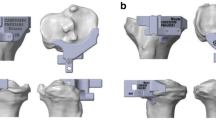
Abstract
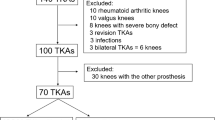
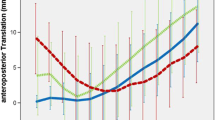
A new generation of implantation instruments were developed for quadriceps sparing surgical approaches during total knee arthroplasty (TKA). There is little information on the accuracy of the bone cuts performed with the side-cutting technique. A total of 100 patients were randomized to undergo computer-assisted TKA or non-navigated TKA using a mini-subvastus surgical approach and side-cutting implant instrumentation. The radiographic parameters, clinical outcomes and knee scores were evaluated 3 months postoperative. The mechanical axis of the limb was within 3° varus/valgus in 76% of the patients who had navigated procedures versus 66% of patients who had conventional surgery. The tibial slope showed a rate of inaccuracy of 3° or less for 78% of the patients in the navigated total knee arthroplasty group versus 66% of the patients in the conventional group. Clinical outcomes and knee scores were similar in both groups. The navigation technique could not compensate for shortcomings of the implantation instruments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Baldini A, Sensi L (2006) Quadriceps-sparing versus mini-subvastus approach in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:106–111
Boerger TO, Aglietti P, Mondanelli N, Sensi L (2005) Mini-subvastus versus medial parapatellar approach in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:82–87
Bonutti PM, Mont MA, McMahon M, Ragland PS, Kester M (2004) Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(Suppl 2):26–32
Chauhan SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Beaver RJ (2004) Computer-assisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jig-based technique: a randomised, prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:372–377
Chen AF, Alan RK, Redziniak DE, Tria AJ Jr (2006) Quadriceps sparing total knee replacement: the initial experience with results at two to four years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:1448–1453
Chin PL, Foo LS, Yang KY, Yeo SJ, Lo NN (2007) Randomized controlled trial comparing the radiologic outcomes of conventional and minimally invasive techniques for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 22:800–806
Coon TM (2007) Quadriceps-sparing minimally invasive technique for total knee arthroplasty: a new classification. Orthopade 36:1113–1119
Dalury DF, Dennis DA (2005) Mini-incision total knee arthroplasty can increase risk of component malalignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:77–81
Dutton AQ, Yeo SJ, Yang KY et al (2008) Computer-assisted minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with standard total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:2–9
Haas SB, Cook S, Beksac B (2004) Minimally invasive total knee replacement through a mini midvastus approach: a comparative study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:68–73
Haas SB, Manitta MA, Burdick P (2006) Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty: the mini midvastus approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:112–116
Hart R, Janecek M, Cizmar I et al (2006) Minimally invasive and navigated implantation for total knee arthroplasty: x-ray analysis and early clinical results. Orthopade 35:552–557
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Keblish PA (1991) The lateral approach to the valgus knee: surgical technique and analysis of 53 cases with over two-year follow-up evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 271:52–62
King J, Stamper DL, Schaad DC, Leopold SS (2007) Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with traditional total knee arthroplasty: assessment of the learning curve and the postoperative recuperative period. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:1497–1503
Laskin RS (2003) New techniques and concepts in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 416:151–153
Laskin RS (2007) Surgical exposure for total knee arthroplasty: for everything there is a season. J Arthroplasty 22:12–14
Mahaluxmivala J, Bankes MJ, Nicolai P, Aldam CH, Allen PW (2001) The effect of surgeon experience on component positioning in 673 press fit condylar posterior cruciate-sacrificing total knee arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty 16:635–640
Martin A, von Strempel A (2006) Two-year outcomes of computed tomography-based and computed tomography free navigation for total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 449:275–282
Martin A, Wohlgenannt O, Prenn M, Oelsch C, Strempel A (2007) Imageless navigation for TKA increases implantation accuracy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 460:178–184
Matziolis G, Krocker D, Weiss U, Tohtz S, Perka C (2007) A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty: three-dimensional evaluation of implant alignment and rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:236–243
Moreland JR (1988) Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Pagnano MW, Meneghini RM (2006) Minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty with an optimized subvastus approach. J Arthroplasty 21:22–26
Paley D, Pfeil J (2000) Principles of deformity correction around the knee. Orthopäde 29:18–38
Plaskos C, Hodgson AJ, Inkpen K, McGraw RW (2002) Bone cutting errors in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 17:698–705
Price AJ, Webb J, Topf H et al (2001) Rapid recovery after oxford unicompartmental arthroplasty through a short incision. J Arthroplasty 16:970–976
Rand JA, Coventry MB (1988) Ten-year evaluation of geometric total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 232:168–173
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement: its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Rosenberger RE, Hoser C, Quirbach S et al (2008) Improved accuracy of component alignment with the implementation of image-free navigation in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:249–257
Scuderi GR, Tenholder M, Capeci C (2004) Surgical approaches in mini-incision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:61–67
Seon JK, Song EK (2006) Navigation-assisted less invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective trial. J Arthroplasty 21:777–782
Siston RA, Goodman SB, Patel JJ, Delp SL, Giori NJ (2006) The high variability of tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:65–69
Siston RA, Patel JJ, Goodman SB, Delp SL, Giori NJ (2005) The variability of femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:2276–2280
Tenholder M, Clarke HD, Scuderi GR (2005) Minimal-incision total knee arthroplasty: the early clinical experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:67–76
Tria AJ Jr, Coon TM (2003) Minimal incision total knee arthroplasty: early experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res 416:185–190
Victor J, Hoste D (2004) Image-based computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty leads to lower variability in coronal alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:131–139
Wysocki RW, Sheinkop MB, Virkus WW, Della Valle CJ (2008) Femoral fracture through a previous pin site after computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 23:462–465
Acknowledgments
We declare that the study complies with the current laws of Austria and the United States of America. Each author certifies that his institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent was obtained.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, A., Sheinkop, M.B., Langhenry, M.M. et al. Accuracy of side-cutting implantation instruments for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17, 374–381 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-008-0704-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-008-0704-x