Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to research which was the most reliable of the four techniques based on local anatomic markers used to determine tibial component rotation in total knee arthroplasty, and whether the markers varied in knees with varus deformity.
Methods
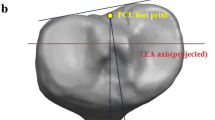
The study included 33 knees with a normal anatomic axis and 32 knees with a varus deformity and osteoarthritis. On the MR images, the femoral transepicondylar axis (TEA) was determined and transposed to the standard tibial resection level. At this level, four axes were drawn on the axial sections: tibial posterior condylar line (PC), tibial plateau anterior line (AC), a vertical line (AA) drawn to Akagi’s line, and the maximal mediolateral distance (MMLD). The relationships of these lines and the transposed TEA were compared between two groups.
Results
In all the knees, the mean values of the PC, AA, and MMLD axes compared to TEA reference were 5.5° ± 5.7 (mean ± SD), 7° ± 3.2, and 6.7° ± 8.1 internal rotation, respectively, and the AC axis was 8.9° ± 6.7 external rotation. In the AC, AA, and MMLD axes, the change occured because of varus deformity was statistically meaningful. For all the observers, the axis with the least SD and the most accuracy was the AA axis.
Conclusions
Of the four axes used to determine tibial component rotation, only the PC axis is not affected by varus deformity, and the least affected axis according to the observers was the AA axis, and thus the AA and PC axes can be used for guidance in determining the rotation of the tibial component.
Level of evidence
Prognostic studies—investigating natural history and evaluating the effect of a patient characteristic: High-quality prospective cohort study with >80% follow-up, and all patients enrolled at same time point in disease, Level I.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Sensi L, Cuomo P, Ciardullo A (2008) Rotational position of femoral and tibial components in TKA using the femoral transepicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2751–2755
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2004) An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:213–219
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Anouchi YS, Whiteside LA, Kaiser AD, Milliano MT (1993) The effects of axial rotational alignment of the femoral component on knee stability and patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty demonstrated on autopsy specimens. Clin Orthop Relat Res 287:170–177
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:40–47
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Chowdhury EA, Porter ML (2005) A study of the effect of tibial tray rotation on a specific mobile bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:793–797
Churchill DL, Incavo SJ, Johnson CC, Beynnon BD (1998) The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:111–118
Czurda T, Fennema P, Baumgartner M, Ritschl P (2010) The association between component malalignment and post-operative pain following navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty: results of a cohort/nested case-control study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:863–869
Dalury DF (2001) Observations of the proximal tibia in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:150–155
Fukagawa S, Matsuda S, Mitsuyasu H, Miura H, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2011) Anterior border of the tibia as a landmark for extramedullary alignment guide in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Orthop Res 29:919–924
Graw BP, Harris AH, Tripuraneni KR, Giori NJ (2010) Rotational references for total knee arthroplasty tibial components change with level of resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:2734–2738
Incavo SJ, Coughlin KM, Pappas C, Beynnon BD (2003) Anatomic rotational relationships of the proximal tibia, distal femur, and patella: implications for rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 18:643–648
Insall JN (1993) Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. In: Insall JN, Windsor RE, Scott WN, Kelly M, Aglietti P (eds) Surgery of the knee, 2nd edn. Churchill-Livingstone, New York, pp 739–804
Jung YB, Lee HJ, Jung HJ, Song KS, Lee JS, Yang JJ (2009) Comparison of the radiological results between fluoroscopy-assisted and navigation-guided total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17:286–292
Lützner J, Krummenauer F, Günther KP, Kirschner S (2010) Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty is beter at the medial third of tibial tuberosity than at the medial border. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:57
Matsui Y, Kadoya Y, Uehara K, Kobayashi A, Takaoka K (2005) Rotational deformity in varus osteoarthritis of the knee: analysis with computed tomography. Clin Orthop Relat Res 433:147–151
Merkow RL, Soudry M, Insall JN (1985) Patellar dislocation following total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67:1321–1327
Miller MC, Berger RA, Petrella AJ, Karmas A, Rubash HE (2001) Optimizing femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:38–45
Moreland JR (1988) Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Nagamine R, Whiteside LA, White SE, McCarthy DS (1994) Patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. The effect of tibial tray malrotation and articular surface configuration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 304:262–271
Page SR, Deakin AH, Payne AP, Picard F (2011) Reliability of frames of reference used for tibial component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg 16:86–92
Rossi R, Bruzzone M, Bonasia DE, Marmotti A, Castoldi F (2010) Evaluation of tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a cadaver study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:889–893
Singerman R, Pagan HD, Peyser AB, Goldberg VM (1997) Effect of femoral component rotation and patellar design on patellar forces. Clin Orthop Relat Res 334:345–353
Siston RA, Goodman SB, Patel JJ, Delp SL, Giori NJ (2006) The high variability of tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:65–69
Sun T, Lu H, Hong N, Wu J, Feng C (2009) Bony landmarks and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty for Chinese osteoarthritic knees with varus or valgus deformities. J Arthroplasty 24:427–431
Whiteside LA, Arima J (1995) The anteroposterior axis for femoral rotational alignment in valgus total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 321:168–172
Yoshioka Y, Siu DW, Scudamore RA, Cooke TD (1989) Tibial anatomy and functional axes. J Orthop Res 7:132–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şahin, N., Atıcı, T., Öztürk, A. et al. Accuracy of anatomical references used for rotational alignment of tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20, 565–570 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1606-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1606-x