Abstract
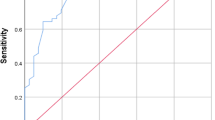
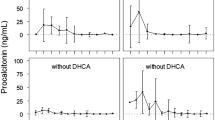
Objective: To determine accuracy of procalcitonin concentrations for diagnosing nosocomial infections in critically ill neonates.¶Design: Case-control study.¶Setting: Neonatal intensive care unit of a teaching hospital.¶Patients: Twenty-three neonates with nosocomial infection. Four controls matched for duration of hospital stay and birth date were chosen for each case patient.¶Measurements and results: PCT concentrations were measured by the LUMItest procalcitonin kit at onset of signs of infection and after recovery. Range of PCT concentrations (ng/ml) was 2.0 to 249.1 in case patients and 0.08 to 1.0 in controls (sensitivity and specificity, 100 %). PCT values returned to normal (< 1.0 ng/ml) by day 3 to 7 of appropriate antibiotic therapy.¶Conclusions: Measurement of PCT concentrations may be useful for early diagnosis and monitoring of infectious complications in neonates during their stay in the neonatal intensive care unit.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiesa, C., Pacifico, L., Rossi, N. et al. Procalcitonin as a marker of nosocomial infections in the neonatal intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med 26 (Suppl 2), S175–S177 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340051139
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340051139