2345
Sampson TG (2006) Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: a proposed technique with clinical experience. Instr Course Lect 55:337–346
Tran P, Pritchard M, O’Donnell J (2012) Outcome of arthroscopic treatment for cam type femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents. ANZ J Surg 83(5):382–386
Zingg PO, Ulbrich EJ, Buehler TC, Kalberer F, Poutawera VR, Dora C (2013) Surgical hip dislocation versus hip arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: clinical and morphological short-term results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133(1):69–79
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dietrich, F., Ries, C., Eiermann, C. et al. Complications in hip arthroscopy: necessity of supervision during the learning curve. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22, 953–958 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2893-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2893-9