Abstract
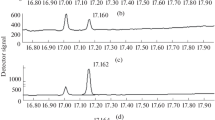
Formaldehyde is a carcinogen to which humans are exposed daily, but few methods are available to quantify formaldehyde in biological samples. We developed a simple, sensitive and rapid technique for the quantification of formaldehyde in urine by derivatization with O-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl)hydroxylamine, using a headspace sampler coupled to a gas chromatograph equipped with an electron capture detector. The detection limit was 1.08 µg/L. The overall recovery of formaldehyde spiked in urine was 99%. The concentration of formaldehyde in urine obtained from healthy volunteers ranged from 56.85 to 144.57 µg/L. This method can be used successfully to measure formaldehyde in urine.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancilla DA, Que Hee SS (1992) O-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorophenyl) methylhydroxylamine hydrochloride: a versatile reagent for the determination of carbonyl-containing compounds. J Chromatogr 627:1–16
de Andrade JB, de Andrade MV, Pinheiro HLC, Martins RA, Borges E (1999) Determination of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde in urine by HPLC Am Lab 31:22–27
Deng C, Zhang X (2004) A simple, rapid and sensitive method for determination of aldehydes in human blood by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and solid-phase microextraction with on-fiber derivatization. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:1715–1720
Hada M, Takino M, Daishima S (2000) Determination of aldehydes in drinking water and river water by headspace GC/negative-ion chemical-ionization MS. Bunseki Kagaku 49:411–418
IARC (2004) IARC Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Formadelhyde, 2-butoxyethanol and 1-tert-butoxy-2-propanol, vol 88, WHO IARC
Ikeda M (1999) Solvents in urine as exposure markers. Toxicol Lett 108:99–106
Luo W, Li H, Zhang Y, Ang CY (2001) Determination of formaldehyde in blood plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 753:253–257
Ohata H, Otsuka M, Ohmori S (1997) Determination of acetaldehyde in biological samples by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 693:297–305
Spanel P, Smith D, Holland TA, Al Singary W, Elder JB (1999) Analysis of formaldehyde in the headspace of urine from bladder and prostate cancer patients using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 13:1354–1359
Szarvas T, Szatloczky E, Volford J, Trezl L, Tyihak E, Rusznak I (1986) Determination of endogenous formaldehyde level in human blood and urine by dimedone-14C radiometric method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 106:357–367
WHO (1989) International programme on chemical safety environmental health craiteria 89 formaldehyde, WHO
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Shohei Kira and Dr. Hiroyuki Kataoka for their support. This study was supported by Health Science Research Grant for Research on Environmental Health from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeuchi, A., Takigawa, T., Abe, M. et al. Determination of Formaldehyde in Urine by Headspace Gas Chromatography. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79, 1–4 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9172-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9172-0