Abstract
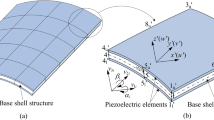
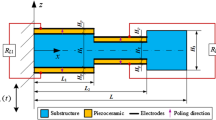
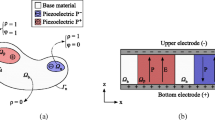
This paper investigates topology optimization of the electrode coverage over piezoelectric patches attached to a thin-shell structure to reduce the energy consumption of active vibration control under harmonic excitations. The constant gain velocity feedback control method is employed, and the structural frequency response under control is analyzed with the finite element method. In the mathematical formulation of the proposed topology optimization model, the total energy consumption of the control system is taken as the objective function, and a constraint of the maximum allowable dynamic compliance is considered. The pseudo-densities indicating the distribution of surface electrode coverage over the piezoelectric layers are chosen as the design variables, and a penalized model is employed to relate the active damping effect and these design variables. The sensitivity analysis scheme of the control energy consumption with respect to the design variables is derived with the adjoint-variable method. Numerical examples demonstrate that the proposed optimization model is able to generate optimal topologies of electrode coverage over the piezoelectric layers, which can effectively reduce the energy consumption of the control system. Also, numerical comparisons with a minimum-volume optimization model show the advantage of the proposed method with respect to energy consumption. The proposed method may provide useful guidance to the layout optimization of piezoelectric smart structures where the energy supply is limited, such as miniature vibration control systems.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aridogan U, Basdogan I (2015) A review of active vibration and noise suppression of plate-like structures with piezoelectric transducers. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 26(12):1455–1476
Bazin L, Mitra S, Taberna PL, Poizot P, Gressier M, Menu MJ, Barnabé A, Simon P, Tarascon J-M (2009) High rate capability pure Sn-based nano-architectured electrode assembly for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Power Sources 188(2):578–582
Beckert W, Kreher WS (2003) Modelling piezoelectric modules with interdigitated electrode structures. Comput Mater Sci 26:36–45
Brennan MC, McGowan A-MR (1997) Piezoelectric power requirements for active vibration control. Proc. SPIE 3039, Smart Structures and Materials 1997: Mathematics and Control in Smart Structures. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.276584
Bruant I, Gallimard L, Nikoukar S (2010) Optimal piezoelectric actuator and sensor location for active vibration control, using genetic algorithm. J Sound Vib 329(10):1615–1635
Carbonari RC, Silva EC, Paulino GH (2009) Multi-actuated functionally graded piezoelectric micro-tools design: a multiphysics topology optimization approach. Int J Numer Methods Eng 77(3):301–336
Chevva K, Sun F, Blanc A, Mendoza J (2015) Active vibration control using minimum actuation power. J Sound Vib 340:1–21
Darivandi N, Morris K, Khajepour A (2013) An algorithm for LQ optimal actuator location. Smart Mater Struct 22(3):035001
Devasia S, Meressi T, Paden B, Bayo E (1993) Piezoelectric actuator design for vibration suppression-placement and sizing. J Guid Control Dyn 16(5):859–864
van Dijk NP, Maute K, Langelaar M, Van Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):437–472
Donoso A, Sigmund O (2009) Optimization of piezoelectric bimorph actuators with active damping for static and dynamic loads. Struct Multidiscip Optim 38(2):171–183
Dou S, Jensen JS (2015) Optimization of nonlinear structural resonance using the incremental harmonic balance method. J Sound Vib 334:239–254
Du J, Olhoff N (2007a) Minimization of sound radiation from vibrating bi-material structures using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4–5):305–321
Du J, Olhoff N (2007b) Topological design of freely vibrating continuum structures for maximum values of simple and multiple eigenfrequencies and frequency gaps. Struct Multidiscip Optim 34(2):91–110
Dühring MB, Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2008) Acoustic design by topology optimization. J Sound Vib 317(3):557–575
Ghasemi H, Park HS, Rabczuk T (2017) A level-set based IGA formulation for topology optimization of flexoelectric materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 313:239–258
Gonçalves JF, De Leon DM, Perondi EA (2017) Topology optimization of embedded piezoelectric actuators considering control spillover effects. J Sound Vib 388:20–41
Hu J, Zhang X, Kang Z (2017) Layout design of piezoelectric patches in structural LQR optimal control using topology optimization. Submitted
Huang X, Xie Y-M (2010) A further review of ESO type methods for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(5):671–683
Kang Z, Tong L (2008) Integrated optimization of material layout and control voltage for piezoelectric laminated plates. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 19:889–904
Kang Z, Wang R, Tong L (2011) Combined optimization of bi-material structural layout and voltage distribution for in-plane piezoelectric actuation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(13):1467–1478
Kögl M, Silva EC (2005) Topology optimization of smart structures: design of piezoelectric plate and shell actuators. Smart Mater Struct 14(2):387
Liu H, Zhang W, Gao T (2015) A comparative study of dynamic analysis methods for structural topology optimization under harmonic force excitations. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(6):1321–1333
Ma Z-D, Kikuchi N, Cheng H-C (1995) Topological design for vibrating structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 121(1):259–280
Mello LAM, Kiyono CY, Nakasone PH, Silva ECN (2014) Design of quasi-static piezoelectric plate based transducers by using topology optimization. Smart Mater Struct 23(2):025035
Mukherjee A, Joshi S (2001) Design of actuator profiles for minimum power consumption. Smart Mater Struct 10(2):305
Nanthakumar S, Lahmer T, Zhuang X, Park HS, Rabczuk T (2016) Topology optimization of piezoelectric nanostructures. J Mech Phys Solids 94:316–335
Nguyen M, Nazeer H, Dekkers M, Blank D, Rijnders G (2013) Optimized electrode coverage of membrane actuators based on epitaxial PZT thin films. Smart Mater Struct 22(8):085013
Noh JY, Yoon GH (2012) Topology optimization of piezoelectric energy harvesting devices considering static and harmonic dynamic loads. Adv Eng Softw 53:45–60
Olhoff N, Du J (2014) Topological design for minimum sound emission from structures under forced vibration. In: Topology Optimization in Structural and Continuum Mechanics. Springer, Vienna 341–357
Olhoff N, Du J (2016) Generalized incremental frequency method for topological designof continuum structures for minimum dynamic compliance subject to forced vibration at a prescribed low or high value of the excitation frequency. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54(5):1113–1141
Peng F, Ng A, Hu Y-R (2005) Actuator placement optimization and adaptive vibration control of plate smart structures. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 16(3):263–271
Ruiz D, Bellido J, Donoso A, Sánchez-Rojas J (2013) Design of in-plane piezoelectric sensors for static response by simultaneously optimizing the host structure and the electrode profile. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(5):1023–1026
Shu L, Wang MY, Fang Z, Ma Z, Wei P (2011) Level set based structural topology optimization for minimizing frequency response. J Sound Vib 330(24):5820–5834
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Sigmund O, Torquato S (1997) Design of materials with extreme thermal expansion using a three-phase topology optimization method. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 45:1037–1067
Silva ECN, Kikuchi N (1999) Design of piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization. Smart Mater Struct 8(3):350
Sun D, Tong L (2005) Design optimization of piezoelectric actuator patterns for static shape control of smart plates. Smart Mater Struct 14(6):1353
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J Optim 12(2):555–573
Takezawa A, Makihara K, Kogiso N, Kitamura M (2014) Layout optimization methodology of piezoelectric transducers in energy-recycling semi-active vibration control systems. J Sound Vib 333(2):327–344
Takezawa A, Daifuku M, Nakano Y, Nakagawa K, Yamamoto T, Kitamura M (2016) Topology optimization of damping material for reducing resonance response based on complex dynamic compliance. J Sound Vib 365:230–243
Vicente W, Picelli R, Pavanello R, Xie Y (2015) Topology optimization of frequency responses of fluid–structure interaction systems. Finite Elem Anal Des 98:1–13
Wallenhauer C, Kappel A, Gottlieb B, Schwebel T, Lüth T (2009) Efficient class-B analog amplifier for a piezoelectric actuator drive. Mechatronics 19(1):56–64
Wang S, Tai K, Quek S (2006) Topology optimization of piezoelectric sensors/actuators for torsional vibration control of composite plates. Smart Mater Struct 15(2):253
Xu B, Jiang J, Ou J (2007) Integrated optimization of structural topology and control for piezoelectric smart trusses using genetic algorithm. J Sound Vib 307(3):393–427
Yamamoto T, Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2015) Topology optimization of free-layer damping material on a thin panel for maximizing modal loss factors expressed by only real eigenvalues. J Sound Vib 358:84–96
Yan K, Cheng G, Wang BP (2016) Topology optimization of plate structures subject to initial excitations for minimum dynamic performance index. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(3):623–633
Yoon GH (2010) Structural topology optimization for frequency response problem using model reduction schemes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(25):1744–1763
Yoon GH (2013) Acoustic topology optimization of fibrous material with Delany–Bazley empirical material formulation. J Sound Vib 332(5):1172–1187
Zhang X, Kang Z (2013) Topology optimization of damping layers for minimizing sound radiation of shell structures. J Sound Vib 332(10):2500–2519
Zhang X, Kang Z (2014a) Dynamic topology optimization of piezoelectric structures with active control for reducing transient response. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 281:200–219
Zhang X, Kang Z (2014b) Topology optimization of piezoelectric layers in plates with active vibration control. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 25(6):697–712
Zhang X, Kang Z, Li M (2014) Topology optimization of electrode coverage of piezoelectric thin-walled structures with CGVF control for minimizing sound radiation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50(5):799–814
Zhang W, Liu H, Gao T (2015) Topology optimization of large-scale structures subjected to stationary random excitation: an efficient optimization procedure integrating pseudo excitation method and mode acceleration method. Comput Struct 158:61–70
Zorić ND, Simonović AM, Mitrović ZS, Stupar SN (2012) Optimal vibration control of smart composite beams with optimal size and location of piezoelectric sensing and actuation. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 24:499–526
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Krister Svanberg for providing the source code of the GCMMA algorithm. The authors also acknowledge the support of the Natural Science Foundation of China (11602049, 11425207, and U1608256), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015 M581328), and Research Project of State Key Laboratory of Mechanical System and Vibration (MSV201603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Takezawa, A. & Kang, Z. Topology optimization of piezoelectric smart structures for minimum energy consumption under active control. Struct Multidisc Optim 58, 185–199 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1886-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1886-y