Abstract
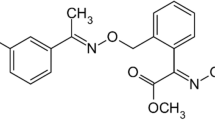
Field trials were carried out to investigate the dissipation and residue levels of bifenthrin in wheat. After extraction with acetonitrile, the samples were cleaned up by dispersive solid-phase extraction and detected by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The half-lives of bifenthrin in wheat seedlings ranged from 2.4 to 10.5 days. At harvest time, the terminal residues of bifenthrin were below the maximum residue limit (0.5 mg/kg) set by Codex Alimentarius Committee or European Union in wheat grain, which suggested that the use of this pesticide was safe for humans. However, the relatively high residue levels of bifenthrin in wheat straw should be paid attention to.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamovic M, Grubic G, Milenkovic I, Jovanovic R, Protic R, Sretenovic L, Stoicevic L (1998) The biodegradation of wheat straw by Pleurotus ostreatus mushrooms and its use in cattle feeding. Anim Feed Sci Technol 71(3–4):357–362
Chen L, Han B, Peng L (2008) Residue analysis and degradation of bifenthrin in cabbage and soil under tropical climate. Mod Agrochem 7:32–35
Chen L, ShangGuan LM, Wu YN, Xu LJ, Fu FF (2011) Study on the residue and degradation of fluorine-containing pesticides in oolong tea by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Control 25(2):433–440
Doyle MA, Kline DL, Allan SA, Kaufman PE (2009) Efficacy of residual bifenthrin applied to landscape vegetation against Aedes albopictus. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 25(2):179–183
Gupta S, Sharma R, Gupta R, Sinha S, Singh R, Gajbhiye V (2009) Persistence of new insecticides and their efficacy against insect pests of okra. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82(2):243–247
Horwood MA (2007) Rapid degradation of termiticides under field conditions. Aust J Entomol 46(1):75–78
Kolberg DI, Prestes OD, Adaime MB, Zanella R (2011) Development of a fast multiresidue method for the determination of pesticides in dry samples (wheat grains, flour and bran) using QuEChERS based method and GC–MS. Food Chem 125(4):1436–1442
Liu H, Zhao M, Zhang C, Ma Y, Liu W (2008) Enantioselective cytotoxicity of the insecticide bifenthrin on a human amnion epithelial (FL) cell line. Toxicology 253(1–3):89–96
Mukherjee I, Singh R, Govil J (2010) Risk assessment of a synthetic pyrethroid, bifenthrin on pulses. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84(3):294–300
Omirou M, Vryzas Z, Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E, Economou A (2009) Dissipation rates of iprodione and thiacloprid during tomato production in greenhouse. Food Chem 116(2):499–504
Reddy DJ, Rao BN (2002) Efficacy of selected insecticides against pests of grapevine. Pestic Res J 14(1):92–99
Tewary DK, Kumar V, Ravindranath S, Shanker A (2005) Dissipation behavior of bifenthrin residues in tea and its brew. Food Control 16(3):231–237
Wang S, Liu F, Jin S, Jiang S (2007) Dissipation of propisochlor and residue analysis in rice, soil and water under field conditions. Food Control 18(6):731–735
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Item No. 21177155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, X., Jiang, N., Liu, F. et al. Dissipation and Residue of Bifenthrin in Wheat under Field Conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90, 238–241 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0903-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0903-5