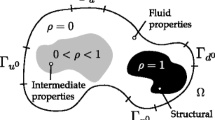
Abstract
This paper studies level set topology optimization of scalar transport problems, modeled by an advection-diffusion equation. Examples of such problems include the transport of energy or mass in a fluid. The geometry is defined via a level set method (LSM). The flow field is predicted by a hydrodynamic Boltzmann transport model and the scalar transport by a standard advection-diffusion model. Both models are discretized by the extended Finite Element Method (XFEM). The hydrodynamic Boltzmann equation is well suited for the XFEM as it allows for convenient enforcement of boundary conditions along immersed boundaries. In contrast, Navier Stokes models require more complex approaches to impose Dirichlet boundary conditions, such as stabilized Lagrange multiplier and Nitsche methods.
The combination of the LSM and the XFEM is an alternative to density-based topology optimization methods which have been applied previously to scalar transport problems. Density methods often suffer from a fuzzy description of boundaries, spurious diffusion through “void” regions, and the presence of fictitious material in the optimized design. This paper illustrates that the LSM/XFEM approach addresses these three concerns. The proposed approach is studied with two dimensional problems at steady state conditions. Both “fluid-void” and “fluid-solid” optimization problems are considered. For the “fluid-void” case, optimization results are obtained without spurious diffusion through “void” regions. For the “fluid-solid” case, the analysis recovers strong gradients of the flow and scalar fields at the fluid-solid interface, using moderately refined meshes.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Andreasen CS, Gersborg AR, Sigmund O (2009) Topology optimization of microfluidic mixers. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 61(5):498–513
Angot P, Bruneau CH, Fabrie P (1999) A penalization method to take into account obstacles in viscous flows. Numer Math 81:497–520
Avila M, Codina R, Principe J (2011) Spatial approximation of the radiation transport equation using a subgrid-scale finite element method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(5-8):425–438
Bhatnagar PL, Gross EP, Krook M (1954) A model for collision processes in gases. I. small amplitude processes in charged and neutral one-component systems. Phys Rev 94(3):511–525
Bijl H, Carpenter MH, Vatsa VN, Kennedy CA (2002) Implicit time integration schemes for the unsteady compressible Navier-Stokes equations: Laminar flow. J Comput Phys 179(1):313–329
Borrvall T, Petersson J (2003) Topology optimization of fluids in stokes flow. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 41(1):77–107
Brooks AN, Hughes TJ (1982) Streamline upwind/Petrov-Galerkin formulations for convection dominated flows with particular emphasis on the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 32(1-3):199–259
Cao N, Chen S, Jin S, Martínez D (1997) Physical symmetry and lattice symmetry in the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys Rev E 55:R21–R24
Chen H (1998) Volumetric formulation of the lattice Boltzmann method for fluid dynamics: Basic concept. Phys Rev E 58:3955–3963
Codina R (1998) Comparison of some finite element methods for solving the diffusion-convection-reaction equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 156(1-4):185–210
Codina R (2001) A stabilized finite element method for generalized stationary incompressible flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(2021):2681–2706
Codina R (2002) Stabilized finite element approximation of transient incompressible flows using orthogonal subscales. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191(39-40):4295–4321
Daux C, Moes N, Dolbow J, Sukumark N, Belytschko T (2000) Arbitrary branched and intersecting cracks with the extended nite element method. Int J Numer Meth Engng 48:1741–1760
Dede E (2010) Multiphysics optimization, synthesis, and application of jet impingement target surfaces. In: Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (ITherm), 2010 12th IEEE Intersociety Conference on, pp 1–7
van Dijk N, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2012) Explicit level-set-based topology optimization using an exact heaviside function and consistent sensitivity analysis. Int J Numer Meth Engng 91(1):67–97
van Dijk N, Maute K, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2013) Levelset methods for structural topology optimization A review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):437–472
Dolbow J, Harari I (2009) An efficient finite element method for embedded interface problems. Int J Numer Meth Engng 78:229–252
Düster A, Demkowicz L, Rank E (2006) High-order finite elements applied to the discrete Boltzmann equation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 67(8):1094–1121
Duysinx P, Miegroet L, Jacobs T, Fleury C (2006) Generalized shape optimization using x-fem and level set methods. , In: IUTAM Symposium on Topological Design Optimization of Structures. Springer, Machines and Materials, pp 23–32
Evans B, Morgan K, Hassan O (2011) A discontinuous finite element solution of the Boltzmann kinetic equation in collisionless and BGK forms for macroscopic gas flows. Appl Math Model 35(3):996–1015
Fries T, Belytschko T (2010) The extended/generalized finite element method: an overview of the method and its applications. Int J Numer Methods Eng 84(3):253–304
Fries TP (2009) The intrinsic xfem for two-fluid flows. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 60(4):437–471
Gersborg-Hansen A, Sigmund O, Haber RB (2005) Topology optimization of channel flow problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 30(3):181–192
Gersborg-Hansen A, Bendse MP, Sigmund O (2006) Topology optimization of heat conduction problems using the finite volume method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 31(4):251–259
Gerstenberger A, Wall WA (2008) An extended finite element method/Lagrange multiplier based approach for fluid-structure interaction. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197:1699–1714
Grad H (1949) On the kinetic theory of rarefied gases. Commun Pur Appl Math 2(4):331–407
Guest J, Prévost J, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238– 254
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhong W (2014) Explicit feature control in structural topology optimization via level set method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 272:354–378
Hansbo A, Hansbo P (2004) A finite element method for the simulation of strong and weak discontinuities in solid mechanics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(3335):3523–3540
Hauke G (2002) A simple subgrid scale stabilized method for the advection-diffusion-reaction equation. Comput Methods Appl Mechanics Eng 191(27–28):2925–2947
Hughes TJR, Mallet M (1986) A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: III. The generalized streamline operator for multidimensional advective-diffusive systems. Comput Methods Appl Mechanics Eng 58(3):305–328
Juntunen M, Stenberg R (2009) Nitsches method for general boundary conditions. Math Comput 78:1353–1374
Kontoleontos EA, Papoutsis-Kiachagias EM, Zymaris AS, Papadimitriou DI, Giannakoglou KC (2013) Adjoint-based constrained topology optimization for viscous flows, including heat transfer. Eng Opt 45(8):941–961
Kreisselmeier G, Steinhauser R (1979) Systematic control design by optimizing a vector performance index. , In: International Federation of Active Contrals Symposium on Computer Aided Design of Control Systems. Zurich, Switzerland
Kreissl S, Maute K (2011) Topology optimization for unsteady flow. Int J Numer Methods Eng 87:1229–1253
Kreissl S, Maute K (2012) Levelset based fluid topology optimization using the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(3):311–326
Kreissl S, Pingen G, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2010) Topology optimization of flexible micro-fluidic devices. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42(4):495–516
Kreissl S, Pingen G, Maute K (2011) An explicit level set approach for generalized shape optimization of fluids with the lattice boltzmann method. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 65(5):496–519
Lang C, Makhija D, Doostan A,Maute K (2013) A simple and efficient preconditioning scheme for xfem with heaviside enrichments. http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6092
Lee T, Lin CL (2001) A characteristic Galerkin method for discrete Boltzmann equation. J Comput Phys 171(1):336–356
Li Y, LeBoeuf EJ, Basu PK (2004) Least-squares finite-element lattice Boltzmann method. Phys Rev E 69(065):701
Li Y, LeBoeuf E, Basu P (2005) Least-squares finite-element scheme for the lattice Boltzmann method on an unstructured mesh. Phys Rev E 72(4)(046):711
Luo Z, Tong L, Wang MY, Wang S (2007) Shape and topology optimization of compliant mechanisms using a parameterization level set method. J Comput Phys 227(1):680–705
Makhija D, Maute K (2014) Numerical instabilities in level set topology optimization with the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(2):185–197
Makhija D, Pingen G, Yang R, Maute K (2012) Topology optimization of multi-component flows using a multi-relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method. Comput Fluids 67(0):104–114
Makhija D, Pingen G, Maute K (2014) An immersed boundary method for fluids using the xfem and the hydrodynamic boltzmann transport equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 273:37–55
Matsumori T, Kondoh T, Kawamoto A, Nomura T (2013) Topology optimization for fluid-thermal interaction problems under constant input power. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47(4):571–581
Maute K, Kreissl S, Makhija D, Yang R (2011) Topology optimization of heat conduction in nano-composites. Shizuoka, Japan
Mei R, Shyy W (1998) On the finite difference-based lattice Boltzmann method in curvilinear coordinates. J Comput Phys 143(2):426–448
van Miegroet L, Duysinx P (2007) Stress concentration minimization of 2d filets using x-fem and level set description. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4-5):425–438
van Miegroet L, Moës N Fleury C, Duysinx P (2005) Generalized shape optimization based on the level set method. In: 6 th World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization
Min M, Lee T (2011) A spectral-element discontinuous Galerkin lattice Boltzmann method for nearly incompressible flows. J Comput Phys 230(1):245–259
Nannelli F, Succi S (1992) The lattice Boltzmann equation on irregular lattices. J Stat Phys 68:401–407
Okkels F, Gregersen M, Bruus H (2009) Topology optimization of fully nonlinear lab-on-a-chip systems. In: Proceedings of 8th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, June 1–5, 2009. Lisbon, Portugal
Othmer C (2006) CFD topology and shape optimization with adjoint methods. , In: VDI Fahrzeug- und Verkehrstechnik. Internationaler Kongress, Berechnung und Simulation im Fahrzeugbau, Würzburg, p 13
Othmer C, de Villiers E, Weller HG (2007) Implementation of a continuous adjoint for topology optimization of ducted flows. In: Proceedings of the 18th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference Miami. AIAA, FL
Patil DV, Lakshmisha K (2009) Finite volume TVD formulation of lattice Boltzmann simulation on unstructured mesh. J Comput Phys 228(14):5262–5279
Peng G, Xi H, Duncan C, Chou SH (1998) Lattice Boltzmann method on irregular meshes. Phys Rev E 58:R4124–R4127
Peng G, Xi H, Duncan C, Chou SH (1999) Finite volume scheme for the lattice Boltzmann method on unstructured meshes. Phys Rev E 59:4675–4682
Pingen G, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2009) Adjoint parameter sensitivity analysis for the hydrodynamic lattice Boltzmann method with applications to design optimization. Comput Fluids 38(4):910–923
Pingen G, Waidmann M, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2010) A parametric level-set approach for topology optimization of flow domains. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(1):117–131
Shi X, Lin J, Yu Z (2003) Discontinuous Galerkin spectral element lattice Boltzmann method on triangular element. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 42(11):1249–1261
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches: A comparative review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Stenberg R (1995) On some techniques for approximating boundary conditions in the finite element method. J Comput Appl Math 63(1-3):139–148
Struchtrup H (2005) Macroscopic Transport Equations for Rarefied Gas Flows. Springer
Struchtrup H, Torrilhon M (2003) Regularization of Grad’s 13 moment equations: Derivation and linear analysis. Fluids 15:2668–2680
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J Optim 12(2):555–573
Terada K, Asai M, Yamagishi M (2003) Finite cover method for linear and non-linear analyses of heterogeneous solids. Int J Numer Methods Eng 58(9):1321–1346
Tölke J, Krafczyk M, Schulz M, Rank E (2000) Discretization of the Boltzmann equation in velocity space using a Galerkin approach. Comput Phys Commun 129(13):91–99
Tran AB, Yvonnet J, He QC, Toulemonde C, Sanahuja J (2011) A multiple level set approach to prevent numerical artefacts in complex microstructures with nearby inclusions within xfem. Int J Numer Methods Eng 85(11):1436–1459
Ubertini S, Succi S (2005) Recent advances of lattice Boltzmann techniques on unstructured grids. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, an International Journal 5(1):85– 96
Ubertini S, Bella G, Succi S (2003) Lattice Boltzmann method on unstructured grids: Further developments. Phys Rev E 68(016):701
Villanueva C, Maute K (2014) Density and level set-xfem schemes for topology optimization of 3-D structures. Comput Mech 54(1):133–150
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mechanics Eng 192(1-2):227–246
Wang S, Wang M (2006) Radial basis functions and level set method for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65(12):2060–2090
Wei P, Wang M, Xing X (2010) A study on X-FEM in continuum structural optimization using a level set model. Comput Aided Des 42(8):708–719
Xi H, Peng G, Chou SH (1999) Finite-volume lattice Boltzmann method. Phys Rev E 59:6202–6205
Yang J, Huang J (1995) Rarefied flow computations using nonlinear model Boltzmann equations. J Comput Phys 120(2):323–339
Yoon G (2009) Topology optimization for stationary fluid-structure interaction problems using a new monolithic formulation , In: Proceedings of 8th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. Lisbon, Portugal
Yu D, Mei R, Luo L, Shyy W (2003) Viscous flow computations with the method of lattice Boltzmann equation. Prog Aerosp Sci 39(5):329–367
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Science Foundation under grant EFRI-SEED 1038305 and CBET 1246854. The opinions and conclusions presented in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsoring organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makhija, D., Maute, K. Level set topology optimization of scalar transport problems. Struct Multidisc Optim 51, 267–285 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1142-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1142-7