Abstract
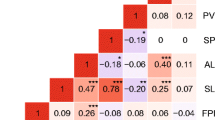
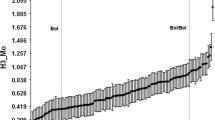
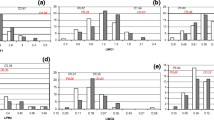
The change from vegetative to reproductive development (earliness) in Lycopersicon chesmannii line L2 was delayed for 20 weeks when compared to other Lycopersicon species under greenhouse conditions. The interspecific hybrid of L. chesmannii L2 and L. esculentum E9, a cherry tomato cultivar, also showed this delay in reproductive development. The distribution of this character in the F2-derived population showed a bimodal shape, plants could be scored easily as “early” or “late” in two nutrient conditions (optimum and high salinity). A QTL with major effects on earliness was detected in salinity, which explained 35.6% of the phenotypic variation. The effect of this QTL greatly diminished under control conditions, indicating differences in the genetic control of earliness between treatments. ACC synthase or phytochrome B2 are the products of candidate genes for such a major QTL. Other QTLs with minor effects, and epistatic interactions, are also involved in earliness under both conditions. A “late” F2 subpopulation yielded twice as much as an “early” F2; conversely, “early” plants were taller than “late” plants, regardless of the treatment. QTL analysis, carried out in both subpopulations, showed that yield differences may be explained by chesmannii alleles showing negative additive effects at some QTLs only in the “early” subpopulation. The effect of population subdivision on QTL analysis was investigated by computer simulations to show sample-size or random effects; thus, important pleiotropic or regulatory effects of genes controlling earliness on yield that affect QTL analysis, have been reveiled. Therefore alleles controlling earliness in L. chesmannii have to be taken into account for a more efficient utilization of the genetic resources of this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 June 1998 / Accepted: 31 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monforte, A., Asíns, M. & Carbonell, E. Salt tolerance in Lycopersicon spp. VII. Pleiotropic action of genes controlling earliness on fruit yield. Theor Appl Genet 98, 593–601 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051109
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051109