Abstract
Purpose
Long-bone segmental defects caused by infection, fracture, or tumour are a challenge for orthopaedic surgeons. Structural allografts are sometimes used in their treatment but their poor biological characteristics are a liability. The objective of this study was to determine whether the addition of recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF) to a structural allograft improved its integration into a rabbit tibial segmental defect in a non-union model.
Methods
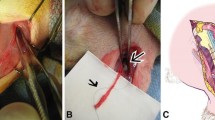
Tibial segmental defects were filled with heat sterilized allogenic tubular tibiae sections and then stabilized with a screw plate. In the VEGF treatment group (n = 6 tibiae), 2 μg of VEGF added to a 50 μl matrigel solution was inserted into the allograft cavity. In the control group (n = 6 tibiae), only matrigel was added. After 12 weeks, macroscopic and microscopic analysis, radiographs, and computerized micro-tomography (micro-CT) were performed. If allograft consolidation was present, a torsional resistance analysis was performed.
Results
Addition of VEGF to the allograft decreased the rate of osteosynthesis failure compared with the control group (1/6 vs. 5/6, p = 0.08), increased trabecular continuity evaluated by micro-CT in the bone–allograft interphases (8/12 vs. 2/12, p = 0.036) and histological trabecular continuity (7/12 vs. 0/12, p = 0.0046). Full consolidation was observed in three tibiae of the VEGF group and one in the control group (differences not significant); however, torsional resistance showed no significant differences (n.s.).
Conclusion
Addition of VEGF to a structural allograph inserted into a rabbit tibial segmental defect increased allograft integration rate. Further research in this direction might help clinicians in dealing with large bone defects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beamer B, Hettrich C, Lane J (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor: an essential component of angiogenesis and fracture healing. HSS J 6(1):85–94
Breitbart EA, Meade S, Azad V, Yeh S, Al-Zube L, Lee YS, Benevenia J, Arinzeh TL, Lin SS (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells accelerate bone allograft incorporation in the presence of diabetes mellitus. J Orthop Res 28(7):942–949
Brownlow HC, Simpson AH (2000) Metabolic activity of a new atrophic nonunion model in rabbits. J Orthop Res 18(3):438–442
Bullens PH, Minderhoud NM, de Waal Malefijt MC, Veth RP, Buma P, Schreuder HW (2009) Survival of massive allografts in segmental oncological bone defect reconstructions. Int Orthop 33(3):757–760
Daines BK, Dennis DA (2013) Management of bone defects in revision total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect 62:341–348
Dedania J, Borzio R, Paglia D, Breitbart EA, Mitchell A, Vaidya S, Wey A, Mehta S, Benevenia J, O’Connor JP, Lin SS (2011) Role of local insulin augmentation upon allograft incorporation in a rat femoral defect model. J Orthop Res 29(1):92–99
Devescovi V, Leonardi E, Ciapetti G, Cenni E (2008) Growth factors in bone repair. Chir Organi Mov 92(3):161–168
Eckardt H, Bundgaard KG, Christensen KS, Lind M, Hansen ES, Hvid I (2003) Effects of locally applied vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF-inhibitor to the rabbit tibia during distraction osteogenesis. J Orthop Res 21(2):335–340
Eckardt H, Ding M, Lind M, Hansen ES, Christensen KS, Hvid I (2005) Recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor enhances bone healing in an experimental nonunion model. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(10):1434–1438
Evans CH (2010) Gene therapy for bone healing. Expert Rev Mol Med 12:e18
Finn HA, Nicholas RW, Webb JE (1990) Skeletal reconstruction with allograft segments following bone tumor resection. Contemp Orthop 21(5):455–471
Fuchs B, Ossendorf C, Leerapun T, Sim FH (2008) Intercalary segmental reconstruction after bone tumor resection. Eur J Surg Oncol 34(12):1271–1276
Gale NW, Thurston G, Davis S, Wiegand SJ, Holash J, Rudge JS, Yancopoulos GD (2002) Complementary and coordinated roles of the VEGFs and angiopoietins during normal and pathologic vascular formation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 67:267–273
Geiger F, Bertram H, Berger I, Lorenz H, Wall O, Eckhardt C, Simank HG, Richter W (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene-activated matrix (VEGF165-GAM) enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in large segmental bone defects. J Bone Miner Res 20(11):2028–2035
Goldstein SA (2006) Tissue engineering solutions for traumatic bone loss. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(10 Spec No):S152–S156. doi:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17003189
Kaipel M, Schutzenberger S, Schultz A, Ferguson J, Slezak P, Morton TJ, Van Griensven M, Redl H (2012) BMP-2 but not VEGF or PDGF in fibrin matrix supports bone healing in a delayed-union rat model. J Orthop Res 30(10):1563–1569
Kanczler JM, Ginty PJ, Barry JJ, Clarke NM, Howdle SM, Shakesheff KM, Oreffo RO (2008) The effect of mesenchymal populations and vascular endothelial growth factor delivered from biodegradable polymer scaffolds on bone formation. Biomaterials 29(12):1892–1900
Kawaguchi H, Nakamura K, Tabata Y, Ikada Y, Aoyama I, Anzai J, Nakamura T, Hiyama Y, Tamura M (2001) Acceleration of fracture healing in nonhuman primates by fibroblast growth factor-2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(2):875–880
Li R, Nauth A, Li C, Qamirani E, Atesok K, Schemitsch EH (2012) Expression of VEGF gene isoforms in a rat segmental bone defect model treated with EPCs. J Orthop Trauma 26(12):689–692
Li R, Stewart DJ, von Schroeder HP, Mackinnon ES, Schemitsch EH (2009) Effect of cell-based VEGF gene therapy on healing of a segmental bone defect. J Orthop Res 27(1):8–14
Lu H, Pei G, Zhao P, Liang S, Jin D, Jiang S (2010) Cyclosporine-impregnated allograft bone sterilized with low-temperature plasma. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 4(8):638–651
McKee MD (2006) Management of segmental bony defects: the role of osteoconductive orthobiologics. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(10 Spec No):S163–S167
Muscolo DL, Ayerza MA, Aponte-Tinao LA (2006) Massive allograft use in orthopedic oncology. Orthop Clin North Am 37(1):65–74
Ochman S, Frey S, Raschke MJ, Deventer JN, Meffert RH (2011) Local application of VEGF compensates callus deficiency after acute soft tissue trauma–results using a limb-shortening distraction procedure in rabbit tibia. J Orthop Res 29(7):1093–1098
Pape HW, TG. (2010) Autologous techniques to fill bone defects for acute fractures and nonunions, an issue of orthopedic clinics, vol 1. The clinics: orthopedics, 1 edn. Saunders
Pneumaticos SG, Triantafyllopoulos GK, Basdra EK, Papavassiliou AG (2010) Segmental bone defects: from cellular and molecular pathways to the development of novel biological treatments. J Cell Mol Med 14(11):2561–2569
Puzas JE, Houck J, Bukata SV (2006) Accelerated fracture healing. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(10 Spec No):S145–S151
Ripamonti U, Ferretti C, Teare J, Blann L (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta isoforms and the induction of bone formation: implications for reconstructive craniofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg 20(5):1544–1555
Shen FH, Werner BC, Liang H, Shang H, Yang N, Li X, Shimer AL, Balian G, Katz AJ (2013) Implications of adipose-derived stromal cells in a 3D culture system for osteogenic differentiation: an in vitro and in vivo investigation. Spine J 13(1):32–43
Yang P, Wang C, Shi Z, Huang X, Dang X, Li X, Lin SF, Wang K (2010) rhVEGF 165 delivered in a porous beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold accelerates bridging of critical-sized defects in rabbit radii. J Biomed Mater Res A 92(2):626–640
Yasuda H, Yano K, Wakitani S, Matsumoto T, Nakamura H, Takaoka K (2012) Repair of critical long bone defects using frozen bone allografts coated with an rhBMP-2-retaining paste. J Orthop Sci 17(3):299–307
Zou XH, Cai HX, Yin Z, Chen X, Jiang YZ, Hu H, Ouyang HW (2009) A novel strategy incorporated the power of mesenchymal stem cells to allografts for segmental bone tissue engineering. Cell Transplant 18(4):433–441
Acknowledgments
This study has been funded by grants provided by the Association Internationale pourl′Ostéosynthèse Dynamique and the Sociedad Española de Cirugía Ortopédica y Traumatología.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Ibán, M.A., Gonzalez-Lizán, F., Diaz-Heredia, J. et al. Effect of VEGF-A165 addition on the integration of a cortical allograft in a tibial segmental defect in rabbits. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23, 1393–1400 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2785-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2785-4